
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business
Models – Final Report
January 2022

2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Moving around this document
Use your browser’s bookmarks
and tools to navigate.
To search on a PC use Ctrl+F or
Command+F on MACs.
Sign up for our
news and publications alerts
See all our latest
press releases,
consultations
and speeches.
Contents
1 Executive summary 3
2 Key ndings 5
3 Abbreviations used in this paper 26

3
Chapter 1
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
1 Executive summary
Why we have undertaken this work
1.1 Banks are transforming their businesses to meet the challenges of increasing
digitalisation and technological change, ring-fencing, changing consumer
expectations, and the need to reduce costs. The pandemic has accelerated the move
to digital channels, had profound effects on consumers and business finances and has
increased financial pressures on banks. We have sought to understand the impact of
these changes, and some potential significant future changes, on competition and
consumer outcomes including for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs), as part
of our role to promote competition in consumers’ interests.
Our approach
1.2 Our analysis updates our previous Strategic Review publication in 2018, allowing us to
explore developments since 2015. It uses business model analysis based on detailed
financial information, data and documents from many deposit-taking institutions. This
includes the largest banks and building societies and a selection of smaller banks and
specialist firms. This helps us understand how firms currently make money, as well as
the strategic factors they consider when making decisions, such as which products
to offer, their price, which channels to use and which customer segments to serve.
Our report and its supporting annexes explore changes in retail bank profitability and
the drivers of those changes. We also provide a detailed analysis of different products
within the retail banking business model, namely Personal Current Accounts (PCAs),
Mortgages, Consumer Credit and SME products.
1.3 We have looked separately at the big 4 banks (LBG, Barclays, HSBC and NatWest), scale
challengers (Santander, Nationwide, Virgin Money UK, and TSB), mid-tier firms (Co-op,
Metro, Tesco and Sainsbury’s), digital challengers (Starling and Monzo) and non- PCA-
providers (Specialist lenders such as Aldermore, Shawbrook and Close Brothers) and
traditional building societies. Although firms provide varying ranges of products and
services within these cohorts, we have based our groupings on similarities in size and
product offerings, and applied them consistently across our report.
1.4 We have complemented this with a detailed analysis of the data we hold or have
acquired on consumers and SMEs and their behaviour. This includes data from our
Financial Lives Survey (FLS), Ipsos MORI, Savanta and other sources to provide a
holistic view of the market.
1.5 Our analysis uses the most recent data available, which includes forecast data for
2021, updated where possible with information on mid-year outcomes for 2021.
Conditions in 2020 and 2021 have, as an under-statement, been highly atypical. This
has driven and continues to drive significant change in the retail banking landscape,
much of which has yet to play out. Wherever possible in our analysis, we have sought
to distinguish what we see as longer-term developments from shorter-term changes

4
Chapter 1
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
resulting from the uncertainty caused by the Covid-19 pandemic. The full impacts will
take time to be fully understood. We will therefore continue to monitor developments
and use our full array of regulatory tools to ensure the markets work as well as possible,
generating good outcomes and fair treatment of consumers.
Summary of Our Key findings
Finding Summary
Large banks are in a strong
position but face increasing
competition, in particular for
Personal Current Accounts (PCAs)
There are signs that some of the historic advantages of large
banks may be starting to weaken through innovation and
digitisation and changing consumer behaviour. The gap in
profitability between large banks and smaller challengers has
reduced in recent years, driven by competition in mortgage
prices, innovations in banking services and reduced ability to lower
fundings costs, with rates on customer deposits already very low.
Low levels of consumer
engagement have historically
contributed to high barriers to
entry and expansion
Building market share has been an expensive and slow process
for traditional challengers, often involving switching incentives
or relatively high interest on balances. Despite this, traditional
challengers have provided additional choice and value for those
consumers that have opened accounts with these challengers.
In contrast, digital challengers
have rapidly gained share in
the PCA and Business Current
Account (BCA) markets
Collectively, digital challengers now have around 8% market share
for PCAs. They have attracted customers in part by offering
innovative mobile apps which make the experience of banking
easier and more convenient and to help consumers manage their
money. Relative to the major banks, a smaller proportion of the
digital challengers’ PCAs are main accounts. This results in lower
balances, lower volumes of transactions, and lower overdraft
usage. These lead to lower funding benefits and less scope to
generate fee income.
Competition in the mortgage
market has intensified, which has
caused yields to come down
In a market with high demand, and following ring-fencing,
competition has intensified leading to falling yields across the
mortgage book. Increased broker usage has led to lower levels of
standard variable rate mortgages, further reducing yields. Smaller
banks and building societies have struggled to compete with
larger firms in the low-risk lending segment. Some have exited
altogether; others have sought yields in other segments, including
higher risk areas of the market.
Yields on consumer credit
have also fallen, particularly on
unarranged overdrafts
Our overdraft remedy came into force in April 2020 and caused a
significant decline in unarranged overdraft yields.
The pandemic has dampened demand for consumer credit
overall as spending fell. We intervened to protect consumers
with temporary support measures such as the payment deferral
guidance.
Large banks did proportionately
more micro-business lending
under the government schemes
than most other banks
Previous trends of reduced lending by major banks to SMEs
reversed during the pandemic. But some smaller banks were
able grow their share of SME accounts and lending during the
pandemic.
Increased competition and
innovation have improved
outcomes for many consumers
and some small businesses
Larger banks have adopted digital innovation in PCA banking – led
by digital challengers – and this has improved service quality for
many consumers.

5
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2 Key findings
2.1 Banks are transforming their businesses. The pandemic has accelerated these
changes. Some developments are likely temporary, as the sector responds to the
challenges of the pandemic. But we believe many reflect longer term changes in how
competition works in retail banking. We have undertaken this work as part of our role to
promote competition in the interests of consumers.
2.2 Our Strategic Review of Retail Banking in 2018 highlighted a number of areas for us to
investigate further . Based on our analysis, we made substantial changes to the way
in which consumers pay for higher-cost credit, particularly for unarranged overdrafts.
We have looked at the ways firms earn revenue from payments, in collaboration with
the Payment Systems Regulator (PSR), and continued to monitor changes in retail
banking business models. We also explored further the prices microbusinesses pay for
business banking services. This forms part of our overall findings in this report.
2.3 This report summarises the results of our analysis of the state of competition in the
retail banking markets, updating our previous Strategic Review publication in 2018. It is
based on data, documents, and meetings with numerous deposit-taking institutions.
This includes the largest banks and building societies and a selection of smaller banks
and specialist firms, together with a selection of consumer research. Our aim is to
provide an evidence-base through which to consider implications for our approach to
regulating this sector, and to contribute to wider debates on regulatory policy.
Large banks have a strong position but face increasing
competition in many markets
2.4 A number of competition reviews, most recently the Competition and Markets
Authority’s (CMA) market investigation into retail banking and our previous Strategic
Review of Retail Banking, concluded that the largest banks benefit from incumbency
advantages and that challenger banks have struggled to compete head-to-head with
them. These advantages include a large and stable customer base built up over several
generations, brand familiarity, large branch networks and aspects of the regulatory
framework that have tended to act in favour of incumbents (refer to Annex 1 for
further information on the impact of the regulatory framework). Combined, these
advantages present significant barriers to entry and expansion for challengers and
have enabled the largest banks to retain high market shares and generate high returns
on capital. Levels of innovation and choice have historically been low. Regulators
have taken action to improve competition in the market, including to lower regulatory
barriers to entry.

