
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
i
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ........................................................................................................................ i
..............................................................................................................................ii
...............................................................................................................................ii
................................................................................................................. 1
................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................................................
................................................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................................................
................................................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................
................................................................................................
................................................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................................................
................................
................................................................
List of Figures
List of Tables
Chapter 1: Introduction
Background 1
Purpose ....... 2
Scope and Applicability .............. 2
Authorities and Foundational Documents ................ 3
Document Management and Maintenance ............. 3
Chapter 2: Disaster Grant Program Preparations ................................................................
................................................................................................
................................
................................................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................................................
........ 5
Mitigation Plan ........................... 6
Other Needs Assistance Administrative Option Selection Form ............. 7
Administrative Plans .................. 8
Payment and Management System Setup ............... 8
Special Conditions and Requirements ..................... 8
Procurement Requirements .. 9
Special Designated Areas ...................................................................................................... 9
Chapter 3: Post-Declaration Requirements ............... 11
Post-Declaration ....................... 11
Pre-Assistance Requirements . 11
Sign FEMA-State/Territory/Tribe Agreement ..... 12
Apply for Disaster Grant Funding ........................ 12
Chapter 4: Public Assistance Program Requirements .............................. 13
Applicant Briefing ..................... 14
Request for Public Assistance . 14
Public Assistance Work Categories ......................... 14
Special Compliance Considerations ................... 16
Alternative Procedures ............ 16
Chapter 5: Individual Assistance Program Requirements ........................ 17
Individuals and Households Program ..................... 18
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
ii
Special Compliance Considerations ................................................................
................................................................
................................................................................................
................................
................................
................................................................................................
................................................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................................................
................................
................................................................
................................
................................
................................
................................................................
................... 18
Mass Care and Emergency Assistance ................... 18
Other IA Program Services ....... 19
Recipient Actions to Activate IA Program Functions .............................. 19
Chapter 6: Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Requirements .................... 23
Hazard Mitigation Planning ..... 24
Hazard Mitigation Funding ...... 24
Special Compliance Considerations ................................................................
................................................................
................................................................................................
................... 25
Hazard Mitigation Planning Assistance .............. 25
Advance Assistance ............. 25
Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist ........................... 27
Appendix A: List of Acronyms ..................................................................................................... A-1
Appendix B: Glossary .................................................................................................................. B-1
Appendix C: Authorities and Foundational Documents ............................................................ C-1
Appendix D: References ............................................................................................................ D-1
List of Figures
Figure 1: Required Recipient Actions Before Receiving Disaster Grant Funding from FEMA . 5
Figure 2: Key Recipient Actions for PA Grants ........... 13
Figure 3: Key Recipient Actions for IA Grants ............ 17
Figure 4: Key Recipient Actions for HMGP Grants ..... 23
List of Tables
Table 1: PA Work Categories and Work Examples ..... 15
Table 2: IA Program Functions and Recipient Requirements ................... 20
Table 3: Amount of Available HMGP Assistance ........ 25
Table 4: Tasks in Preparation for Stafford Act Program Funds ................ 27
Table 5: Post-Declaration Requirements for PA Program ......................... 30
Table 6: Post-Declaration Requirements for IA Program .......................... 35
Table 7: Post-Declaration Requirements for HMGP .. 40
Table 8: FEMA Disaster Assistance Grant Programs Guidance References.......................... D-1
Table 9: FEMA Disaster Assistance Grant Programs Form References ................................. D-2

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
1
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Background
The Robert T. Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance Act (Stafford Act)
authorizes the President to provide federal assistance when the magnitude of an incident or
threat of an incident exceeds the affected state, territorial, Indian tribal (tribal), and local
governments’ capability to respond or recover. To receive federal disaster assistance, a
governor or tribal chief executive must submit a request for an emergency or major disaster
declaration to the President through the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA).
