
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-1
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Note: For the benefit of the students, specially the aspiring ones, the question of JEE(advanced), 2023 are also
given in this booklet. Keeping the interest of students studying in class XI, the questions based on topics
from class XI have been marked with ‘*’, which can be attempted as a test. For this test the time
allocated in Mathematics, Physics and Chemistry are 30 minutes, 25 minutes and 25 minutes
respectively.
FIITJEE
SOLUTIONS TO JEE (ADVANCED) – 2023
(PAPER-1)
Mathematics
SECTION 1 (Maximum
Marks: 12)
This section contains THREE (03) questions.
Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four option(s)
is(are) correct answer(s).
For each question, choose the option(s) corresponding to (all) the correct answer(s).
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : + 4 ONLY if (all) the correct option(s) is(are) chosen;
Partial Marks : + 3 If all the four options are correct but ONLY three options are chosen;
Partial Marks : + 2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two options are chosen, both of which
are correct;
Partial Marks : + 1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it is a correct
option;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : – 2 In all other cases.
For example, in a question, if (A), (B) and (D) are the ONLY three options corresponding to correct answers,
then
choosing ONLY (A), (B) and (D) will get +4 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) and (B) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) and (D) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (B) and (D) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) will get +1 mark;
choosing ONLY (B) will get +1 mark;
choosing ONLY (D) will get +1 mark;
choosing no option (i.e. the question is unanswered) will get 0 marks; and
choosing any other combination of options will get –2 marks.
Q.1. Let S = (0, 1)(1, 2)(3, 4) and T = {0, 1, 2, 3} . Then which of the following statements is(are) true?
(A) There are infinitely many functions from S to T
(B) There are infinitely many strictly increasing functions from S to T
(C) The number of continuous functions from S to T is at most 120
(D) Every continuous function from S to T is differentiable
Sol. A, C, D
Set S has infinite elements while set T has only 4 elements, therefore it is not possible to make any strictly
increasing function from set S to set T.
According to structure of domain, it is possible to make a continuous function from set S to set T and
number of such possible functions is 64.
Also, every continuous function from S to T is differentiable.

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-2
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
There are many ways to assign a value of T to elements of domain, hence infinitely many functions will
exist from set S to set T.
*Q.2. Let T
1
and T
2
be two distinct common tangents to the ellipse
2 2
x y
E : 1
6 3
and the parabola P : y
2
= 12x.
Suppose that the tangent T
1
touches P and E at the points A
1
and A
2
, respectively and the tangent T
2
touches P and E at the points A
4
and A
3
, respectively. Then which of the following statements is(are) true?
(A) The area of the quadrilateral A
1
A
2
A
3
A
4
is 35 square units
(B) The area of the quadrilateral A
1
A
2
A
3
A
4
is 36 square units
(C) The tangents T
1
and T
2
meet the x -axis at the point (– 3, 0)
(D) The tangents T
1
and T
2
meet the x -axis at the point (– 6, 0)
Sol. A, C
y = mx
2
6m 3
(eq. of tangent for ellipse)
y = mx +
3
m
(eq. of tangent for parabola)
2
3
6m 3
m
2
2
9
6m 3
m
3 = 2m
4
+ m
2
2m
4
+ m
2
3 = 0
2m
4
+ 3m
2
2m
2
3 = 0
m
2
(2m
2
+ 3) 1(2m
2
+ 3) = 0
m = 1, 1
Equations of tangents are y = x + 3
and y = x 3
Point of intersection = (3, 0)
Eq. of l
1
T = 0 (chord of contact for ellipse)
(3, 0)
(
2,
1)
(3,
6)
l
1
(2, 1)
l
2
(3, 6)
3x
1
6
, x = 2
Eq. of l
2
T = 0
0 = 12
x 3
2
x = 3
area of quadrilateral A
1
A
2
A
3
A
4
=
1
2
(2 + 12) 5 = 35 sq. units

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-3
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Q.3. Let f : [0, 1] [0, 1] be the function defined by
3
2
x 5 17
f x x x
3 9 36
. Consider the square region
S = [0, 1] [0, 1]. Let G ={(x, y) S : y > f (x)} be called the green region and R = {(x, y) S : y < f (x)}
be called the red region. Let L
h
= {(x, h) S : x [0, 1]} be the horizontal line drawn at a height
h [0, 1]. Then which of the following statements is(are) true?
(A) There exists an
1 2
h ,
4 3
such that the area of the green region above the line L
h
equals the area of
the green region below the line L
h
(B) There exists an
1 2
h ,
4 3
such that the area of the red region above the line L
h
equals the area of the
red region below the line L
h
(C) There exists an
1 2
h ,
4 3
such that the area of the green region above the line L
h
equals the area of
the red region below the line L
h
(D) There exists an
1 2
h ,
4 3
such that the area of the red region above the line L
h
equals the area of the
green region below the line L
h
Sol. B, C, D
1
2/3
181/324
17/36
13/36
1/
4
0
1/3
1
Area
red
=
1
0
f x dx 0.5
Area
green
= 0.5
(A)
1/3
1/6
0.5
1/4
13/36
17/36
181/324
2/3
h
Green area
above line L
h
Green area
below line L
h
Both graph doesn’t intersect

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-4
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
(B)
1/4
1/2
1/4 13/36
17/36
181/324
2/3
h
Red area below line
L
h
Red area above line L
h
Both Graph intersect at h =
1
4
(C)
1/
4
0.5
1/4 13/36
17/36
181/324
2/3
h
Red area below line
L
h
Red area above line
L
h
1/3
Both Graph intersect.
(D)
1/4
1/6
1/4
13/36
17/36
181/324
2/3
h
Green area below
line L
h
Red above line L
h
Both graph intersect
SECTION 2 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains FOUR (04) questions.
Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is the correct answer.
For each question, choose the option corresponding to the correct answer.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : –1 In all other cases.
Q.4. Let f : (0, 1) R be the function defined as
f x n
if
1 1
x ,
n 1 n
where n N. Let g : (0, 1) R
be a function such that
2
x
x
1 t
dt g x 2 x
t
for all x (0, 1) . Then
x 0
limf x g x
(A) does NOT exist (B) is equal to 1
(C) is equal to 2 (D) is equal to 3

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-5
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. C
x 0 n
1 1
limf x g x lim f g
n n
2
1/n
n n n
1/n
1 t 1 1 2
lim n 1 dt limf g lim n 1
t n n
n
`
2
1/n
n n
1/n
1 t 1 1
lim n 1 dt limf g 2
t n n
2
1/n
2
2 3
1/n
n n
3/2
1 t
1 2
dt
n 1 n 1
t
n n
lim lim
1 1
n 1
2 n 1
=
2 3/ 2
2
2 3
n
2 n 1 4 n 1 n 1
lim 2
n n
so
n
1 1
2 lim f g 2
n n
n
1 1
limf g 2
n n
Q.5. Let Q be the cube with the set of vertices {(x
1
, x
2
, x
3
) R
3
: x
1
, x
2
, x
3
{0, 1}} . Let F be the set of all
twelve lines containing the diagonals of the six faces of the cube Q. Let S be the set of all four lines
containing the main diagonals of the cube Q; for instance, the line passing through the vertices (0, 0, 0) and
(1, 1, 1) is in S. For lines
1
and
2
, let d
1 2
,
denote the shortest distance between them. Then the
maximum value of
1 2
d ,
as
1
varies over F and
2
varies over S, is
(A)
1
6
(B)
1
8
(C)
1
3
(D)
1
12
Sol. A
DR's of
OG
= (1, 1, 1)
DR's of
AC
= (1, 1, 0)
Equation of
x y z
OG
1 1 1
Equation of
x 1 y z
AC
1 1 0
ˆ
OA i
Normal of
OG
and
AC
=
ˆ ˆ ˆ
i j k
ˆ ˆ ˆ
1 1 1 i j 2k
1 1 0
B(1, 1, 0)
C(0, 1, 0)
A(1, 0, 0)
F(1, 0, 1)
E(0, 0, 1)
D
(0, 1, 1)
O
(0,0,0)
G(1, 1, 1)
S.D. =
ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ
i i j 2k
1
ˆ ˆ ˆ
6
i j 2k