6
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2.5 There are signs that some of these historic advantages may be starting to weaken.
Several factors have contributed to this. Changing consumer behaviour and the
acceleration of digitalisation over the last few years have opened up the possibility of
branchless banking and reduced the importance of the large branch networks of the
Big 4 in attracting and retaining customers. Technological development, supported
by the lowering of regulatory barriers to entry, has supported the entry of digital-
only banks with innovative, user-friendly banking apps. As a result, the established
banks, including Big 4 and scale challengers, have slowly lost market share in personal
current accounts (PCA). The pandemic accelerated similar changes in micro-business
accounts (BCA), as shown in the charts below.
Figure 2.1 - Share of personal current accounts by account numbers
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
Big 4
68%
67%
65%
64%
1%
4%
6%
8%
4% 4% 4% 4%
26% 26%
25%
24%
Digital Challengers
Mid-tier Banks Scale Challengers
2018 - Account Numbers
2019 - Account Numbers
2020 - Account Numbers
2021* - Account Numbers
Source: FCA Analysis, sample includes big 4 banks, 3 scale challengers, 2 mid-tier banks and 2 digital challengers.
Figure 2.2 - Share of micro-business current accounts by account numbers
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
Big 4
Digital Challengers
Mid-tier Banks
Scale Challengers
2019
2020
2021
74%
71%
67%
1%
4%
10%
7% 7% 7%
18%
18%
16%
Source: FCA Analysis. Micro-businesses for the purposes of our analysis are SMEs with turnover of <£2m per year.
Sample includes big 4 banks, 3 scale challengers, 2 mid-tier banks and 2 digital challengers.
2.6 As seen in Figure 2.3, many more PCA customers now have more than 1 bank account
than in the past, enabling them to try out new products and services without having to
switch accounts. As an indication of this trend, our data indicates that over the last four
years, the number of PCAs has increased by 15%, from 87 million to over 100 million.
This means that, on average, each adult in the UK now has approximately 1.9 current
accounts. We believe that this is a positive development for competition as it allows
consumers to try out different products and build trust in other brands.

7
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Figure 2.3 – Personal Current Accounts per Capita
2018 2019 2020 2021
UK Adult population (estimate)
PCA Numbers
PCA/Adult
0m
10m
20m
30m
40m
50m
60m
70m
80m
90m
100m
1.5
1.55
1.6
1.65
1.7
1.75
1.8
1.85
1.9
Source: FCA calculations based on ONS and UK-wide firm data
2.7 Government and regulators have also played a part in creating a more competitive
environment. For example, we and the PRA have streamlined our authorisations
process and put in place new measures to make switching quicker and easier. Following
its market investigation, the CMA introduced various pro-competitive measures
including improved service quality metrics and Open Banking. In SME banking, money
has been awarded to help challengers as part of the Capability & Innovation Fund and
Incentivised Switching Schemes.
2.8 Big 4 banks’ net interest margins (NIMs) have fallen, due to a range of factors.
Competition in mortgages has driven down prices on new lending, contributing to
reduced all-in lending yields (calculated as the total of lending interest income and
lending fee income divided by average lending balances). Yields have also fallen on
overdraft lending following changes we made to overdraft pricing, which came into
force in April 2020, as well as temporary guidance we issued as part of our pandemic
response. As shown in the chart below, funding costs have not fallen by as much,
creating a decline in NIM. This decline was pronounced in 2020, but the trend was
apparent in prior years.
Figure 2.4 – Decline in NIM
0.00%
0.50%
1.00%
1.50%
2.00%
2.50%
3.00%
3.50%
4.00%
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
All-in lending yield
Cost of funding
3.12%
3.13%
3.06%
3.00%
3.00%
2.59%
Source: FCA Analysis. Net interest margin has been calculated as the total of lending interest income and lending fee income less
interest paid out on deposits, divided by lending assets.
2.9 Banks were able to partly compensate by reducing funding costs, the interest paid
out to deposit holders. However, the low rates of interest on deposits has limited how
much banks could further reduce funding costs, while not falling below zero.

8
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2.10 The underlying pre-tax Return on equity (RoE) has also fallen. RoE is a wide measure of
profitability that captures factors such as operating costs and impairments. We have
used pre-tax returns because our focus is on the returns generated by the businesses’
primary operating activities. Our aim is to make fair comparisons between cohorts and
analyse changes over time consistently, rather than looking at final return on equity
figures. As such, the amounts presented will not be equal to firms’ public returns on
equity.
2.11 In addition to falling NIM, which the chart above shows as the difference between
yields and funding costs, increased impairments, leverage and falling fee income have
contributed to reduced bank profitability, and have been amplified by the pandemic.
Figure 2.5 – Return on Equity Bridge
26.6%
18.0%
ROE - 3 year
Average
(2015-17)
Reduced opex
NIM reduction Lower fee
income
Increased
impairments
ROE - 3 year
Average
(2018-20)
Other
expenditure and
leverage
Big Four - Return on Equity Bridge
3.1%
4.8%
0.6%
3.5%
2.8%
Source: FCA Analysis. Return on equity has been calculated using underlying profit before tax divided by our calculation of CET1 capital.
CET1 capital has been calculated at 15% of Risk-weighted Assets (RWAs), with adjustments made accordingly to ensure each firm
meets the minimum leverage threshold.
2.12 Banks’ scope for reducing operating expenditure through branch closures has
been affected by steps we have taken. During the pandemic, along with the PSR,
we worked closely with industry to address the challenges of ensuring cash access
for the people who want to use it. We published a shortstatementon this work in
June 2020 and anInsight articlein September 2020. Also in September 2020, we
publishedguidancesetting out our expectation that firms should consider the impact
of branch and ATM closures on their customers’ everyday banking needs and consider
the availability and provision of alternatives.We continue to work with the Government
as it develops legislation to provide a framework to protect access to cash for those
who need it.
2.13 Despite the ongoing uncertainty caused by the pandemic, the banks’ financial position
has improved during 2021. As of HY 2021, most banks have reversed a substantial
portion of the impairment provisions recorded in 2020, with actual impairments much
lower than predicted. Some factors are dependent on changes in the base rate (see
below). However, we still expect intense competition in mortgages and continued
pressure on banks to reduce operating expenditure to be features of the market in the
future.
2.14 Big 4 banks continue to achieve higher returns on capital than most other banks, but
the gap has narrowed. Pre-tax underlying ROE fell from an average of 27% in the 3-year
period 2015-2017 to around 18% in the 3-year period 2018-2020. Between these 2
periods, the gap between ROE for Big 4 and scale challengers fell from [10] percentage
points] to [6] percentage points.