The Stafford Act (as amended) provides
federally recognized tribal governments the
option to request an emergency or major
disaster declaration directly from the
President. This enables tribal governments
to receive assistance in the form of grants
or cooperative agreements through FEMA
Public Assistance (PA), Individual
Assistance (IA), and Hazard Mitigation Grant
Programs (HMGP) as Recipients
independent of a state’s disaster
declaration. This provides tribal
governments more autonomy to determine
how they want to seek Stafford Act
assistance and which assistance to pursue.
In addition to this option, tribal
governments retain the authority to apply
for assistance as a Recipient or
Subrecipient (as allowed by state law)
under a state’s disaster declaration. Tribal
governments may not receive the same
type of assistance (i.e., PA, IA, or HMGP) for
both tribal and state declarations for the
same incident.
The declaration request, once approved by the President, designates disaster-impacted
areas and establishes the incident period, the type of incident, the type(s) of assistance
available, and the federal cost share amount for the provision of requested assistance, if
applicable. While an approved declaration authorizes FEMA disaster assistance grant
programs, the requesting state, territorial, or tribal government has additional requirements
Key Terminology
All terminology pertaining to the disaster
declaration process and PA, IA, and HMGP is
derived from FEMA doctrine and other
federal guidance. Key terms that appear
throughout this document are “Recipient,”
“Applicant,” and “Subrecipient.”
Recipient – A non-federal entity that
receives an award from a federal agency
(e.g., state, territorial, or tribal government)
to carry out an activity under a federal
program.
Applicant – A non-federal entity that applies
to be a Subrecipient of assistance under a
Recipient’s federal award (e.g., local
government agency, housing authority, or
private nonprofit organization).
Subrecipient – An Applicant that receives a
sub-award from a Recipient to carry out part
of a federal program.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
2
to complete before FEMA allocates and dispenses grant funds. The FEMA New Recipients of
Disaster Grants Guide describes the most critical requirements for Recipients in requesting
and receiving FEMA disaster assistance grant funding.
Purpose
The FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide is intended to provide streamlined
guidance to state, territorial, and tribal governments on the essential elements of PA, IA, and
HMGP and required actions to request, initiate, and receive FEMA disaster assistance
grants.
Scope and Applicability
The FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide outlines the critical statutory, policy, and
procedural requirements for Recipients of FEMA disaster assistance grants. The scope of
the FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide includes pre-disaster preparations and
post-disaster actions and is tailored to an audience of current (or prospective) Recipients of
federal disaster grant funding. The information in the FEMA New Recipients of Disaster
Grants Guide is meant to supplement available programmatic guidance and assist new
Recipients with limited experience in navigating the FEMA disaster grant process.
The FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants
Guide describes Recipient requirements for
the three FEMA categories of disaster grant
assistance available to Recipients following a
Presidential emergency or major disaster
declaration: PA, IA, and HMGP. FEMA
provides specific guidance for state-led PA
and is developing state-led housing options
to allow Recipients to manage greater
portions of the recovery effort. Recipients
interested in pursuing these options should
consult with regional program staff for details
and requirements.
In addition to internal program requirements, the FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants
Guide highlights critical connections with FEMA’s National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP)
that impact eligibility for federal assistance.
1
Furthermore, the FEMA New Recipients of
Disaster Grants Guide includes a checklist (Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist) to assist
1
For additional information on special designations and requirements that may impact your community, refer
to NFIP participation guidance at https://www.fema.gov/participation-national-flood-insurance-program.
Scope Limitations
The scope of the FEMA New Recipients
of Disaster Grants Guide
does not
include the Fire Management Assistance
Grant (FMAG) program. The scope also
does not include HMGP Post Fire, which
allows for mitigation assistance absent a
major disaster declaration, contingent on
the occurrence of an FMAG event. For
more information on the FMAG program,
refer to the FEMA
Fire Management
Assistance Grant Program Guide.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
3
new Recipients in pre-disaster preparations and post-disaster execution of key actions
required for facilitating the provision of FEMA disaster assistance grant program funds.