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-6
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Q.6. Let
2 2
2
x y
X : x,y Z Z: 1 and y 5x
8 20
. Three distinct points P, Q and R are randomly chosen
from X . Then the probability that P, Q and R form a triangle whose area is a positive integer, is
(A)
71
220
(B)
73
220
(C)
79
220
(D)
83
220
Sol. B
2 2
x y
1
8 20
and y
2
< 5x
2 2
x y
1
8 20
…(1)
y
2
= 5x …(2)
On solving (1) and (2)
2
x x
1
8 4
x
2
+ 2x = 8
x
2
+ 2x 8 = 0
(0, 0)
(2,
10
)
(2,
10
)
x = 2, 4
X = {(1, 1), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (1, 2), (2, 1), (2, 1), (2, 3), (2, 3), (2, 2), (2, 2), (2, 0)}
n (S) =
12
C
3
A is event of selecting 3 points for which area of is positive integer.
n(A) = 4 7 + 9 5 = 73
P(A) =
12
3
73 73
220
C
*Q.7. Let P be a point on the parabola y
2
= 4ax , where a > 0. The normal to the parabola at P meets the x-axis at
a point Q. The area of the triangle PFQ, where F is the focus of the parabola, is 120. If the slope m of the
normal and a are both positive integers, then the pair (a, m) is
(A) (2, 3) (B) (1, 3)
(C) (2, 4) (D) (3, 4)
Sol. A
y = mx
2am
am
3
2
1
a am 2am 120
2
a
2
(1 + m
2
)m = 120
(2, 3) satisfy
P
Q
F(a, 0)
(am
2
,
2am)
(2a + am
2
,0)
O

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-7
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
SECTION 3 (Maximum Marks: 24)
This section contains SIX (06) questions.
The answer to each question is a NON-NEGATIVE INTEGER.
For each question, enter the correct integer corresponding to the answer using the mouse and the onscreen
virtual numeric keypad in the place designated to enter the answer.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +4 If ONLY the correct integer is entered;
Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
Q.8. Let
1
tan x ,
2 2
, for x R. Then the number of real solutions of the equation
1
1 cos 2x 2 tan tan x
in the set
3 3
, , ,
2 2 2 2 2 2
is equal to
Sol. 3
1
tan x ,
2 2
1
1 cos2x 2 tan tanx
1
2 cosx 2 tan tan x
|cosx| = tan
1
tanx
3
2
2
2
3
2
O
Q.9. Let n 2 be a natural number and f :[0, 1] R be the function defined by
1
n 1 2nx if 0 x
2n
1 3
2n 2nx 1 if x
2n 4n
f x
3 1
4n 1 nx if x
4n n
n 1
nx 1 if x 1
n 1 n
If n is such that the area of the region bounded by the curves x = 0 , x = 1 , y = 0 and y = f (x) is 4 , then the
maximum value of the function f is

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-8
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. 8
Area
1 1 1 n 1
4
4 8 8 2
1 n 1
4
2 2
n = 8
So maximum value of f(x) is 8
(0, n)
1
,0
2n
1
,0
n
(1, 0)
O
*Q.10. Let
r
75 57
denote the (r + 2) digit number where the first and the last digits are 7 and the remaining r
digits are 5. Consider the sum S = 77 + 757 + 7557 + … +
98
75 57
. If
99
75 57 m
S
n
, where m and n
are natural numbers less than 3000, then the value of m + n is
Sol. 1219
T
r
= 7 10
r1
+ 5(10
r2
+ 10
r3
+ ….. + 10) + 7 r 2
= 7 10
r1
+
r 2
1 10
5 10 7
1 10
= 7 10
r1
+
r 1
50
10 1 7
9
= 7 10
r1
+
r 2
50 13
10
9 9
S =
100 100
r 1 r 2
r
r 2 r 2
50 13
T 7 10 10
9 9
=
90 92
10 1 50 10 1 13
70 99
10 1 9 10 1 9
Now,
99 99
2
70 50
10 1 10 1 13 11
9 9
=
100 99
50 13
7 10 10 m
9 9
n
100 99
2
7 50 50 70
10 10 13 11
9 9 9 9
9
=
100 99
7 50 13 m
10 10
n 9n 9n n
n = 9
13 11 9
2
50 70 9 = 13 + 9m
m = 1210
m + n = 1219
*Q.11. Let
1967 1686isin
A : R
7 3icos
. If A contains exactly one positive integer n, then the value of n is
Sol. 281
281(7 6isin ) 7 3icos
7 3icos 7 3icos

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-9
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
=
2 2
281 49 9sin 2 562i 2sin cos
49 9cos 49 9cos
for it to be positive integer (i.e. real number)
2sin + cos = 0
281(7 6isin )
7 3icos
=
281(7 3icos )
7 3icos
= 281
Q.12. Let P be the plane
3x 2y 3z 16
and let
2 2 2
ˆ ˆ ˆ
S i j k : 1
and the distance of
(, , ) from the plane P is
7
2
. Let
u, v
and
w
be three distinct vectors in S such that
u v v w w u
. Let V be the volume of the parallelepiped determined by vectors,
u,v
and
w
.
Then the value of
80
3
V is
Sol. 45
ˆ ˆ ˆ
u,v,w
are equally inclined and its
ˆ ˆ ˆ
u,v,w
are vertices of equilateral triangle lying on circle which is
intersection of sphere
r 1
and plane at a distance of 1/2 unit from origin & parallel to
3x 2y 3z 16
.
So radius of circle is
3
2
and area of triangle joining points with p.v's
u, v, w
is
9 3
16
. So volume of
parallelepiped is
1 9 3 9 3
2
2 16 16
, so
80v
45
3
.
*Q.13. Let a and b be two nonzero real numbers. If the coefficient of x
5
in the expansion of
4
2
70
ax
27bx
is equal
to the coefficient of x
–5
in the expansion of
7
2
1
ax
bx
, then the value of 2b is
Sol. 3
General term of
4
2
70
ax
27bx
is
r r
4 r
4 2 4 4 r 8 3r
r r
r
70 70
C ax C a x
27bx
27b
for coefficient of x
5
we put 8 3r = 5 r = 1
coeff. of x
5
is
3 3
4
1
a 70 280 a
C
27b 27 b
General term of
7
2
1
ax
bx
is
r
7 r
7 7 3r
r
r
a 1
C x
b
for coeff. of x
5
we put 7 3r = 5 r = 4
coeff. of x
5
is
3 3
7
4
4 4
a 35a
C
b b
Given
3 3
3
4
280 a 35a 27 3
b b
27 b 8 2
b
2b = 3

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-10
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
SECTION 4 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains FOUR (04) Matching List Sets.
Each set has ONE Multiple Choice Question.
Each set has TWO lists: List-I and List-II.
List-I has Four entries (P), (Q), (R) and (S) and List-II has Five entries (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5).
FOUR options are given in each Multiple Choice Question based on List-I and List-II and ONLY ONE of these
four options satisfies the condition asked in the Multiple Choice Question.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 ONLY if the option corresponding to the correct combination is chosen;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : –1 In all other cases.
Q.14. Let , and be real numbers. Consider the following system of linear equations
x + 2y + z = 7
x + z = 11
2x – 3y + z =
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entries in List-II.
List
–
I
List
–
II
(P)
If
1
7 3
2
and = 28, then the system
has
(1)
A unique solution
(Q)
If
1
7 3
2
and
28
, then the
system has
(2)
No solution
(R)
If
1
7 3
2
where = 1 and
28
,
then the system has
(3)
Infinitely many solution
(S)
If
1
7 3
2
where = 1 and = 28,
then the system has
(4)
x = 11, y =
–
2 and z = 0 as a solution
(5)
x =
–
15, y = 4 and z = 0 as a solutio
n
The correct option is:
(A) (P) (3) (Q) (2) (R) (1) (S) (4)
(B) (P) (3) (Q) (2) (R) (5) (S) (4)
(C) (P) (2) (Q) (1) (R) (4) (S) (5)
(D) (P) (2) (Q) (1) (R) (1) (S) (3)
Sol. A
1 2 1
1 0 7 3 2
2 3
x
7 2 1
11 0 21 22 2 33
3
y
1 7 1
1 11 14 4 22
2