9
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Figure 2.6 – Return on Equity
26.6%
18.0%
16.3%
12.1%
0.0%
5.0%
10.0%
15.0%
20.0%
25.0%
30.0%
2015-17 2018-20
Big Four
Scale Challengers
5.9%
10.3%
Return on Equity - Big 4 vs Scale Challenge
Source: FCA Analysis, sample includes big 4 banks, 4 scale challengers
2.15 Increasing demand for digital services as well as strategic drives towards online and
mobile banking has led traditional banks to seek to cut costs by closing branches
and automating services. When comparing the 3-year periods 2015-17 and 2018-20,
average cost asset ratios for Big 4 banks fell by 17 bps (10%). Under Government
proposals, large banks will have a significant role in ensuring that the necessary
infrastructure to give consumers and SMEs access to deposit-making and withdrawal
facilities is maintained at a suitable level.
2.16 Some trends are dependent on the Bank of England base rate. Mortgage yields
tend to be sensitive to changes. We have seen evidence that prices on new fixed
rate mortgages rose in H2 2021 in response to expectations of a rate rise. This was
confirmed by the Bank of England in December 2021, with the rate rising from 0.1% to
0.25%. So banks with a greater share of mortgages as a proportion of lending balances
may see yields rise faster. On the funding side, wholesale funding costs are more likely
to rise in response to a base rate rise. Retail funding costs will depend on factors such
as the level of consumer engagement in rising savings rates, and competition.
2.17 Different cohorts of banks will likely be impacted differently by any changes in the
base rate. The Big 4 have a high proportion of mortgage lending and a low proportion
of wholesale funding compared to other cohorts. Given the expectations we set out
above, returns may stabilise or improve for the Big 4 as a result of rising interest rates.
Low levels of consumer engagement have historically
contributed to high barriers to entry and expansion
2.18 Low levels of consumer engagement and response to price and quality in PCA and BCA
markets have been noted as a feature of the retail banking market in previous studies
including our Strategic Review and the CMA’s market investigation. Levels of searching
and switching on current accounts have been low, despite potential consumer gains on
price or quality. Many consumers have seen switching accounts as overly burdensome
and having little benefit.
2.19 This low customer response has acted as a barrier to expansion because current
accounts are a fundamental part of the business model required to operate a bank
at scale. Together with instant access savings accounts, typically opened alongside
PCAs, banks can gain large volumes of low cost and stable funding necessary to

10
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
compete in the mainstream consumer lending markets. This generates a funding
benefit, which represents the value of the deposits to the bank and depend on factors
such as how much interest the bank pays depositors, how long the depositors are likely
to keep their money at the bank, and the margin the bank can earn from lending the
deposits out. The funding benefit derived by firms from deposits is examined in more
detail in Appendix 2.
2.20 The value of this low cost, stable funding is an important component of the value that
Big 4 banks derive from their PCA and BCAs. Our analysis indicates that, on average
between 2018-2020, a typical PCA contributes around £104 to a Big 4 bank. Of this,
approximately 53% is funding benefit, 24% from overdraft fees and charges and 23%
from other fees and charges, including interchange revenues received by the bank on
debit card transactions. We acknowledge that as these figures are an average across
all PCAs, the value brought in by individual customers might vary. Micro-BCAs have
higher balances and incur higher fees and charges. The average contribution made by
a typical micro-BCA account is £490. Of this, around 52% comes from funding benefit,
34% from fees and charges and 14% from overdrafts. As well as these direct benefits,
banks benefit indirectly from savings accounts, lending products and other services
they cross-sell to current account customers.
Figure 2.7 – PCA/BCA Contributions (Big 4)
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
Charges & Interchange Fees
Overdraft Income
Funding Benefit
PCA - average 2018-2020
BCA - average 2019-2020
Contribution from a typical PCA or BCA account (Big 4)
24
168
25
69
55
253
Source: FCA Analysis. Contribution per account is calculated by total charges & interchange fees/overdraft income/funding benefit
divided by number of PCA/BCA account.
2.21 Switching rates in the PCA market have been low due to weak consumer engagement
and building market share has historically been a slow and expensive process.
Strategies to grow have involved relatively high interest rates on balances, switching
incentives or acquisitions of existing banks. For example, Nationwide and Santander
have slowly gained market share of PCAs over a number of years to become sizable
competitors. Santander has achieved this through a series of acquisitions and its
interest and cashback-bearing 123 Account, Nationwide by offering attractive rates of
interest on savings accounts and switching incentives. Like the Big 4, these firms have
lost some market share in recent years.
2.22 Some mid-tier banks have struggled to reach scale in the PCA market in a cost-
effective manner and have suffered from relatively high funding and operating costs.
The scale required to operate a cost-effective business model, coupled with low
consumer engagement, has meant some banks have found it difficult to grow in the
mainstream mortgage and consumer lending markets.

11
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2.23 Despite this, traditional challengers have provided additional choice and value for
consumers that have switched to them. Metro, for example, had the highest CMA
customer satisfaction score for branch-based service. Given that some consumers
value the ability to visit a bank branch, as part of a multi-channel service offering, this
diversity in business models is welcome from a competition point of view.
Digital challengers have rapidly gained share in the PCA and
BCA markets
2.24 Over the last 4-5 years, digital challengers have rapidly increased market share in
the PCA market. They have attracted customers by offering easy account opening
processes and innovative mobile apps which make the experience of banking easier
and more convenient for digitally-confident consumers, and to help consumers
manage their money. They have won customers through a combination of switches
from other banks using the Current Account Switching Service (CASS), customers
opening their first PCA and customers opening an additional PCA alongside their main
PCA. Collectively, they now have around 8% market share by account numbers.
2.25 Digital challengers have a lower proportion of ‘main’ banking relationships than
traditional banks. Ipsos Mori FRS commissioned data for the 6 months to 31 July
2021, involving 48,267 online and offline interviews with current account holders
(face-to-face interviews were replaced by telephone in April 2020). According to this
data, around 25% of their accounts are thought to be main accounts compared to
around 55% for the broader market. This results in lower balances, lower volumes of
transactions, and lower overdraft usage. In turn, this leads to lower funding benefits
and less scope to generate fee income. In addition, digital challengers do not yet have a
fully developed lending business, so are not yet able to earn significant funding benefit
from customer deposits, as is the case in more established banks. If recent trends
continue, we would expect to see consumers steadily increasing use of their digital
bank accounts as they gain familiarity. Both Starling and Monzo have seen increasing
average balances per account. In its Q2 2021 trading update, Starling reported average
balances of £2,000 per account (up around 100% on the previous year).
2.26 Starling has also increased market share (measured by total number of accounts) in
the BCA market since launching the product in 2018. It now has around 7% market
share in terms of number of accounts. It has done this largely through winning start-up
businesses, but also attracted switchers as part of the BCR’s Incentivised Switching
Scheme. It grew its BCA customer base during the pandemic, as other larger banks
closed to new customers. Starling was also able to offer eligible customers access
to the Bounce-Back Loan Scheme (BBLS). Monzo launched its BCA product more
recently in 2020 and was not part of the BBLs schemes.
2.27 If digital challengers are able to develop a viable and sustainable business model in the
future, it could help them to potentially attract more customers. Several factors could
play into the favour of digital challengers, such as increased consumer comfort with
digital channels, lower cost base and increased ability to innovate due to modern IT
systems built more recently.