New Recipients should use the FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide in
conjunction with the assistance of FEMA PA, IA, and HMGP representatives to ensure a
comprehensive understanding of all available program options and requirements.
For more detailed guidance on each disaster assistance program, coordinate with your
regional program representative and refer to the following program-specific documents:
• Public Assistance Program and Policy Guide (PAPPG)
) • Individual Assistance Program and Policy Guide (IAPPG
• Hazard Mitigation Assistance (HMA) Guidance
Authorities and Foundational Documents
The following are the foundational documents and authorities for the FEMA New Recipients
of Disaster Grants Guide:
• Robert T. Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance Act (Public Law 93-288,
as amended, 42 U.S.C. § 5121-5207)
• Title 2 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) § 200
• Title 44 CFR §§ 201 and 206
• Sandy Recovery Improvement Act of 2013 (Public Law 113-2)
• Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance, January 2017
• Damage Assessment Operations Manual, April 2016
• FEMA National Disaster Recovery Framework (Second Edition), June 2016
• FEMA Individual Assistance Program and Policy Guide (IAPPG), March 2019
• FEMA Public Assistance Program and Policy Guide, April 2018
• FEMA Hazard Mitigation Assistance Guidance, February 2015
• FEMA Policy: State Mitigation Plan Review Guide (Guide), March 2015
• FEMA Policy: Tribal Mitigation Plan Review Guide, December 2017
Appendix C provides additional information about authorities and foundational documents.
Document Management and Maintenance
The FEMA Office of Response and Recovery, Doctrine and Policy Office is responsible for the
management and maintenance of this document. Comments and feedback from FEMA
personnel and stakeholders regarding this document should be directed to the Doctrine and
Policy Office at FEMA headquarters (HQ).
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
4
This Page Intentionally Left Blank

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
5
CHAPTER 2: DISASTER GRANT PROGRAM
PREPARATIONS
State, territorial, and tribal governments
should work to complete FEMA’s required
tasks and to achieve a thorough
understanding of their own internal grant
administration processes and federal
regulations prior to requesting a
Presidential declaration. FEMA requires