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-11
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
z
1 2 7
1 0 11 2 56
2 3
(P) If
1
7 3 & 28
2
, then
x y z
0
So infinitely many solution
(Q) If
1
7 3 & 28
2
, then = 0 but
z
0 so no solution.
(R) If
1
7 3 , 1 & 28, then 0
2
so unique solution.
(S) If
1
7 3 , 1, 28, then 0
2
7 3 2 4 2
x
44 22
y
4 8
z
0
x = 11, y = – 2, z = 0
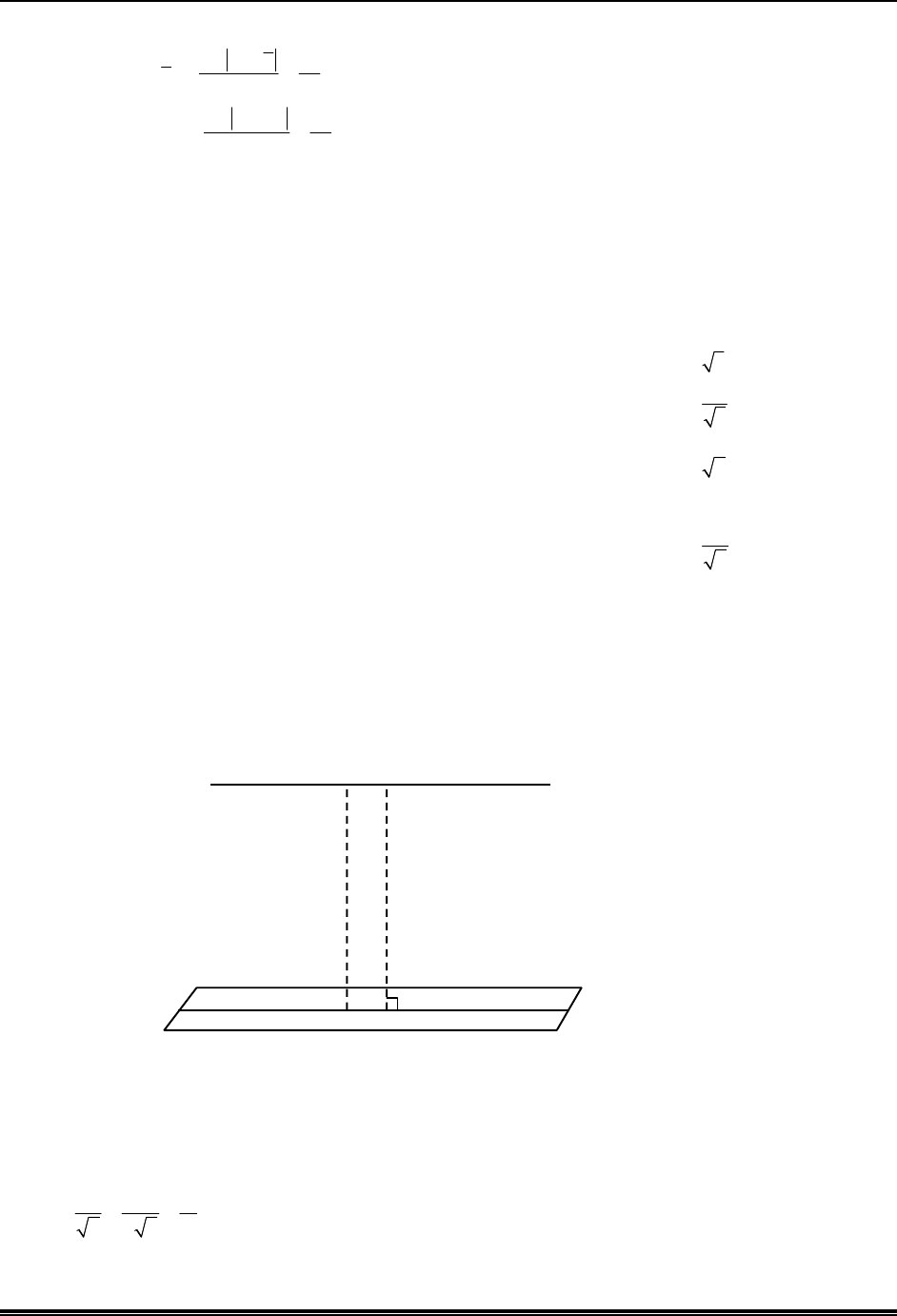
*Q.15. Consider the given data with frequency distribution
x
i
3 8 11 10 5 4
f
i
5 2 3 2 4 4
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entries in List-II.
List
–
I
List
–
II
(P)
The mean of the above data is
(1)
2.5
(Q)
The median of the above data is
(2)
5
(R)
The mean deviation about the mean of th
e
above data is
(3)
6
(S)
The mean deviation about the median of
the above data is
(4)
2.7
(5)
2.4
The correct option is:
(A) (P) (3) (Q) (2) (R) (4) (S) (5)
(B) (P) (3) (Q) (2) (R) (1) (S) (5)
(C) (P) (2) (Q) (3) (R) (4) (S) (1)
(D) (P) (3) (Q) (3) (R) (5) (S) (5)
Sol. A
x
i
f
i
f
i
x
i
i i
f x x
f
i
|x
i
M|
3
5
15
15
10
4
4
16
8
4
5
4
20
4
0
8
2
16
4
6
10
2
20
8
10
11
3
33
15
18
f
i
= 20
f
i
x
i
= 120
sum = 54
sum = 48
(P) Mean
120
x 6
20
(Q) Median =
th th
10 11 observation
5
2
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-12
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
(R) M.D.
i i
i
f x x
54
x 2.7
f 20
(S) M.D. (M) =
i i
i
f x M
48
2.4
f 20
Q.16. Let
1
and
2
be the lines
1
ˆ ˆ ˆ
r i j k
and
2
ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ
r j k i k
, respectively. Let X be the set of all
the planes H that contain the line
1
. For a plane H, let d(H) denote the smallest possible distance between
the points of
2
and H . Let H
0
be a plane in X for which d(H
0
) is the maximum value of d(H) as H varies
over all planes in X .
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entries in List-II.
List
–
I
List
–
II
(P)
The value of
d
(
H
0
) is
(1
)
3
(Q)
The distance of the point (0,
1, 2) from
H
0
is
(2)
1
3
(R)
The distance of origin from
H
0
is
(3)
0
(S)
The distance of origin from the point of
intersection of planes
y = z , x = 1 and H
0
is
(4
)
2
(5)
1
2
The correct option is:
(A) (P) (2) (Q) (4) (R) (5) (S) (1)
(B) (P) (5) (Q) (4) (R) (3) (S) (1)
(C) (P) (2) (Q) (1) (R) (3) (S) (2)
(D) (P) (5) (Q) (1) (R) (4) (S) (2)
Sol. B
P 5, Q 4, R 3, S 1
P
(0, 1, 1)
M
H
(0, 0, 0)
l
1
2
ˆ ˆ ˆ ˆ
r j k i k
1
ˆ ˆ ˆ
r i j k
l
2
Line l
2
is parallel to plane containing l
1
Let l, m, n be D. cosine of plane H
l + m + n = 0 …(1)
l + n = 0 …(2)
n + m + n = 0, m = 0
l n m
0
2 2