12
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2.28 However, there are still several risks to the business models that digital challengers
have developed. They have to achieve further economies of scale and have yet to
substantially grow in mortgage and consumer lending (although Starling gained share
of microbusiness lending through BBLs). Furthermore, as digital challengers scale-up
in size and complexity, they must maintain appropriate service standards and provide
adequate controls and systems to protect consumers. This is likely to increase their
cost base.
2.29 Digital challengers don’t appeal to everyone and are likely to co-exist alongside
other business models for the foreseeable future. The figure below shows that while
younger consumers are more likely to switch to digital challengers, these services are
relatively less attractive to older consumers and other consumers that value face-
to-face services. Moreover, while the number of adults regularly visiting branches
has fallen (27% adults reported regularly using a branch in February 2020 down from
40% in 2017), some banks told us that many consumers valued face-to-face service
for significant or more complex transactions. An increased focus on digitalisation by
firms might mean that these consumers are left behind and have worse outcomes.
We will continue to monitor developments in the market and firms’ conduct to
ensure that there is strong focus on consumer needs, especially those in vulnerable
circumstances.
Figure 2.8 - Customer Profiles of Switchers
0%
5%
10%
15%
20%
25%
30%
35%
40%
45%
16 - 20 21 - 24 25 - 34 35 - 44 45 - 54 55 - 64 65+
Big 4 Scale Challengers Mid-tier Banks Digital Challengers
13%
15%
6%
14%
13%
13%
15%
22%
38%
29%
35%
42%
21%
20%
30%
14%
7%
10%
6%
6%
4%
7%
4%
1%
5%
8%
5%
1%
Source: Ipsos MORI FRS. Data shown is for the twelve months ended 31st July 2021 (All switching account in last 12 months; Big 4
Banking Groups (n=1,806), Mid tiers (137), Scale challengers (873), Digital challengers (n=308). Fieldwork is a mixture of online
and offline interviews, with the offline methodology changing from face-to-face to telephone in April 2020.
Competition in the mortgage market has intensified and yields
have come down
2.30 The residential mortgage market has been growing in value since the 2007/2008
financial crisis, partly due to the increased availability of low cost funding, a return of
credit risk appetite for mortgages and increasing house price inflation. More recently,
the market has seen a boost from government intervention such as the temporary
reduction in stamp duty land tax, extension of help to buy and reintroduction of the
mortgage guarantee scheme. There has also been pent-up demand post Covid-19
lockdowns, combined with an increase in aggregate household savings and shifts in
demand for larger properties which has led to a higher number of home movers.

13
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2.31 The value of gross mortgage advances in H1 2021 reached £172 billion, which was the
highest level since H1 2007. However, the number of property transactions completed
in the UK above £40,000 has not reached the pre financial crisis peak. As of October
2021 the number of such transactions stood at 1.21m, in comparison to 1.61m pre-
crisis peak in 2007, according to HMRC data.
2.32 Recent temporary support measures such as the Coronavirus Job Retention Scheme
(CJRS) and the FCA guidance on payment deferrals, as well as a temporary restriction
on possessions, helped to stabilise the housing market and protect consumers.
2.33 The mortgage market has historically been profitable for larger banks, particularly
when measured in terms of return on equity. Regulatory capital requirements have
meant that they can hold relatively low amounts of capital against mortgage lending,
in comparison to other banks, enabling them to generate relatively high returns on
capital. The PRA has introduced policy changes that will come into effect in January
2022 that will reduce some of these differences in risk weight calculation methods.
2.34 Some banks have told us that the 2019 Ring-Fencing regulation has resulted in the
retail part of the bank gaining additional liquidity. These banks have used this for
mortgage lending, especially as demand for consumer credit fell in 2020. We believe
that ring-fencing alone does not explain the growth in mortgage market share for the
major firms and that additional factors are involved. Among the Big 4 firms, some have
achieved increased growth through expanding their brokerage network.
2.35 Share of gross residential mortgage advances, measured by value, for the Big 4 banks
increased from 46% in 2018 to 53% in 2020. At the same time, scale challengers, mid-
tiers and building societies’ market share declined by the same amount.
Figure 2.9 – Residential Mortgages Gross Advances Market Share
0%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021
up to Q2
Big 4 Scale Challengers Building Societies Mid-tier Banks Specialist Lenders
46% 46% 46% 46%
48%
53% 52%
30% 30%
28% 28%
27%
24% 24%
7% 7% 6%
6%
6%
5%
6%
2%
3%
5%
4%
3% 3%
4%
Source: BOE & FCA MLAR (2021 is only up to Q2)
Includes big 4 banks, 4 scale challengers & 4 mid-tier banks, 2 building societies & 4 specialist lenders
2.36 There is evidence that consumers have benefited from the intensified competition
in residential mortgages through lower prices. Yields have fallen by around 90 basis
points (0.9%) between 2015 and 2020, or around 30% on average across the residential
mortgage book as a whole. This reflects increased volumes of new advances on lower
rates than in the past.

14
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Figure 2.10 – Residential Mortgages Risk Adjusted Yields
0.00%
0.50%
1.00%
1.50%
2.00%
2.50%
3.00%
3.50%
2015
2016
2017
2018
2019 2020
Residential Mortgages Risk Adjusted Yields
Residential Mortgages
3.00%
2.76%
2.51%
2.42%
2.44%
2.10%
Source – FCA Analysis - Risk adjusted yields for residential mortgages (sample includes 4 big 4 banks, 4 scale challengers & 4 mid-tier
banks, 2 building societies & 4 specialist lenders)
Risk adjusted yields calculated as gross interest income plus non-interest income minus impairments divided by average lending
balances
2.37 Yields have also fallen due to fewer consumers on reversionary rates, which tend to
be priced higher than new deals. In 2015, around 22% of mortgages were on standard
variable rates (SVR) compared to around 8% in 2020. Yields on SVR mortgages fell by
40 basis points from an average of 3.6% to 3.2% over the same period.
Figure 2.11 – Mortgage Book Composition
2015 Mortgage Book Composition
2020 Mortgage Book Composition
Fixed
Non-SVR Reversionary
SVR
Non-SVR Variable
Variable_Other
Fixed
Non-SVR Reversionary
SVR
Non-SVR Variable
19%
22%
12%
45%
76%
10%
8%
5%
1%
Source – FCA Analysis
Sample includes Big 4 banks, 4 Scale Challengers, 3 Mid-Tier Banks, 2 building societies, 4 Specialist Lenders
Note: Includes BTL mortgages
2.38 In our view the increased use of mortgage brokers has contributed to increased
price competition and lower numbers of consumers on SVRs. Consumers’ use of
mortgage brokers (excluding internal product transfers) has increased from 63% of
new mortgage product sales in 2015 to 73% in 2020. Brokers typically offer a range
of mortgages to consumers and receive commission from lenders for successful
completions. This is reflected in our 2020 FCA Financial Lives Survey where 81% of
consumers, that have used a broker in the last 3 years, agreed when asked if the broker
had helped them consider wider options in the marketplace.
2.39 As competition has intensified, many smaller banks and building societies have
struggled to compete head-to-head with larger firms. Their higher funding and
operating cost-base has meant that they have been unable to match larger firms’
prices as these have trended downwards. Some smaller firms have exited altogether;