Recipients to complete each task before
releasing approved disaster grant funds.
Completion of these tasks before a
declaration request will expedite
disbursement of approved funds; addressing these tasks post-declaration will delay the
delivery of disaster grant funding. The status of each task will not affect a state, territorial, or
tribal government’s eligibility to request or be approved for a disaster declaration.
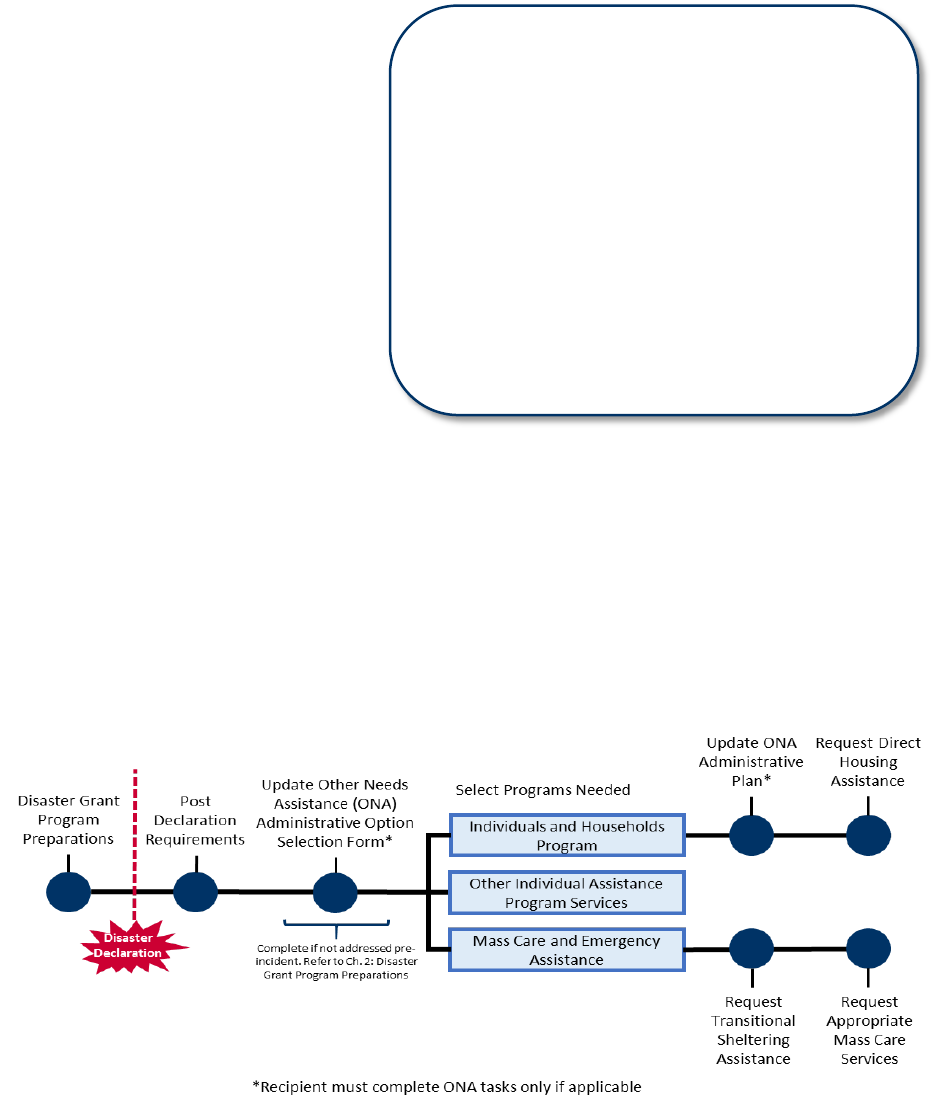
Figure 1 identifies required tasks that a Recipient must complete before it can receive FEMA
disaster assistance grant funds.
Figure 1: Required Recipient Actions Before Receiving Disaster Grant Funding from FEMA
Technical Assistance for Preparations
Completing certain preparatory tasks (e.g.,
preparing a Mitigation Plan) can be complex, time-
consuming, and require in-depth research and
analysis. FEMA staff are available to provide
technical assistance to state, territorial, and tribal
governments in completing each task. State,
territorial, and tribal representatives should
coordinate with a FEMA regional program
representative if they require technical assistance.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
6
Program-specific requirements for PA, IA, and HMGP can be found in subsequent chapters.
Refer to Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist for additional details and deadlines for FEMA
disaster assistance grant program preparedness tasks. Refer to Appendix D: References for
a list of guidance documents and forms applicable to each of FEMA’s disaster assistance
grant programs.
Mitigation Plan
FEMA requires Recipients to have an
approved Mitigation Plan in place before
receiving disaster grant program funding
for HMGP or the Permanent Work
categories of PA.
2, 3
Recipients must
review and revise Mitigation Plans to
reflect changes in development,
progress in mitigation efforts, and
changes in priorities and resubmit for
approval to the appropriate Regional
Administrator (RA) every 5 years.
However, Recipients must also submit
an updated Mitigation Plan if the current
plan does not reflect the priorities of the
current disaster. The Mitigation Plan
requirement encourages Recipients to
engage in hazard mitigation planning to
identify risks and vulnerabilities associated with natural disasters and to develop long-term
strategies for protecting people and property against future hazards.