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-13
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
l m n
0
2 2
so equation of plane H
0
is
2 x 0 0 y 0 2 z 0 0
x z = 0
equation of plane H.
(P) d[H
0
] = PM =
0 1 1
1 1 2
(Q)
0 2
2
2
(R) Distance of origin from H
0
= 0
(S) Distance of origin from the point of intersection of planes y = z, x = 1, x = z.
Intersection T(1, 1, 1), Distance from origin =
1 1 1 3
*Q.17. Let z be a complex number satisfying | z |
3
+ 2z
2
+ 4
z
– 8 = 0, where
z
denotes the complex conjugate of
z . Let the imaginary part of z be nonzero.
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entries in List-II.
List
–
I
List
–
II
(P)
2
z
is equal to
(1)
12
(Q)
2
z z
is equal to
(2)
4
(R)
2 2
z z z
is equal to
(3)
8
(S)
2
z 1
is equal to
(4)
10
(5)
7
The correct option is:
(A) (P) (1) (Q) (3) (R) (5) (S) (4)
(B) (P) (2) (Q) (1) (R) (3) (S) (5)
(C) (P) (2) (Q) (4) (R) (5) (S) (1)
(D) (P) (2) (Q) (3) (R) (5) (S) (4)
Sol. B
P 2, Q 1, R 3, S 5
|z|
3
+ 2z
2
+
4z
8 = 0, imaginary part of z is non-zero
Let z = x + iy, y 0
Put |x + iy|
3
+ 2(x + iy)
2
+ 4(x iy) 8 = 0
x = 1, y
2
= 3
(P) |z
2
| = x
2
+ y
2
= 1 + 3 = 4
(Q)
2
z z
= |x + iy x + iy|
2
= 4y
2
= 12
(R) |z|
2
+
2
z z
= x
2
+ y
2
+ |x + iy + x iy|
2
= x
2
+ y
2
+ 4x
2
= 5x
2
+ y
2
= 5 + 3 = 8
(S) |z + 1|
2
= |x + iy + 1|
2
=
2
1 i 3 1 4 3 7
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-14
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Physics
SECTION 1 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains THREE (03) questions.
Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four option(s) is(are)
correct answer(s).
For each question, choose the option(s) corresponding to (all) the correct answer(s).
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : + 4 ONLY if (all) the correct option(s) is(are) chosen;
Partial Marks : + 3 If all the four options are correct but ONLY three options are chosen;
Partial Marks : + 2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two options are chosen, both of which are
correct;
Partial Marks : + 1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it is a correct option;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : – 2 In all other cases.
For example, in a question, if (A), (B) and (D) are the ONLY three options corresponding to correct answers, then
choosing ONLY (A), (B) and (D) will get +4 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) and (B) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) and (D) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (B) and (D) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) will get +1 mark;
choosing ONLY (B) will get +1 mark;
choosing ONLY (D) will get +1 mark;
choosing no option (i.e. the question is unanswered) will get 0 marks; and
choosing any other combination of options will get –2 marks.
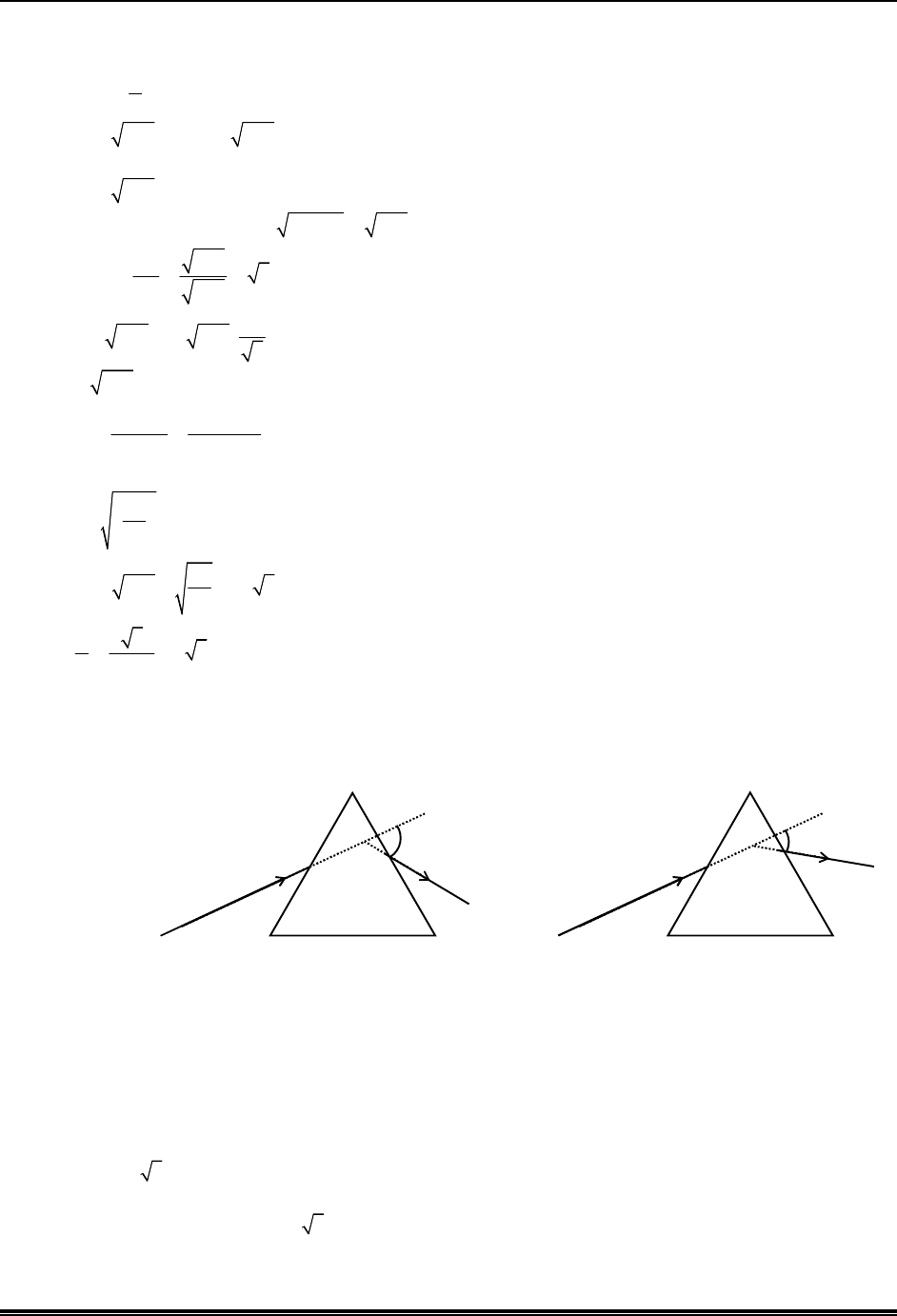
*Q.1 A slide with a frictionless curved surface, which becomes horizontal at its lower end, is fixed on the terrace
of a building of height 3 h from the ground, as shown in the figure. A spherical ball of mass m is released
on the slide from rest at a height h from the top of the terrace. The ball leaves the slide with a velocity
0 0
ˆ
u u x
̂ and falls on the ground at a distance d from the building making an angle with the horizontal.
It bounces off with a velocity
v
and reaches a maximum height h
1
. The acceleration due to gravity is g and
the coefficient of restitution of the ground is 1⁄√3. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
h
1
d
v
3h
h
0
u
g
x
z
(A)
0
ˆ
u 2ghx
(B)
v
=
ˆ ˆ
2gh(x z)
(C) = 60
0
(D) d/h
1
= 2
3
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-15
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. A, C, D
mgh =
2
0
1
mu
2
u
0
=
2gh
0
ˆ
u 2ghx
On ground horizontal component of velocity
v
x
=
2gh
Vertical component, V
Z
=
2g 3h 6gh
tan =
Z
x
6gh
V
3
V
2gh
= 60
0
1
ˆ ˆ
v 2gh x ( 6gh) z
3
ˆ ˆ
2gh(x z)
h
1
=
2
z
eV
(1/ 3)6gh
h
2g 2g
Time to hit ground after leaving slide
t =
6h
g
d =
6h
2gh 2 3 h
g
d 2 3h
2 3
h h
.
Q.2 A plane polarized blue light ray is incident on a prism such that there is no reflection from the surface of
the prism. The angle of deviation of the emergent ray is = 60° (see Figure-1). The angle of minimum
deviation for red light from the same prism is
min
= 30° (see Figure-2). The refractive index of the prism
material for blue light is √3. Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
= 60
Figure-1
Plane polarized blue
light
= 30
Figure-2
Plane polarized red
light
(A) The blue light is polarized in the plane of incidence.
(B) The angle of the prism is 45°.
(C) The refractive index of the material of the prism for red light is √2.
(D) The angle of refraction for blue light in air at the exit plane of the prism is 60
0
Sol. A, C, D
For Figure -1 (Blue light)
= tani
p
i
p
= tan
-1
3
= 60
0
= i + e – A 60
0
= 60
0
+ e – A e = A … (i)
At incident surface, sin60
0
=
3
sinr
1
r
1 =
30
0

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-16
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
r
1
+ r
2
= A
r
2
= A – 30
0
At emergent surface,
0
3sin( 30 )
A sinA
3 3
sin A cosA sin A
2 2
tan A =
3
A = 60
0
e = 60
0
For Figure 2 (red line)
For minimum deviation
m
R
A
sin
2
A
sin
2
0
R
0
sin45
sin30
Or,
R
=
2
Q.3 In a circuit shown in the figure, the capacitor C is initially uncharged and the key K is open. In this
condition, a current of 1 A flows through the 1 Ω resistor. The key is closed at time t = t
0
. Which of the
following statement(s) is(are) correct? [Given: e
-1
= 0.36]
R
1
3
3
I
1
K
15V
5V
C = 2F
(A) The value of the resistance of R is 3
(B) For t < t
0
, the value of current I
1
is 2A
(C) At t = t
0
+ 7.2 s, the current in the capacitor is 0.6 A.
(D) For t , the charge on the capacitor is 12 C.
Sol. A, B, C, D
E
e
=
15 0
45
R 3
1 1
R 3
R 3
i =
45
5
R 3
3R
1
R 3
1 =
30 5R
4R 3
R = 3
R
1
3
3
G
A
C
E
H
F
D
B
i
1
i
2
i
3

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-17
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
V
CD
= 5 + 1
1 = 6 Volt.
i
1
=
6
2
3
A A
.
E
e
=
15 5 0
3 1 3
1 1 1
3 1 3
= 6 Volts
e
1 1 1 5
1
r 3 3 3
r
e
=
3
5
i
2
3R
3 R
1
C
D
E
e
As t
, charge on capacitor,
q
0
= 2 6 =12 C
Current through capacitor at time t is,
i = i
0
0
6
t t
7.2 10
e
At t = t
0
+ 7.2 s
i =
1
6
[e ] 0.6A
3
3
5
3/5
3
G
H
6V
i
SECTION 2 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains FOUR (04) questions.
Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is the correct answer.
For each question, choose the option corresponding to the correct answer.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : –1 In all other cases.
*Q.4 A bar of mass M = 1.00 kg and length L = 0.20 m is lying on a horizontal frictionless surface. One end of
the bar is pivoted at a point about which it is free to rotate. A small mass m = 0.10 kg is moving on the
same horizontal surface with 5.00 ms
-1
speed on a path perpendicular to the bar. It hits the bar at a distance
L/2 from the pivoted end and returns back on the same path with speed v. After this elastic collision, the
bar rotates with an angular velocity . Which of the following statement is correct?
(A) = 6.98 rad s
-1
and v = 4.30 ms
-1
(B) = 3.75 rad s
-1
and v = 4.30 ms
-1
(C) = 3.75 rad s
-1
and v = 10.0 ms
-1
(D) = 6.80 rad s
-1
and v = 4.10 ms
-1
Sol. A
Li = Lf
2
L ML L
m 5 mv
2 3 2
4
5 v
3
v
2
v
1
= e(u
1
u
2
)
L
v 1 5 0
2
(hinge)
m