15
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
others have looked to find areas of the market where price competition is less intense,
or there are fewer competitor lenders and in which better yields can be achieved.
This includes, for example, higher loan-to-value (LTV) or mortgage lending products
requiring specialist underwriting such as for the self-employed, self-build or non-
standard construction properties and later-life or family mortgages. Some banks have
entered into forward flow agreements to fund specialist lenders in higher yielding
mortgages, enabling them to participate in these market segments indirectly.
2.40 A key example is found in the Buy to Let (BTL) sector. Major banks have continued to
focus on lending to consumer landlords, alongside their growth in prime residential
mortgages. Big 4 banks can often do this within their existing underwriting processes.
By contrast, scale challengers and specialist lenders gained share by lending to
professional landlords, often requiring more manual, specialist underwriting. As a
result, Big 4 share of the BTL lending fell from 51% to 40% between 2015 and 2020.
Whilst market share in BTL lending for specialist lenders and scale challengers has
grown by a corresponding amount.
2.41 We believe that this increased focus on non-standard lending on the part of some
smaller lenders will increase choice for some consumers who might not have
otherwise been able to get a mortgage. As such, we consider that the diversity of
business models provided by smaller and more specialised lenders can be beneficial to
consumers, provided lenders maintain sound underwriting standards.
2.42 Aligned with our proposals for a new Consumer Duty, we want to see a mortgage
market that provides good outcomes for all borrowers, to enable choice and
competition, fair value products and services and where customers in financial
difficulty are treated fairly. Following our 2019 FCA Mortgage Market Study we changed
our rules to require advisors to justify their reasoning when they do not recommend
the cheapest suitable mortgage to a borrower. We will continue to focus on those
areas in the mortgage market where we identify the greatest harm.
Yields on consumer credit have also fallen, particularly on
unarranged overdrafts
2.43 The pandemic dampened demand for consumer credit as spending fell. Consumer
credit balances declined in 2020 with customers repaying a net amount of £16.6bn.
In 2020, we enacted key reforms to align unarranged overdraft prices with arranged
overdrafts. We also published temporary guidance for lenders that allowed customers,
affected by coronavirus, to request payment deferrals for up to three months at a time
on credit products.
2.44 The combined impact of these reforms, alongside factors such as competition and
the fall in the base rate, meant that consumer credit lending yields fell in 2020. Risk
adjusted yields fell in Overdrafts from 28.5% to 10.1%, in Credit Cards from 8.9% to
5.9% and in Personal Loans from 5.3% to 3.2%.

16
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Figure 2.12 - Consumer Credit Lending Balances and Risk Adjusted Yields
0.0%
5.0%
10.0%
15.0%
20.0%
25.0%
30.0%
35.0%
-
10,000
20,000
30,000
40,000
50,000
60,000
70,000
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021F
Average Lending Balance – Cards Average Lending Balance – Loans
Average Lending Balance – Overdrafts
Risk Adjusted Yield – Cards
Risk Adjusted Yield - Loans Risk Adjusted Yield – Overdrafts
Source – FCA Analysis
Sample includes Big 4 banks, 4 Scale challengers, 4 Mid-Tier banks and (2 Specialist Lenders for personal loans only)
Note 2021 are forecasted figures
Risk-adjusted all-in-yields calculated as gross interest income plus non-interest income minus impairments divided by average annual
lending balances
2.45 Risk adjusted yields on overdrafts were high and stable between 2015-2019. They then
fell steeply in 2020 as we introduced new regulations to make overdrafts simpler and
fairer for consumers. These changes aimed to stop banks and building societies from
charging higher prices for unarranged overdrafts than for arranged overdrafts. As
shown in the chart below, all-in-yields on unarranged overdrafts have now come in line
with those on arranged overdrafts.
2.46 The fall in yields for arranged overdrafts was driven by the temporary support
measures we made in April 2020, that allowed customers affected by coronavirus to
request for an arranged interest-free overdraft of up to £500, for three months, on
their main personal current account. As a result, yields on arranged overdrafts may
return to pre-pandemic levels in 2022.
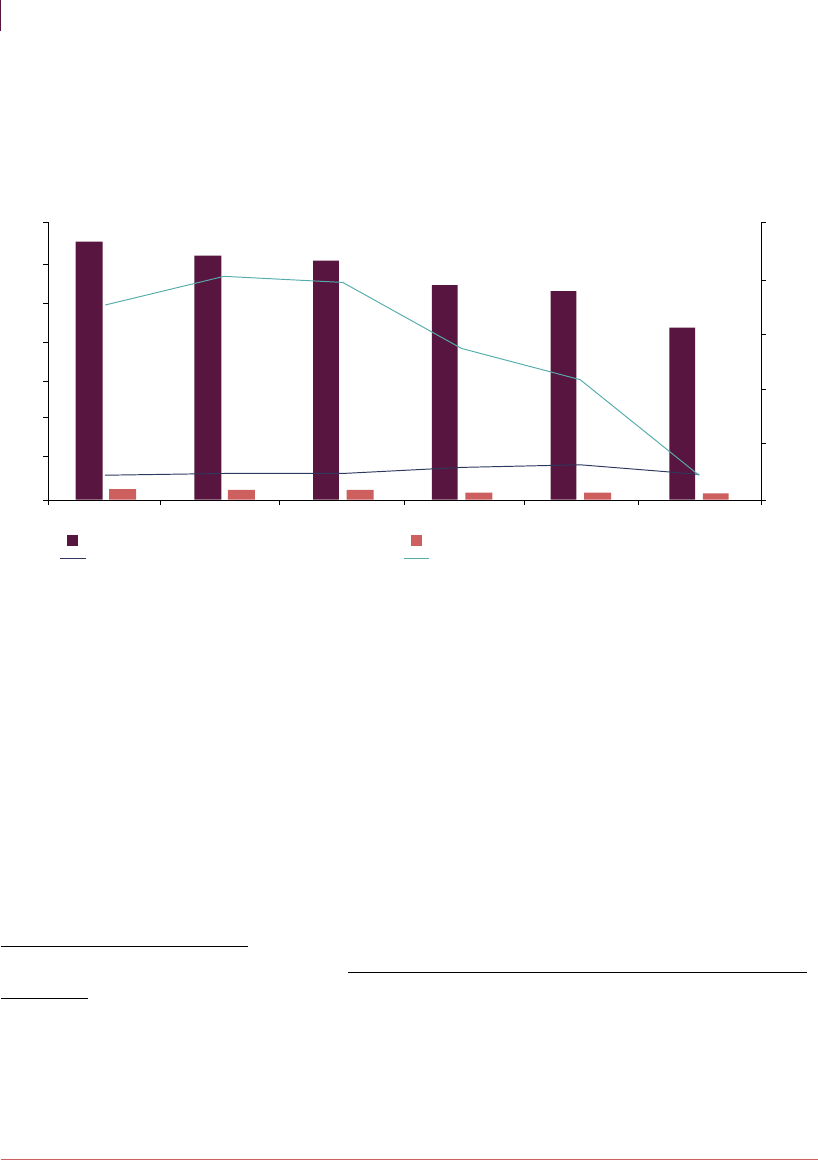
17
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Figure 2.13 - All-in-yields and total annual lending balances in Arranged and Unarranged
Overdrafts
0.0%
50.0%
100.0%
150.0%
200.0%
250.0%
-
1,000
2,000
3,000
4,000
5,000
6,000
7,000
2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020
All-in-yields and total lending balances on arranged and unarranged overdrafts
Arranged Overdrafts- Average Lending Balance
Unarranged Overdrafts - Average Lending Balance
Arranged Overdrafts - All-in yield Unarranged Overdrafts - All-in yield
Source – FCA Analysis
Sample includes Big 4 banks, 3 Scale challengers, 2 Mid-Tier banks and 2 Digital challengers
All-in-yields calculated as gross interest income plus non-interest income minus impairments divided by average annual lending
balances
2.47 In Credit Cards and Personal Loans, there’s some evidence that competition has been
driven by scale challengers and mid-tier banks. Yields in Credit Cards and Personal
Lending have been falling since 2015, and the Big 4 banks have been losing market
share of bank credit card lending and personal loans over time. Across all forms of
consumer lending we find that the Big 4 earn higher yields than scale challengers and
mid-tier banks, although overdrafts have been affected to a lesser extent.
2.48 Although our analysis has been focused on bank lenders in the consumer credit
market, there are a number of non-banks providing competition in the sector. The
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) market more than trebled in size in 2020 and is especially
popular among younger consumers. Some banks have sought to compete with BNPL
products by allowing existing cardholders to create fixed instalment plans for individual
purchases.
Large banks did proportionately more micro-business lending
under the government schemes than most other banks
2.49 Before the pandemic, the share of microbusiness lending by the Big 4 banks was
declining, as challenger banks, specialist lenders and a range of non-bank and peer-to-
peer lenders entered the market. This trend reversed during the pandemic, as large
banks advanced large volumes of loans under the government lending programs, such
as the Bounce Bank Loan Scheme (BBLS) and the Coronavirus Business Interruption
Loan Scheme (CBILS). Even so, micro-business lending represents a relatively small
proportion (under 5%) of the large banks’ overall lending portfolio. A possible reason for
this is the comparatively low yield that large banks achieve on this type of lending: risk
adjusted yields in microbusiness overdrafts and unsecured lending were lower than in
the personal equivalent. Microbusinesses also cost more to serve – many businesses
may prefer to speak to a lender before borrowing, and banks were concerned about
the risks of lending to microbusinesses who subsequently fall into arrears.