Development of a well-crafted and applicable Mitigation Plan requires significant foresight
and research to identify potential mitigation projects. Recipients should ensure they are
aware of all applicable eligibility conditions, laws, regulations, and insurance requirements
that impact the provision of PA and HMGP, including participation in the NFIP. Refer to
FEMA’s Mitigation Planning Guidance for more information, or contact FEMA Hazard
Mitigation staff to request technical assistance for developing a Mitigation Plan. Refer to
Chapter 6: Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Requirements for additional details on FEMA
2
44 CFR § 201.4 says that states must have an approved standard State Mitigation Plan (SMP) that meets the
requirements included in the section as a condition of receiving non-emergency Stafford Act assistance and
FEMA mitigation grants.
3
44 CFR § 201.7 says that Indian tribal governments applying to FEMA as a Recipient must have an approved
Tribal Mitigation Plan meeting the requirements included in the section as a condition of receiving non-
emergency Stafford Act assistance and FEMA mitigation grants.
Tribal Mitigation Plan Requirements
Tribal government Recipients must submit an
approved Mitigation Plan within 30 days of
signing the FEMA-Tribal Agreement (FTA) and
may request an extension for up to 90
additional days. The Regional Administrator
(RA) may grant exceptions to this requirement
in extraordinary circumstances. In these cases,
the Mitigation Plan must be completed within
12 months of the award of the mitigation grant.
If a plan is not provided within this
timeframe,
all mitigation projects funded through the grant
will be terminated and costs incurred after
notice of grant termination will not be
reimbursed, as described under the 44 CRF
§§
206.434(b)(2); 201.6(a)(3).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
7
support for hazard mitigation planning. FEMA also provides the following resources for
mitigation planning:
• State Mitigation Plan Review Guide
• Tribal Mitigation Plan Review Guide
Other Needs Assistance Administrative Option Selection Form
FEMA’s IA programs provide assistance to survivors through a variety of functions and
coordinated services, including Other Needs Assistance (ONA). ONA provides financial
assistance to survivors for disaster-related expenses and serious needs not covered by
insurance or another source.
FEMA requires Recipients to complete an ONA Administrative Option Selection Form (ONA
Administrative Form) before they can receive financial assistance under the ONA program.
Recipients use the ONA Administrative Form to indicate who will be responsible for
administering assistance under ONA. Recipients have the following options:
• FEMA-administered ONA,
• Recipient-administered ONA (requires an accompanying administrative plan), or
• Recipient and FEMA joint-administered ONA (requires an accompanying
administrative plan).
All Recipients must submit their ONA selections to FEMA annually, regardless of the
administrative option selected. With this annually updated form, the Recipient establishes
the maximum amount of assistance that may be awarded to eligible individuals for
transportation assistance, funeral assistance, and child care assistance. This process
requires an evaluation of the Recipient’s capacity to administer ONA and identifies cost
thresholds and item exemptions for certain categories of ONA.
In addition, the ONA Administrative Form provides an opportunity for the Recipient to make
adjustments to the established personal property line items. FEMA uses a standardized list
of personal property items to determine which disaster-damaged items may be eligible for
ONA. Recipients have the option to modify these lists. The Recipient may request the
addition of line items other than those on FEMA’s standard personal property line item list
when submitting or updating the ONA Administrative Form. All updates to the form must be
completed by the Recipient within 72 hours of authorization of the IA Program.
If the Recipient chooses to administer a part of ONA, FEMA requires it submit an ONA
Administrative Plan.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
8
Administrative Plans
To receive PA and HMGP funding, Recipients must develop and submit to FEMA an
administrative plan that describes how the Recipient intends to administer the grant
funding. Recipients must have a current administrative plan for each program approved by
FEMA before receiving PA and HMGP funds.
FEMA requires Recipients of disaster assistance grant funding to complete an ONA
Administrative Plan only if the Recipient elects to take on part or all of the administrative
role of the ONA process. Recipients must update their ONA Administrative Plan every 3
years. If the Recipient chooses the option in which FEMA maintains full administrative
responsibility for ONA, it does not need to complete an ONA Administrative Plan.