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-18
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
v 5
10
Solving (1) & (2)
= 6.98 rad/sec
v = 4.3 m/s
Q.5 A container has a base of 50 cm × 5 cm and height 50 cm, as shown in the figure. It has two parallel
electrically conducting walls each of area 50 cm × 50 cm. The remaining walls of the container are thin and
non-conducting. The container is being filled with a liquid of dielectric constant 3 at a uniform rate of 250
cm
3
s
-1
. What is the value of the capacitance of the container after 10 seconds?
[Given: Permittivity of free space
0
= 9 × 10
-12
C
2
N
-1
m
-2
, the effects of the non-conducting walls on the
capacitance are negligible
50 cm
50 cm
5 cm
(A) 27 pF (B) 63 pF
(C) 81 pF (D) 135 pF
Sol. B
Let container is filled upto height x in 10 sec
250 10 = 50 5 x
X = 10 cm
1 2
C C C
1 0 2 0
A KA
C
d d
40cm
x=10cm
0
1 2
C A KA
d
12
4 4
2
9 10
C 40 50 10 3 50 10 10
5 10
12
63 10 F
C = 63 pF
*Q.6 One mole of an ideal gas expands adiabatically from an initial state (T
A
, V
0
) to final state
(T
f
, 5V
0
). Another mole of the same gas expands isothermally from a different initial state (T
B
,V
0
) to the
same final state (T
f
, 5V
0
). The ratio of the specific heats at constant pressure and constant volume of this
ideal gas is . What is the ratio T
A
/T
B
?
(A) 5
-1
(B)
5
1-
(C) 5
(B)
5
1+

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-19
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. A
1 1
1 1 2 2
TV T V
1
1
A 0 f 0
T V T 5V
1
A
f
T
5
T
as T
f
= T
B
1
A
B
T
5
T
*Q.7 Two satellites P and Q are moving in different circular orbits around the Earth (radius R). The heights of P
and Q from the Earth surface are h
P
and h
Q
, respectively, where h
P
= R/3. The accelerations of P and Q due
to Earth’s gravity are g
P
and g
Q
, respectively. If g
P
/g
Q
= 36/25, what is the value of h
Q
?
(A) 3R/5 (B) R/6
(C) 6R/5 (D) 5R/6
Sol. A
P
2
GM
g
R
R
3
Q
2
Q
GM
g
R h
Q
P
Q
R h
g36 36
4R
25 g 25
3
4R 6
3 5
= R+h
Q
Q
3R
h
5
SECTION 3 (Maximum Marks: 24)
This section contains SIX (06) questions.
The answer to each question is a NON-NEGATIVE INTEGER.
For each question, enter the correct integer corresponding to the answer using the mouse and the onscreen virtual numeric
keypad in the place designated to enter the answer.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +4 If ONLY the correct integer is entered;
Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
Q.8 A Hydrogen-like atom has atomic number Z. Photons emitted in the electronic transitions from level n = 4
to level n = 3 in these atoms are used to perform photoelectric effect experiment on a target metal. The
maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons generated is 1. 95 eV. If the photoelectric threshold
wavelength for the target metal is 310 nm, the value of Z is _______.
[Given: hc = 1240 eV-nm and Rhc = 13.6 eV, where R is the Rydberg constant, h is the Planck’s constant
and c is the speed of light in vacuum]

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-20
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. 3
4 3
E E E
2 2
1 1 7
h 13.6z 13.6 z
9 16 9 16
max
KE h
1.95 =
1240
h
310
h 1.95 4
5.95
2
7
13.6 z
9 16
z
2
= 9
z = 3
Q.9 An optical arrangement consists of two concave mirrors M
1
and M
2
, and a convex lens L with a common
principal axis, as shown in the figure. The focal length of L is 10 cm. The radii of curvature of M
1
and M
2
are 20 cm and 24 cm, respectively. The distance between L and M
2
is 20 cm. A point object S is placed at
the mid-point between L and M
2
on the axis. When the distance between L and M
1
is n/7 cm, one of the
images coincides with S. The value of n is _______
M
1 L
M
2
S
20 cm
Sol. 220 or 80 or 150 and you can explore other possibilities also
Case I:If M
1
is placed at distance
80
20
7
cm from lens, the rays retrace its path and image will be
formed at S.
60cm
10cm
80
7
cm
20cm
M
1
L
M
2
S
n = 220
From mirror
1 1 1
V 60cm
V 10 12
Refraction from lens
1 1 1
V 80 10
80
V cm
7

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-21
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Case II: Consider reflection from M
2
then refraction from lens. Image is at
80
cm
7
left of lens if M
1
is
placed at position of this image by lens, rays reflect back and final image is formed at S n = 80.
60cm
10cm
80
7
cm
M
1
L
M
2
S
Case III: First consider refraction from lens then reflection from M
1
if image due to this reflection is
formed at
80
cm
7
left of the lens, then image after refraction with lens and reflection with M
2
will be
formed at S. Then distance between L and M
1
= 10 +
80 150 n
n 150
7 7 7
60cm
10cm
80
7
cm
10cm
m
1
L
M
2
s
10cm
Q.10 In an experiment for determination of the focal length of a thin convex lens, the distance of the object from
the lens is 10 ± 0.1 cm and the distance of its real image from the lens is 20 ± 0.2 cm. The error in the
determination of focal length of the lens is n%. The value of n is _______.
Sol. 1
1 1 1
f v u
2 2 2
f v u
f v u
2 2
f v u
f
f v u
2 2
0.2 0.1 20
3
20 10
f
0.01
f
f
100% 1%
f
*Q.11 A closed container contains a homogeneous mixture of two moles of an ideal monatomic gas
( = 5/3) and one mole of an ideal diatomic gas ( = 7/5). Here, is the ratio of the specific heats at constant
pressure and constant volume of an ideal gas. The gas mixture does a work of 66 Joule when heated at
constant pressure. The change in its internal energy is ________ Joule.
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-22
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. 121
for isobaric process, work done
W = (n
1
+ n
2
) RT
W = 3RT
66 = 3RT
RT = 22
Change in internal energy
1 2
1 2
f f
u n R T n R T
2 2
2
Degree of freedom, f
1
3 5
2 R T 1 R T
2 2
11
R T 121
2
Joule
*Q.12. A person of height 1.6 m is walking away from a lamp post of height 4 m along a straight path on the flat
ground. The lamp post and the person are always perpendicular to the ground. If the speed of the person is
60 cm s
-1
, The speed of the tip of the person’s shadow on the ground with respect to the person is _______
cm s
−1
Sol. 40
2 2 1
4 1.6
x x x
2 1
3x 5x
2 1
dx dx
3 5
dt dt
2
dx 5
60 100 cm / s
dt 3
V
rel
= 40 cm/sec
x
2
x
1
4 m
1.6 m
V
m
= 60 cm/s
*Q.13 Two point-like objects of masses 20 gm and 30 gm are fixed at the two ends of a rigid massless rod of
length 10 cm. This system is suspended vertically from a rigid ceiling using a thin wire attached to its
center of mass, as shown in the figure. The resulting torsional pendulum undergoes small oscillations. The
torsional constant of the wire is 1.2×10
-8
Nm rad
-1
. The angular frequency of the oscillations in n ×10
−3
rad
s
-1
. The value of n is _____
g
30 gm
20 gm

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-23
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Sol. 10
Time period of oscillation
I
T 2
K
I = Moment of inertia
K = Torsional constant
moment of inertia I = 30 16 + 20 36
I = 12 10
5
kg m
2
I
T 2
K
5
8
12 10
2
1.2 10
= 200 sec
2
T
3
10 10 rad / s
n = 10
4 cm
6 cm
30gm
20gm
SECTION 4 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains FOUR (04) Matching List Sets.
Each set has ONE Multiple Choice Question.
Each set has TWO lists: List-I and List-II.
List-I has Four entries (P), (Q), (R) and (S) and List-II has Five entries (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5).
FOUR options are given in each Multiple Choice Question based on List-I and List-II and ONLY ONE of these four
options satisfies the condition asked in the Multiple Choice Question.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 ONLY if the option corresponding to the correct combination is chosen;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : –1 In all other cases.
Q.14 List-I shows different radioactive decay processes and List-II provides possible emitted particles. Match
each entry in List-I with an appropriate entry from List-II, and choose the correct option.
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P)
238 234
92 91
U Pa
(1)
one particle and one
+
particle
(Q)
214 210
82 82
Pb Pb
(2)
three
particles and one particle
(R)
210 206
81 82
T Pb
(3)
two
particles and one particle
(S)
228 224
91 88
Pa Ra
(4)
one particle and one
particle
(5)
one
particle and two
+
particles
(A) P 4, Q 3, R2, S1 (B) P 4, Q 1, R2, S5
(C) P 5, Q 3, R1, S4 (D) P 5, Q 1, R3, S2
Sol. A
Let x = No of particles
& y = No of
particles (if y = +ve)
= No of
+
particles (if y = ve)
(P) 238 4x = 234 x = 1 (one particle)
and, 92 2x + y = 91
y = 1 (one
particle)
(Q) 214 4x = 210 x = 1 (one particle)