18
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
2.50 Banks with larger numbers of micro-BCAs did most lending under these schemes,
reflecting that many microbusinesses turned to their BCA provider to access funding.
Many banks also closed their doors to new business customers during the pandemic,
citing operational overload and a preference to serve their own customers first.
2.51 We considered whether the government lending schemes may have benefited larger
banks at the expense of smaller lenders and whether they might weaken competition
in the SME banking markets in the foreseeable future. This could be the case if the
schemes damaged smaller lenders’ prospects or enabled larger banks to compete
more effectively in the future. At this stage we see little evidence on either point.
Specialist lenders did not grow during the pandemic, but expect business to pick up
again as the recovery continues. In the longer term, we wouldn’t expect the schemes
to have materially changed the underlying economics of small business lending or the
lending appetite of large banks.
2.52 Some smaller banks – notably Starling and Metro – remained open to new business
during the pandemic and allowed new customers to open business current accounts
and apply for loans under the schemes. The timing of the schemes was particularly
opportune for Starling and Metro as they had received sizeable grants from the
Capability and Innovation Fund (CIF) in 2019 to invest in SME banking capability. Starling
was able to attract a large number of new micro-business customers in 2020 who were
seeking to access the BBLS, enabling it to use some of its deposit funding to finance
the loans. Metro and TSB also grew, but by less.
2.53 There are areas of innovation in microbusiness lending. Challenger banks told us that
they have made or are targeting improvements to their lending processes to boost
scale, such as automated decision making, and integrating third-party firms to make
better lending decisions. The non-bank alternative finance sector also represents
potential growth of microbusiness lending in the future - recipients of the CIF outside
the banking sector include Iwoca, MarketFinance, and Funding Xchange.
2.54 Innovation and new entry in microbusiness banking needs to be tied to the obligations
banks have to protect consumers and the economy against harm. Banks serving
microbusinesses have obligations to ensure that there is commensurate investment in
their systems and controls to protect against consumer harm, as well as wider financial
crime and related risks that could threaten the integrity of UK financial services.
2.55 Many SMEs may be paying high charges on BCAs due to the perceived difficulty of
switching bank account and the complexity of charging structures on these accounts.
Our work indicates that while many start-up businesses are benefiting from increased
choice and lower prices, established SMEs may not be benefiting to the same extent.
This is a complex market and one in which prices can be opaque.
Increased competition and innovation have improved outcomes
for many consumers and some small businesses
2.56 On balance, we think increased competition has the potential to offer sizeable benefits
to many consumers and microbusinesses, through innovation, increased choice and
lower prices. However, we know that there are a significant proportion of consumers
and businesses for whom competition may not deliver the same benefits. These
include consumers with low balances, heavy branch users, charities, or businesses in

19
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
higher risk industries, that are less attractive to firms or have additional costs to serve.
Some of these consumers, businesses and charities have struggled to gain access to
current accounts or adequate service from their current account provider. We have
a role to play in ensuring that banks continue to have a strong focus on consumer
outcomes, especially for users in vulnerable circumstances.
2.57 Given the rapid growth in digital challengers, we also recognise the importance for
these firms to develop their controls framework to manage the risks of harm to
consumers. This means that growth by digital challengers has to be sustainable, and
that they have adequate controls to meet our regulatory requirements in areas such as
fraud, financial crime, money laundering, operational resilience and the fair treatment
of consumers in vulnerable circumstances.
2.58 The figure below shows that digital challengers have higher satisfaction scores
compared to other cohorts and that overall satisfaction has increased across
most major banks since 2012. However, we believe that this might mask significant
differences across different types of consumers, especially based on their preferred
distribution channels.
Figure 2.14 – Consumer Satisfaction
62.00%
64.00%
66.00%
68.00%
70.00%
72.00%
74.00%
76.00%
78.00%
Jul 2012 Jul 2013 Jul 2014 Jul 2015 Jul 2016 Jul 2017 Jul 2018 Jul 2019 Jul 2020 Jul 2021
Big 4 Scale Challengers Mid-tier Banks Digital Challengers
Source: Ipsos MORI FRS. Data shown is for the twelve months ended 31st July 2021, based on 24,840 interviews (All main current
account holders giving a response to satisfaction) and compared against twelve months ended data for the periods as indicated.
Fieldwork is a mixture of online and offline interviews, with the offline methodology changing from face-to-face to telephone in April
2020.
2.59 Some consumers may be indifferent or averse to digital banking and may prefer the
more traditional channels of telephone and branch. According to our Financial Lives
Survey, the satisfaction of these consumers has seen a statistically significant decline
in satisfaction between 2017 and February 2020, falling from 86% to 78%. This might
have been exacerbated due to the pandemic, where some branches were temporarily
closed or had reduced opening hours. A challenge for the industry is to continue
to meet the needs of those customers who wish to continue to access in-person
customer service via branches or call centres, some of whom may have characteristics
of vulnerability. As part of our ongoing work on access to cash, we are consulting with
industry and Government for future standards and are supervising firms against our
existing Guidance on branch closures.
2.60 Digital innovation in PCA banking – led by digital challengers – has been adopted
by larger banks and this has improved service quality for some consumers. Mobile
banking app functionality pioneered by digital challengers has been widely adopted
by traditional firms, bringing widespread consumer benefits. While digital challengers
have higher service quality ratings than traditional banks, service quality metrics for