Payment and Management System Setup
State, territorial, and tribal governments must ensure proper registration in the federal
grants system by obtaining a Data Universal Number System (DUNS) number. The DUNS
number allows the Federal Government to track the allocation of federal funds. Recipients
must look up their organization’s existing DUNS number or register for a new number
through the Dun and Bradstreet (D&B) Website. It may take up to 2 business days for
Recipients to obtain a DUNS number.
To access federal funds, Recipients must have a direct deposit account via the Payment
Management System (PMS)/Smartlink. To establish an account, first-time Recipients must
create a PMS account online and submit a written request to the RA, including a completed
Direct Deposit Sign-Up Form (SF1199A). The PMS Access Form and Direct Deposit Sign-Up
Form are available at pms.psc.gov/. Recipients should allow up to 3 weeks to receive PMS
access and for Direct Deposit Sign-Up Form processing.
Special Conditions and Requirements
State, territorial, and tribal governments should ensure familiarity and compliance with all
program eligibility conditions, in addition to completing recommended tasks in preparation
for future incidents.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
9
Procurement Requirements
Federal procurement standards for
state and territorial governments
differ from those of tribal and local
governments, nonprofits, and other
non-federal entities. Recipients
should ensure that staff
responsible for coordinating the
request and administration of
disaster grant funding for IA, PA,
and HMGP have a complete
understanding of—and comply
with—all procurement standards
and regulations.
Special Designated Areas
Special eligibility restrictions and
conditions for PA, IA, and HMGP
may apply to communities located within special designated areas, including those in
special flood hazard areas (SFHA). To qualify for the full amount of assistance available
under each of FEMA’s disaster assistance programs, Recipients should be knowledgeable of
all special designations that may impact their communities and comply with applicable
FEMA and National Flood Insurance Reform Act (NFIRA) requirements. Refer to the FEMA
webpage on Participation in the National Flood Insurance Program for further information.
Procurement Requirements
State and territorial governments must follow the same
policies and procedures it uses for procurements from
its non-federal funds. In addition, they must also:
• Comply with 2 CFR §
200.322, “Procurement of
Recovered Materials”; and
• Ensure every purchase order or other contract
includes all clauses required by 2 CFR §
200.326, “Contract Provisions.”
Tribal and local governments, and private nonprofits
must conduct procurement transactions in a manner
that complies with 2 CFR §
200.318 to 2 CFR §
200.326 when procuring property and services under a
federal award.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
10
This Page Intentionally Left Blank

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
11
CHAPTER 3: POST-DECLARATION REQUIREMENTS
To receive FEMA disaster assistance grant funds, state, territorial, or tribal governments
must request a declaration from the President through FEMA within 30 days of the incident.
State, territorial or tribal governments may also submit a declaration request prior to an
imminent incident (e.g., hurricane). FEMA may extend the request deadline if the governor or
tribal chief executive submits a written time extension request within 30 days of the
incident, stipulating the reason for the delay. Refer to the Guide to the Disaster Declaration
Process and Federal Disaster Assistance or the Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance for
additional information on declaration requirements.
Post-Declaration
When the President approves a request for an emergency or major disaster declaration,
FEMA personnel may deploy to the impacted areas to support Recipient staff in response
and recovery activities. In the case of smaller incidents, FEMA may provide Recipients with
virtual support from a regional office or FEMA HQ. FEMA personnel will assist Recipients in
fulfilling post-declaration requirements, including the following:
• Signing the FEMA-State/Territory/Tribe Agreement (FSA/FTA), and
• Submitting the Application for Federal Assistance (SF-424) and other required
documentation to receive PA, IA, and HMGP funding.
Pre-Assistance Requirements
Immediately following a Presidential
disaster declaration, the Recipient must
sign an FSA/FTA and submit a formal
Application for Federal Assistance (SF-
424) to receive PA, IA, and HMGP funds.
In addition, FEMA requires the Recipient
to complete all tasks described in Chapter
2: Disaster Grant Program Preparations
before receiving FEMA disaster
assistance grant funding. Refer to
Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist for
more detailed guidance on each task,
including important deadlines.