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-24
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
and, 82 2x + y = 82
y = 2 (two
particle)
(R) 210 4x = 206 x = 1 (one particle)
and, 81 2x + y = 82
y = 3 (three
particle)
(S) 228 4x = 224 x = 1 (one particle)
and, 91 2x + y = 88
y = 1 (one
+
particle)
Q.15. Match the temperature of a black body given in List-I with an appropriate statement in List-II, and choose
the correct option. [Given: Wien’s constant as 2.9 10
-3
m-K and
6
hc
1.24 10 V m
e
]
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P) 2000 K (1)
The radiation at peak wavelength can lead to emission of
photoelectrons from a metal of work function 4 eV
(Q)
3000 K
(2)
The radiation at peak wavelength is visible to human eye.
(R) 5000 K (3)
The radiation at peak emission wa
velength will result in
the widest central maximum of a single slit diffraction
(S) 10000 K (4)
The power emitted per unit area is 1/16 of that emitted by
a blackbody at temperature 6000 K.
(5)
The radiation at peak emission wavelength can be used to
image human bones.
(A) P 3, Q 5, R2, S3 (B) P 3, Q 2, R4, S1
(C) P 3, Q 4, R2, S1 (D) P 1, Q 2, R5, S3
Sol. C
List-2
(1) radiation at peak
6
hc 1.24 10
4eV 4
6
0.31 10
0
3100A
3
m
T 2.9 10
3
10
m
2.9 10
3100 10
T
7
2.9 10
T 9354K
3100
10000 K
(2)
m
visible to human eye (violet to red)
(For 700 nm)
3
10
2.9 10 29000
T 4142
7000 10 7
5000 K
(For 400 nm)
3
10
2.9 10
T 7250
4000 10
(3) widest central maximum
max
T
min
2000 K
(4) power per unit area
1
16
(power by block body at T = 6000 K)
4
4
1
6000 T
16
T = 3000 K
(5) = 1
0
A

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-25
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
3
7
10
2.9 10
T 2.9 10
10
K
(p) 3, (q) 4, (r) 2, (s) 1
Q.16 A series LCR circuit is connected to a 45 sin(t) Volt source. The resonant angular frequency of the circuit
is 10
5
rad s
-1
and current amplitude at resonance is I
0
. When the angular frequency of the source is = 8 ×
10
4
rad s
−1
, the current amplitude in the circuit is 0.05 I
0
. If L = 50 mH, match each entry in List-I with an
appropriate value from List-II and choose the correct option.
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P)
0
in mA (1) 44.4
(Q)
The quality factor of the circuit
(2)
18
(R)
The bandwidth of t
he circuit in
rad s
−1
(3) 400
(S)
The peak power dissipated at
resonance in Watt.
(4) 2250
(5)
500
(A) P 2, Q 3, R5, S1 (B) P 3, Q 1, R4, S2
(C) P 4, Q 5, R3, S1 (D) P 4, Q 2, R1, S5
Sol. B
v = 45 sin (t)
r
= 10
5
rad/s
r
1
LC
5
3
1
10
50 10 C
9
C 2 10 F
L
X L 4000
C
1
X
C
= 6250
X = X
C
X
L
0.25 I
0
45
Z
R = 0.05 Z
2 2
R 0.05 2250 R
R = 112.6
0
45
I 400mA
R
L
X
Q 44.4
R
Bandwidth
R
2250 rad / s
L
2
V
P 18
R
W

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-26
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
(p) 3, (q) 1, (r) 4, (s) 2
Q.17 A thin conducting rod MN of mass 20 gm, length 25 cm and resistance 10 Ω is held on frictionless, long,
perfectly conducting vertical rails as shown in the figure. There is a uniform magnetic field B
0
= 4 T
directed perpendicular to the plane of the rod-rail arrangement. The rod is released from rest at time t = 0
and it moves down along the rails. Assume air drag is negligible. Match each quantity in List-I with an
appropriate value from List-II, and choose the correct option.
[Given: The acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m s
-2
and e
-1
= 0.4]
25cm
g
M
N
0
B
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P) At
= 0.2 s, the magnitude of the induced emf in Volt (1) 0.07
(Q)
At
= 0.2 s, the magnitude of the magnetic force in
Newton
(2) 0.14
(R)
At
= 0.2 s, the power dissipated as heat in Watt
(3)
1.20
(S)
The magnitude of terminal velocity of the rod in
m s
−1
(4)
0.12
(5)
2.00
(A) P 5, Q 2, R3, S1 (B) P 3, Q 1, R4, S5
(C) P 4, Q 3, R1, S2 (D) P 3, Q 4, R2, S5
Sol. D
mg i B ma
B v
i
R
2 2
B mdv
mg v
R dt
2 2
dv B
g v g cv
dt mR
where
2 2
B
c
mR
= 5
5t
v 2 1 e
at t = 0.2 v = 1.20
at t = 0.2 F
m
= 0.12
P = i
2
R = 0.14
V
T
= 2
(p) 3, (q) 4, (r) 2, (s) 5

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-27
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Chemistry
SECTION 1 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains THREE (03) questions.
Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONE OR MORE THAN ONE of these four
option(s) is(are) correct answer(s).
For each question, choose the option(s) corresponding to (all) the correct answer(s).
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +4 ONLY if (all) the correct option(s) is(are) chosen;
Partial Marks : +3 If all the four options are correct but ONLY three options are chosen;
Partial Marks : +2 If three or more options are correct but ONLY two options are chosen, both of which are
correct;
Partial Marks : +1 If two or more options are correct but ONLY one option is chosen and it is a correct
option;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : −2 In all other cases.
For example, in a question, if (A), (B) and (D) are the ONLY three options corresponding to correct answers,
then
choosing ONLY (A), (B) and (D) will get +4 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) and (B) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) and (D) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (B) and (D) will get +2 marks;
choosing ONLY (A) will get +1 mark;
choosing ONLY (B) will get +1 mark;
choosing ONLY (D) will get +1 mark;
choosing no option (i.e. the question is unanswered) will get 0 marks; and
choosing any other combination of options will get −2 marks.
Q.1. The correct statement(s) related to processes involved in the extraction of metals is (are)
(A) Roasting of Malachite produces Cuprite.
(B) Calcination of Calamine produces Zincite.
(C) Copper pyrites is heated with silica in a reverberatory furnace to remove iron.
(D) Impure silver is treated with aqueous KCN in the presence of oxygen followed by reduction with zinc
metal.
Sol. (B, C, D)
Malachite
CuCO .Cu OH CuO H O CO
3 2 2
2
2
Cuprite – Cu
2
O
Zincite
Calamine
ZnCO ZnO CO
3 2
Copper pyrite
CuFeS O Cu O FeO SO
2 2 2 2
11
2 2 4
2
Slag
FeO SiO FeSiO
2 3
Impure
Ag KCN H O O K Ag CN KOH
2 2
2
4 8 2 4 4
K Ag CN Zn K Zn CN Ag
2
2 4
2 2