20
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
mobile banking have increased for larger banks over time. For many consumers, this is
likely to have increased convenience through saved time not having to visit branches
or phone their bank and an ability to make payments more easily. It is likely to have also
improved their ability to manage their finances through the use of spending pots and
budgeting tools, instant payment notifications and similar.
Figure 2.15 – Mobile Banking Satisfaction
55.0%
60.0%
65.0%
70.0%
75.0%
80.0%
Jul 2013 Jul 2014 Jul 2015 Jul 2016 Jul 2017 Jul 2018 Jul 2019 Jul 2020 Jul 2021
Big 4 Scale Challengers Mid-tier Banks Digital Challengers
Source: Ipsos MORI FRS. Data shown is for the twelve months ended 31st July 2021, based on 13,540 interviews (All main current
account holders using mobile banking to manage account) and compared against twelve months ended data for the periods as
indicated. Fieldwork is a mixture of online and offline interviews, with the offline methodology changing from face-to-face to telephone
in April 2020.
2.61 From a pricing point of view, it is difficult to identify any material impact from
competition on the revenues that large banks obtain from PCAs, which might indicate
downwards pressure on prices. Some banks mentioned a threat of disintermediation
(unbundling of services) from competing payment services providers, for example
in international payments. However, fees and charges on a per account basis have
remained stable over the recent past.
2.62 Innovations in mobile banking have been slower to reach business consumers. Digital
challengers launched BCA products later than PCA products and incumbent banks
have only recently started to adopt mobile banking products and integrate Open
Finance technology. The pandemic has likely accelerated this as more SMEs have
sought to bank remotely. Microbusinesses who have opened accounts with the digital
challengers are likely to have benefited from lower prices (as these accounts typically
don’t carry an upfront monthly fee), and the convenience and time savings of being
able to conduct more transactions on the app. Some microbusinesses will have
benefited from being more easily able to integrate banking data with accountancy
packages using Open Banking. We see some evidence of non-digital banks developing
similar propositions in response. Service quality metrics in microbusiness banking
are materially higher for digital challengers than for traditional banks, and – unlike in
personal banking – the metrics for traditional banks have not risen.

21
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Figure 2.16 – Satisfaction levels BCAs. Data weighted by region and turnover to be
representative of businesses in G.B.
50
55
60
65
70
75
80
85
Q4 2016 Q4 2017 Q4 2018 Q4 2019 Q4 2020
Big 4 Scale Challengers Mid-tier Banks Digital Challengers
2.63 Not all small businesses have benefited from increased digitalisation. Those, for
example, who are heavy users of cash may have lower satisfaction levels due to an
inability to use branches as their preferred service as a result of branch closures. We
have also found that larger banks are reducing their relationship management services;
data from Savanta MarketVue Business Banking suggests a smaller proportion of
microbusinesses now benefit from a named relationship manager than did 5 years ago.
However, we recognise that the pandemic caused substantial operational challenges
and additional effort for banks in keeping their services running, therefore a decline in
satisfaction throughout the pandemic may be a reflection of this challenge.
2.64 Unlike in personal banking, microbusinesses are often charged for their current
accounts, through a combination of monthly fees and various types of transaction
charges. Small business customers of digital challengers have benefited from lower
prices, and there is competition on the length of introductory free banking offers,
some as much as 30 months. However, innovations have not addressed the difficulty
of switching for established businesses. Our analysis suggests that there continue to
be material gains from switching for many small businesses.
2.65 Innovation in microbusiness banking has started to have an impact in business lending
markets, with fintechs addressing lending needs which have previously not been well
served by traditional banks. Fintech innovation has driven new forms of lending such as
invoice finance and revenue-based finance. Major banks are partnering with fintechs in
this area, and accounting platforms are also making these products more available to
small businesses.
2.66 Innovations in payments have driven further benefits for consumers and small
businesses. Over the past few years, the Payments Service Directive 2 (PSD2) has
led to the entry of a large number of new payments firms offering a diverse range
of different services. These include e-money wallets, crypto-currency offerings,
foreign exchange services and money remitters, Payment Initiation Service Providers/
Account Information Service Providers, BNPL providers and others. Many of these
innovations are positive for consumers, providing increased choice and lower prices,
such as in foreign exchange. In addition, some firms which started off as payment
providers have become or applied to become deposit-taking institutions.
2.67 In mortgage markets, our analysis suggests that competition has contributed to lower
prices for consumers and increased product availability, so that some customers have
been able to get mortgages who might not otherwise have been able to. Banks told

22
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
us that a further impact of increased competition has been innovation in the broker
channel. Banks have developed software for brokers to help them identify appropriate
mortgages for customers more easily and quickly, which is likely to have improved
the service that brokers can offer for consumers. Further, banks told us that they
had developed improved credit-decisioning functionality to enable them to compete
effectively in the broker channel.
Implications for our work
2.68 Our work on retail banking business models directly supports the development of our
strategy across a range of priorities and gives us a data-led evidence-base upon which
to carry out further investigations. This section highlights the organisational-wide
priorities where our strategic review can inform further work.
2.69 There remains significant room for further interventions to increase competition and
innovation in retail banking. Some of this involves the easier sharing of consumer data
in a secure and convenient environment, via Open Banking or Open Finance.
• Open Banking fits squarely with our objectives of promoting effective competition
in consumers’ interests. It has gradually gained traction and momentum since its
introduction in 2016 with close to 4 million active users in 2021. We will continue
to work closely with the industry to make Open Banking work well for users. In
particular, we will engage with banks and third-party providers to make sure that
consumers can conveniently manage and provide consent to sharing of their data.
Alongside this, it is crucial that the interface is robust and secure and consumer
data is protected.
• Open Finance could build on Open Banking by allowing the same kind of access
to data from a wider range of products, given explicit consent from end users.
It involves extending open banking-like data sharing and third-party access to a
wider range of financial sectors and products. This will deliver benefits through
personalised products and advice, price comparison, facilitating switching among
service providers, spurring innovation and empowering consumers to make more
informed decisions. We are continuing to work with Government and industry
to develop the roadmap to Open Finance, including the proposal for Smart Data
Legislation, and published our Feedback Statement in March 2021.
2.70 Innovation comes with risk. New products and new firms can fail. However, even
failed entry can lead to improved outcomes across the market if incumbent firms
respond to it. Firm exit can create concerns about consumer protection, and it will
remain important for us to ensure that any exit is orderly. As a regulator, we need to
understand new ideas and stay close to innovative firms, to ensure an appropriate
balance between support for innovative firms and adequate consumer protections.
• We set up Innovate in recognition of the fact that new entrants required additional
regulatory support, both into the retail banking sector and elsewhere in financial
services. Through Innovate we have supported over 500 highly innovative
firms across the whole spectrum of financial services. We recognise that, once
authorised, new firms continue to need higher levels of our support, and often,
greater oversight. That is why we have set up the Early Oversight project for newly
authorised firms as they develop and grow used to their regulated status.