Legal Review for Federal Assistance Agreement
Recipients should enlist legal counsel to review
the FSA/FTA
prior to signing to ensure complete
understanding of the conditions associated with
the provision of disaster grant funding. Under 44
CFR §
205.44 (a), “this Agreement imposes
binding obligations on FEMA, states, their local
governments, and private nonprofit organizations
within the states in the form of conditions for
assistance which are legally enforceable.”

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
12
Sign FEMA-State/Territory/Tribe Agreement
Recipients must sign an FSA/FTA for each disaster in order to document commitments and
conditions under which FEMA will provide assistance. The FSA/FTA must be signed by the RA
or his/her designee and the governor or tribal chief executive.
Apply for Disaster Grant Funding
To receive approved FEMA disaster assistance grant funds, a Recipient must submit an SF-
424 for each program. An SF-424 is required to formally request each type of assistance
made available in the approved declaration, based on the needs of the designated areas.
The Assurances for Construction Programs (SF-424D) accompanies the SF-424 for PA and
HMGP and provides additional certification of a Recipient’s compliance with construction
contracting practices and procedures per federal grant requirements. In addition, state,
territorial, tribal, and local government entities and private nonprofits seeking PA funding
must review and sign the Damage Description and Dimension, which FEMA uses to
determine what damages are eligible for PA.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
13
CHAPTER 4: PUBLIC ASSISTANCE PROGRAM
REQUIREMENTS
The PA Program is FEMA’s largest grant program, providing funds to assist communities
responding to and recovering from Presidential-declared major disasters or emergencies.
Figure 2 provides an overview of the key actions a Recipient must complete to receive and
manage PA grant funding. Refer to Chapter 2: Disaster Grant Program Preparations for
guidance on tasks FEMA requires Recipients to complete before applying for and receiving
disaster grant assistance. Refer to Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist for more detailed
program requirements, including important deadlines for the PA Program.
Figure 2: Key Recipient Actions for PA Grants
Public Assistance Cost Share
The standard federal cost share for PA is 75-percent of the eligible costs. If the actual federal
obligations, excluding administrative costs, meet or exceed a qualifying threshold, then FEMA may
make a recommendation to the President to increase the federal share to up to 90-percent. In limited
cases, the President may increase the federal share for Emergency Work, if warranted.
Management Costs: Under the “FEMA Recovery Policy, Public Assistance Management Costs
(Interim),” which applies retroactively to disasters declared on or after August 1, 2017, FEMA may
provide funding (up to 7-percent for Recipients and 5-percent for Subrecipients) for management
costs incurred by a Recipient or Subrecipient in administering a PA grant. There is no cost share
requirement for this policy. Contact your regional FEMA representative or regional tribal liaison for
more information about this policy.
Donated Resources: FEMA allows Recipients and Subrecipients to apply the value of donated
resources used during the performance of eligible Emergency and Permanent Work toward the non-
federal cost share of its eligible Emergency and Permanent Work projects. Recipients and
Subrecipients must meet certain conditions to apply the offset to specific Emergency and Permanent
Work. Refer to the FEMA Recovery Policy, “
Public Assistance Donated Resources,” for more
information. Permanent and Emergency Work are detailed in this chapter.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
14
Applicant Briefing
As soon as possible following a Presidential declaration, the Recipient conducts briefings for
all potential Applicants (i.e., state, territorial, tribal, and local government entities and
private nonprofits). The Recipient is responsible for notifying potential Applicants of the date,
time, and location of the Applicant briefing. Prior to the Applicant briefing, the FEMA regional
office will coordinate with the Recipient to ensure the Recipient has all necessary
information and materials to educate Applicants on the PA Program.
Request for Public Assistance
Recipients are responsible for ensuring that
entities who wish to seek assistance under the
PA Program submit a Request for Public
Assistance (RPA) to FEMA within 30 days of the
respective area designation in the declaration.