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-28
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
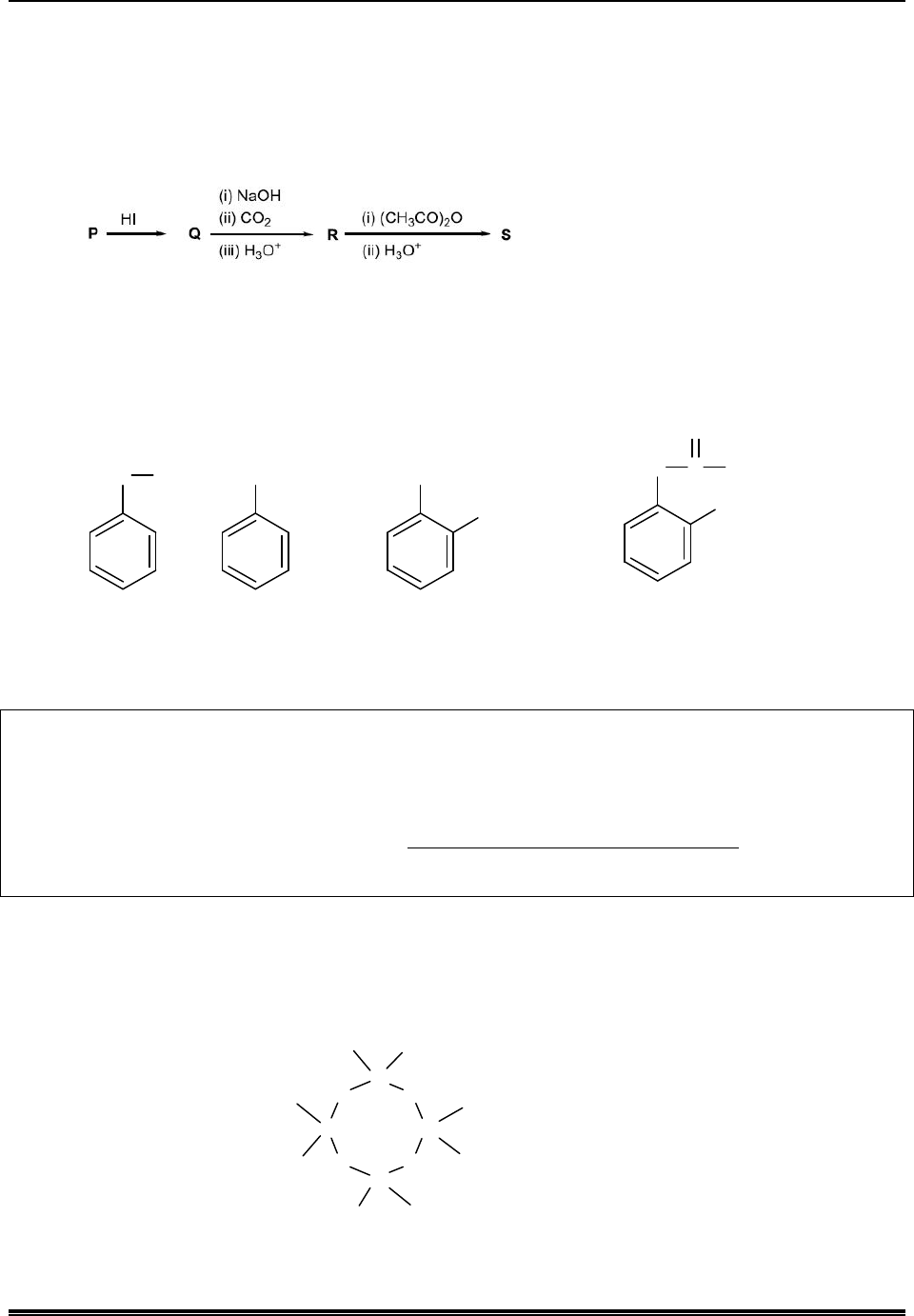
Q.2. In the following reactions, P, Q, R, and S are the major products.
The correct statement(s) about P, Q, R, and S is (are)
(A) Both P and Q have asymmetric carbon(s).
(B) Both Q and R have asymmetric carbon(s).
(C) Both P and R have asymmetric carbon(s).
(D) P has asymmetric carbon(s), S does not have any asymmetric carbon.
Sol. (C, D)
CH
3
CH
2
HC
CH
3
CH
2
CN
i PhMgBr then H O
3
CH
3
CH
2
HC
CH
3
CH
2
C
O
Ph
PhMgBr then H O
2
CH
3
CH
2
HC
CH
3
CH
2
C
Ph
OH
Ph
(P)
Ph H H
3
C C
O
Cl
anhy. AlCl
3
Ph C
O
CH
3
PhMgBr
then H O
2
Ph C
CH
3
OH
Ph
(Q)
CH
2
C
O
Cl
C
H
3
PhCH Cd
2
2
1
2
H
3
CH
2
C
C
O
CH
2
Ph
PhMgBr
H O
2
CH
2
C
OH
CH
2
C
H
3
Ph
Ph
(R)
PhMgBr, H O
PhCH CHO
2
2
Ph CH
2
C
Ph
H
OH
CrO
dil. H SO
3
2 4
Ph CH
2
C
O
Ph
HCN
PhH
2
C C
Ph
OH
CN
H SO
2 4
Ph CH C
Ph
COOH
(S)

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-29
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Q.3 Consider the following reaction scheme and choose the correct option(s) for the major products Q, R and S.
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Sol. (B)
HC C
H
2
i B H
ii NaOH, H O , H O
2 6
2 2 2
CH
2
CH
2
OH
(P)
CrO , dil. H SO
3 2 4
CH
2
COOH
Cl , Red P
H O
2
2
COOH
Cl
(Q)
H
2
C CH
2
OH
(P)
SOCl
2
CH
2
CH
2
Cl
NaCN
CH
2
CH
2
CN
H O
3
CH
2
CH
2
COOH
conc. H SO
2 4
O
(S)
(R)

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-30
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
SECTION 2 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains FOUR (04) questions.
Each question has FOUR options (A), (B), (C) and (D). ONLY ONE of these four options is the correct
answer.
For each question, choose the option corresponding to the correct answer.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 If ONLY the correct option is chosen;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : −1 In all other cases.
Q.4 In the scheme given below, X and Y, respectively, are
(A)
2
4 2
CrO and Br
(B)
2
4 2
MnO and Cl
(C)
4 2
MnO and Cl
(D)
4
MnSO and HOCl
Sol. (C)
NaOH
White
MnCl Mn OH NaCl
2
2
2
2
(P) (Q)
PbO excess
aq. H SO
X
Mn OH HMnO purple
2
2 4
4
2
P
MnO OH
conc. H SO
Y
warm
NaCl Cl
Q
2
2 4
2
Cl
2
+ KI – Starch Blue colouration
Q.5 Plotting 1/Λ
m
against cΛ
m
for aqueous solutions of a monobasic weak acid (HX) resulted in a straight line
with y-axis intercept of P and slope of S. The ratio P⁄S is
[Λ
m
= molar conductivity
0
m
= limiting molar conductivity
c = molar concentration
K
a
= dissociation constant of HX]
(A)
0
a m
K
(B)
0
a m
K / 2
(C)
0
a m
2K
(D)
0
a m
1/ K
Sol. (A)
m
m
a
m
m
C
K
2
0
0
1

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-31
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
m
m
a
m m
C
K
2
0
0
m
a
m m m
C
K
2
0 0
a m a m m m
K K C
2
0 0 2
m
a a m m
m
K K C
2
0
0
a mm
m
a M a m
kc
K K
0
2 2
0 0
1
m
m
m
a M
c
K
2 0
0
1 1
m
a m
S ; P
K
2 0
0
1 1
a m
P
K
S
0
*Q.6 On decreasing the pH from 7 to 2, the solubility of a sparingly soluble salt (MX) of a weak acid
(HX) increased from 10
–4
mol L
–1
to 10
–3
mol L
–1
. The pK
a
of HX is
(A) 3 (B) 4
(C) 5 (D) 2
Sol. (B)
Lets assume solubility of the salt MX is S at pH = 7.
sp
S S
MX s M X K S
2
...(1)
Lets assume solubility of the salt MX is S at pH = 2.
S S
MX s M X
S
S
X H HX
2
2
10
10
a
HX
K
X H
1
a
S
K
X
2
1
10
sp
a
K
S
K
2
2
10
…(2)
Equation (2) divided by equation (1)
sp
a sp
K
S
K K
S
2
2 2
1
10
a
K
3
2
4 2
10
1
10 10
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-32
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
K
a
= 10
4
pK
a(HX)
= 4
Q.7 In the given reaction scheme, P is a phenyl alkyl ether, Q is an aromatic compound; R and S are the major
products.
The correct statement about S is
(A) It primarily inhibits noradrenaline degrading enzymes.
(B) It inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandin.
(C) It is a narcotic drug.
(D) It is ortho-acetylbenzoic acid.
Sol. (B)
O R
(P)
HI
OH
i NaOH
ii CO
iii H O
2
3
OH
CO
2
H
(Q) (R)
i CH CO O
iii H O
3
2
3
O
CO
2
H
C
O
C
H
3
(S)
Aspirin is a non – narcotic analgesics.
It inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandin.
SECTION 3 (Maximum Marks: 24)
This section contains SIX (06) questions.
The answer to each question is a NON-NEGATIVE INTEGER.
For each question, enter the correct integer corresponding to the answer using the mouse and the on-screen
virtual numeric keypad in the place designated to enter the answer.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +4 If ONLY the correct integer is entered;
Zero Marks : 0 In all other cases.
*Q.8 The stoichiometric reaction of 516 g of dimethyldichlorosilane with water results in a tetrameric cyclic
product X in 75% yield. The weight (in g) of X obtained is___.
[Use, molar mass (g mol
−1
): H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, Si = 28, Cl = 35.5]
Sol. (222)
mol
CH SiCl
3 2
2
4
4
Si
O
O
Si
Si
O
O
Si
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
CH
3
(Molar mass of product = 296)
4 mol 0.75 mol (because efficiency = 75 %)
Mass of product = 0.75 296 = 222 gm