23
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
• As part of the Payments Landscape Review, the Government is considering
changes to the payments regulatory and legislative framework, for example to
increase consumer protections. The sector is developing rapidly, and an increasing
number of firms are entering the market. Consumers don’t always understand the
different levels of protection that apply to them. We will continue to proactively
supervise firms in the payments and e-money sector and act swiftly where firms fail
to meet safeguarding and other regulatory requirements.
• Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) is an example of innovation in consumer credit that has
developed rapidly in recent years, providing competition to traditional credit card
providers. However, the regulatory framework has not yet adapted to it. We have
said that there is a strong and pressing case to bring BNPL into regulation and are
working with the Government to achieve this.
• Big Tech firms are increasingly collaborating with financial institutions and fintechs
to provide a wide array of new and enhanced financial services, and in the future we
can expect more, and larger scale, entry, particularly in payments. Big Tech firms
can use their strong data and technology advantages to increase functionality and
quality of the products, potentially delivering benefits to consumers. However, Big
Tech entry may also pose competition and regulatory risks that stem from their
size and access to data. This could result in a wide range of regulatory challenges,
many of them unfamiliar and not envisaged by our current rules.
2.71 There continues to be a need for us to ensure fair treatment for consumers, including
those consumers in vulnerable circumstances, who may not be well-placed to benefit
from competition.
• We are consulting on a Consumer Duty that would set a higher level of consumer
protection in retail financial markets where firms are competing vigorously in the
interests of consumers. We see a range of good practices by firms in retail sectors.
However, we also see that firms are not consistently and sufficiently prioritising
good consumer outcomes. We have found cases where firms have not acted in
good faith, supported their customers or acted to prevent foreseeable harm.
We also know that, even without deliberate exploitation, consumers’ ability to
make good decisions can be impaired by various factors, including asymmetries
of information, lack of understanding or cognitive and behavioural biases. These
factors can be intensified where consumers display characteristics of vulnerability.
This causes consumer harm and erodes consumer trust in the financial services
industry. The lack of engagement we observe in retail banking could be a symptom
of this.
• Protecting consumers in vulnerable circumstances is a key focus for us and more
important than ever due to the pandemic’s impact. Our recent Guidance highlights
the actions firms should take to understand the needs of these customers to make
sure they treat them fairly.
• As part of our ongoing supervisory work, we are monitoring how banks are
implementing new charging structures and business models. New charging
structures could be positive for competition if they are transparent and fair.
However, changes could also lead to charges falling disproportionately on low-
income consumers or those in vulnerable circumstances, or to firms offering
reduced services to these consumers. We will continue to supervise firms to ensure
that any such changes result in continued fair treatment of consumers.
• We supervise the activity of the largest retail banks with the greatest potential
impact on consumers and markets through dedicated teams which proactively
assess the potential harm that the firm may cause and agree a strategy to reduce
or prevent it. This includes proactive assessment of these firms’ business models

24
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
and strategies and the drivers of harm which may be inherent in them, and
considering the extent to which the culture, leadership, governance and oversight
arrangements within the firm are adequate to mitigate those risks.
• We supervise smaller retail banks as a portfolio of firms. Here, we analyse a wide
range of data to identify outliers and firms of interest, and common issues and
themes affecting firms, engaging with firms individually or through multi-firm
project work as appropriate.
• For all banks, we examine a wide range of intelligence including complaints from
customers and their representatives, notifications from firms themselves and
whistle-blower evidence to identify and investigate issues of concern. Where we
determine that there is a problem, we intervene robustly to remedy it using the full
range of our powers as appropriate and proportionate.
• Issuing portfolio strategy letters continues to be a key way we set out our
expectations for action by firms to reduce harms we have identified in the sector.
Portfolios are different groups of firms based on their business models. Our
website has the most recent portfolio letters we have sent to retail banks and to
payments and e-money firms.
2.72 The FCA’s Business Plan sets out our current consumer priorities, all of which touch
on the retail banking sector. These are: enabling effective consumer investment
decisions; ensuring consumer credit markets work well; making payments safe and
accessible; and delivering fair value in a digital age.
2.73 To support these priorities we are engaging in a number of workstreams. Of particular
relevance to retail banks are:
• our focus on how firms support borrowers in financial difficulty, particularly due to
the uncertain economic environment
• work to ensure consumers and smaller businesses have access to a variety of
payments services, including cash
• work to assess the impacts of digitalisation on competition, in collaboration
with the Government, the Digital Markets Unit and other members of the Digital
Regulation Cooperation Forum
• the introduction of a new Consumer Duty requiring firms and the individuals within
them to act to deliver good outcomes for retail customers
• working with our partners to help drive down the incidence and impact of fraud,
including Authorised Push Payment fraud
• working alongside the Bank of England and the PRA to assess firms’ progress
in implementing new operational resilience requirements set out in our Policy
Statement of March 2021
• a focus on firms’ progress in improving diversity of representation at all levels,
fostering inclusive cultures and delivering products and services which reflect the
diverse needs of customers
• work to adapt our regulatory framework to enable a market-based transition to a
low carbon economy.
2.74 Many of the areas we have considered underline the importance of our analysis being
led by accurate data. We will continue to work with banks to develop our strategy,
ensuring we collect the right data to carry out our work to protect consumers. For
example, greater knowledge of BCA prices would increase our understanding of where
harm may be happening in this market and help us take prompt action if needed.

25
Chapter 2
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Your views are important
2.75 We look forward to receiving submissions in response to this report. We will be
engaging directly with a wide range of firms and consumer organisations to discuss
some of the points raised but are also keen to hear from other stakeholders.
2.76 Please send written submissions to StrategicReviewofRetailBanking@fca.org.uk by
31 March 2022. If you would like to discuss alternative ways to provide input, please
contact us using the same email address.

26
Annex 1
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
3 Abbreviations used in this paper
Abbreviation Description
ATM Automated Teller Machine
BBLS Bounce-Back Loan Scheme
BCA Business Current Account
BCR Banking Competition Remedies Limited
BNPL Buy Now Pay Later
BOE Bank of England
BTL Buy to Let
CASS Current Account Switching Service
CBILS Coronavirus Business Interruption Loan Scheme
CIF Capability and Innovation Fund
CJRS Coronavirus Job Retention Scheme
CMA Competition and Markets Authority
FLS Financial Lives Survey
HY Half-year
HMRC Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs
ISS Incentivised Switching Scheme
LBG Lloyds Banking Group
LTV Loa n-To-Value
MLAR Mortgage Lending and Administration Return
NIM Net Interest Margin
PCA Personal Current Account
PRA Prudential Regulation Authority

27
Annex 1
Financial Conduct Authority
Strategic Review of Retail Banking Business Models – Final Report
Abbreviation Description
PSR Payment Systems Regulator
RoE Return on Equity
RWA Risk-weighted asset
SMEs Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
SVR Standard Variable Rates
All our publications are available to download from www.fca.org.uk. If you would like
to receive this paper in an alternative format, please call 020 7066 7948 or email:
publication[email protected]rg.uk or write to: Editorial and Digital team, Financial
Conduct Authority, 12 Endeavour Square, London, E20 1JN
Sign up for our news and publications alerts

© Financial Conduct Authority 2022
12 Endeavour Square London E20 1JN
Telephone: +44 (0)20 7066 1000
Website: www.fca.org.uk
All rights reserved
Pub ref: 007779