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-33
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
*Q.9 A gas has a compressibility factor of 0.5 and a molar volume of 0.4 dm
3
mol
–
1
at a temperature of
800 K and pressure x atm. If it shows ideal gas behaviour at the same temperature and pressure,
the molar volume will be y dm
3
mol
–
1
. The value of x/y is ___.
[Use: Gas constant, R = 8 × 10
-2
L atm K
-1
mol
-1
]
Sol. (100)
Z = 0.5
V = 0.4 dm
3
mol
1
T = 800 K
P = x
PV x .
Z .
RT .
0 4
0 5
0 08 800
X = 80
When Z = 1, Ideal condition molar volume y dm
3
PV
Z
RT
y
.
80
1
0 08 800
y = 0.8
x
y .
80
100
0 8
*Q.10 The plot of log k
f
versus 1/T for a reversible reaction
A g P g
is shown
Pre-exponential factors for the forward and backward reactions are 10
15
s
−1
and 10
11
s
−1
, respectively. If the
value of log K for the reaction at 500 K is 6, the value of | log k
b
| at 250 K is ___.
[K = equilibrium constant of the reaction
k
f
= rate constant of forward reaction
k
b
= rate constant of backward reaction]
Sol. (5)
f
logk 9
at 500 K,
9
f
k 10
a
b
b b
E
1
logk logA
2.303R T
9
6
eq
b
10
K 10
k
3
b
k 10
a
b
E
3 0.02 11
2.303R

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-34
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
a
b
E
8
4000
2.303R 0.002
b
1
logk 4000 11
250
16 11
5
b
logk 5
*Q.11 One mole of an ideal monoatomic gas undergoes two reversible processes (A B and B C) as shown in
the given figure:
A B is an adiabatic process. If the total heat absorbed in the entire process (A B and B C) is
RT
2
ln 10, the value of 2 log V
3
is ___.
[Use, molar heat capacity of the gas at constant pressure,
p,m
5
C R
2
]
Sol. (7)
A B
(reversible adiabatic),
5
3
total AB BC BC BC
q E q 0 q q
BC 2
q RT n10
For the process A to B
1 1
1 1 2 2
T V T V
1
2 1
1 2
V T
600
10
V T 60
5
1
3
2
1
V
10
V
3
2
2
1
V
10
V
3 5
2 2
2
V 10 10 10
5
2
2
V 10
3
2 2
2
V
RT n10 RT n
V

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-35
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
3
2
V
10
V
5 7
2 2
3 2
V 10V 10 10 10
7
2
3
2lnV 2 ln10
3
7
2logV 2 1
2
= 7
*Q.12 In a one-litre flask, 6 moles of A undergoes the reaction A (g)
P (g). The progress of product
formation at two temperatures (in Kelvin), T
1
and T
2
, is shown in the figure:
If
1 2 2 1 2
T 2T and G G RT lnx,
then the value of x is ……
[
1 2
[ G and G
are standard Gibb’s free energy change for the reaction at temperatures T
1
and T
2
,
respectively.]
Sol. (8)
1
2
1 eq
T
2 eq
T
A g P g
Initial mole 6 0
4
at eq.atT 2 4 K 2
2
2 1
at eq. T 4 2 K
4 2
o
1 1
G RT n2
o
2 2 2
1
G RT n RT n2
2
o o
2 1 2 1
G G RT n2 RT n2
1 2
T 2T
o o
2 1 2 2
G G RT n2 2RT n2
2 2
3RT n2 RT n8
2 2
RT n8 RT nX
So, X = 8
Q.13 The total number of sp
2
hybridised carbon atoms in the major product P (a non-heterocyclic
compound) of the following reaction is ___.
Sol. (28)

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-36
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
CN
NC
NC
CN
4 2
LiAlH ex then H O
CH
2
NH
2
H
2
NH
2
C
H
2
NH
2
C CH
2
NH
2
||
3
O
4Ph C CH
CH
2
NNCH
2
NCH
2
CH
2
N
C
CH
3
Ph
C
CH
3
Ph
C
CH
3
Ph
C
Ph
CH
3
SECTION 4 (Maximum Marks: 12)
This section contains FOUR (04) Matching List Sets.
Each set has ONE Multiple Choice Question.
Each set has TWO lists: List-I and List-II.
List-I has Four entries (P), (Q), (R) and (S) and List-II has Five entries (1), (2), (3), (4) and (5).
FOUR options are given in each Multiple Choice Question based on List-I and List-II and ONLY ONE of
these four options satisfies the condition asked in the Multiple Choice Question.
Answer to each question will be evaluated according to the following marking scheme:
Full Marks : +3 ONLY if the option corresponding to the correct combination is chosen;
Zero Marks : 0 If none of the options is chosen (i.e. the question is unanswered);
Negative Marks : −1 In all other cases.
Q.14 Match the reactions (in the given stoichiometry of the reactants) in List-I with one of their products given
in List-II and choose the correct option.
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P) P
2
O
3
+ 3H
2
O
(1) P(O)(OCH
3
)Cl
2
(Q) P
4
+ 3NaOH + 3H
2
O
(2) H
3
PO
3
(R) PCl
5
+ CH
3
COOH
(3) PH
3
(S) H
3
PO
2
+ 2H
2
O + 4AgNO
3
(4) POCl
3
(5) H
3
PO
4
(A) P 2; Q 3; R 1; S 5
(B) P 3; Q 5; R 4; S 2
(C) P 5; Q 2; R 1; S 3
(D) P 2; Q 3; R 4; S 5
Sol. (D)
2 3 2 3 3
P O 3H O 2H PO
4 2 3 2 2
P 3NaOH 3H O PH 3NaH PO
5 3 3 3
PCl CH COOH CH COCl POCl HCl
3 2 2 3 3 4 3
H PO 2H O 4AgNO H PO 4Ag 4HNO
P 2, Q 3, R 4, S 5
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-37
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Q.15 Match the electronic configurations in List-I with appropriate metal complex ions in List-II and choose the
correct option.
[Atomic Number: Fe = 26, Mn = 25, Co = 27]
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P)
6 0
2g g
t e
(1)
2+
2 6
[Fe(H O) ]
(Q)
3 2
2g g
t e
(2)
2+
2 6
[Mn(H O) ]
(R)
2 3
2
e t
(3)
3
3 6
[Co(NH ) ]
(S)
4 2
2g g
t e
(4)
-
4
[FeCl ]
(5)
2
4
CoCl
(A) P 1; Q 4; R 2; S 3
(B) P 1; Q 2; R 4; S 5
(C) P 3; Q 2; R 5; S 1
(D) P 3; Q 2; R 4; S 1
Sol. (D)
6 0
2g
P t eg
3
5
6
Co NH
6
3d
0
4s
0
4p
3
Co
NH
3
strong ligand, pairing takes place
eg
P – 3
3 2
2g g
Q t e
2
2
6
Mn H O
, H
2
O is weak ligand
2 5 0
Mn 3d 4s
Q 2
2 3
g 2g
R e .t
4
FeCl
3 5
Fe 3d

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-38
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
R 4
4 2
2g g
S t e
2
2
6
Fe H O
2 6
Fe 3d
S 1
Q.16 Match the reactions in List-I with the features of their products in List-II and choose the correct option.
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P)
(1) Inversion of configuration
(Q)
(2) Retention of configuration
(R)
(3) Mixture of enantiomers
(S)
(4) Mixture of structural isomers
(5) Mixture of diastereomers
(A) P 1; Q 2; R 5; S 3
(B) P 2; Q 1; R 3; S 5
(C) P 1; Q 2; R 5; S 4
(D) P 2; Q 4; R 3; S 5
Sol. (B)
P 2
2
* *
aq.NaOH
SN
C C C C C Br C C C C C OH Retention
| |
C C C C
JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-39
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
Q 1
2
| *
aq.NaOH
SN
*
Br
C C C C C C C C C C inversion
|
OH
R 3
2
|| |
aq.NaOH
SN
Br C
OH
C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C C
C C
| |
|
C C OH
S 5
Me H Me
Br
1
aq.NaOH
SN
Me H Me
OH
+
Me H Me
OH
Q.17 The major products obtained from the reactions in List-II are the reactants for the named reactions
mentioned in List-I. Match List-I with List-II and choose the correct option.
List
-
I
List
-
II
(P) Etard reaction
(1)
(Q) Gattermann reaction
(2)
(R) Gattermann-Koch reaction
(3)
(S) Rosenmund reduction
(4)
(5)
(A) P 2; Q 4; R 1; S 3
(B) P 1; Q 3; R 5; S 2
(C) P 3; Q 2; R 1; S 4
(D) P 3; Q 4; R 5; S 2
17. (D)
P 3
3 3
CH Cl / AlCl
CH
3
2 2
2 2
CrO Cl Etard
CS ,H O/H
CHO
Etardreaction
Q 4
NH
2
Cu
HCl
Cl
2
NaNO /HCl
273 278K
2
N Cl
Gattermanreaction

JEE(ADVANCED)-2023-Paper-1-MPC-40
FIITJEE Ltd., FIITJEE House, 29-A, Kalu Sarai, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi -110016, Ph 46106000, 26569493, Fax 26513942
website: www.fiitjee.com.
R 5
OH
3
CO,HCl
Anh.AlCl
CHO
Zn/
Gattermann Koch reaction
S 2
CH
3
COOH
2
SOCl
COCl
4
KMnO /KOH/
2 4
H Pd/BaSO
Rosenmund reduction
CHO
*****