The RPA is an Applicant’s official notification to
FEMA of the intent to apply for PA funds. Using
the RPA, the Applicant provides general
information about its organization, including
physical location and point of contact.
Public Assistance Work Categories
FEMA processes PA grant funding based on the type of work the Applicant undertakes.
There are two main project types for PA: Emergency Work and Permanent Work.
• Emergency Work categories provide assistance for debris removal and emergency
protective measures to save lives and protect property.
• Permanent Work categories assist with permanently restoring community
infrastructure affected by a declared incident.
Table 1 identifies the categories of PA Emergency Work and Permanent Work and applicable
examples of each work category.
Mitigation Plan Requirement
FEMA requires Recipients to have an
approved, up-to-date Mitigation Plan in place
before receiving disaster grant program
funding for Permanent Work categories of PA.
Refer to Chapter 2: Disaster Grant Program
Preparations for additional details on
Mitigation Plan requirements. Refer to
Chapter 6: Hazard Mitigation Grant Program
Requirements for additional guidance on
mitigation planning assistance.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
15
Table 1: PA Work Categories and Work Examples
Category of Work
Examples
Emergency Work
A: Debris Removal
• Clearance, removal, and disposal of the following:
o Vegetation
o Construction and demolition debris
o Vehicle and vessel wreckage
B: Emergency
Protective Measures
•
Expenses related to operating a facility or providing an emergency service
• Firefighting and rescue activities
• Assistance to private nonprofit organizations
• Emergency Operations Center-related costs
• Evacuation and sheltering
Permanent Work
C: Roads and Bridges
•
Applies to components of paved, gravel, or dirt roads
• Covers bridge components, including the following:
o Guardrails
o Pavement
o Lighting, sidewalks, and signs
D: Water Control
Facilities
• Dams and reservoirs
• Levees and floodwalls
• Pumping facilities
• Engineered drainage channels
• Irrigation facilities
E: Public Buildings and
Contents
• All structural and non-structural components, including mechanical,
electrical, and plumbing
• Furnishings
F: Public Utilities
•
Water storage facilities, treatment plants, and delivery systems
• Power generation, transmission, and distribution facilities
• Natural gas transmission and distribution facilities
• Sewage collection systems and treatment plants
• Communication systems
G: Parks, Recreational,
and Other Facilities
•
Mass transit facilities (railways)
• Beaches
• Parks, playground equipment, and picnic tables
• Swimming pools, tennis courts, ball fields, golf courses
• Ports and harbors, boat docks, and piers
• Fish hatcheries

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
16
Special Compliance Considerations
Special restrictions and conditions apply to PA funding for projects located within an SFHA
and other designated areas. FEMA must reduce the amount of assistance made available
when a facility is in an area that FEMA has identified as an SFHA for more than one year, has
been damaged by flooding, and is uninsured for flood loss through the NFIP. For additional
requirements and terms refer to the PAPPG or NFIP.
Alternative Procedures
Prior to beginning Permanent Work, Recipients should evaluate whether they intend to opt
for using the alternative procedures for administering Permanent Work under the PA
Program. Initiating Permanent Work activities before notifying FEMA of the intent to
participate in the PA Program will render the Recipient and all work ineligible for the
alternative procedures program.
The alternative procedures option for Permanent Work allows the Recipient (and
Subrecipient) to receive grant funding for Permanent Work projects based on fixed
estimates of the cost needed to complete the projects; however, costs above the awarded
amount must be paid for by the Recipient. Recipients should coordinate with FEMA recovery
staff at the regional office or in the Joint Field Office (JFO) (if established) to determine if the
alternative procedures option is suitable to address their Permanent Work requirements.
Refer to the Public Assistance Alternative Procedures Pilot Guide for Permanent Work for
additional details on alternative procedures for Permanent Work.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
17
CHAPTER 5: INDIVIDUAL ASSISTANCE PROGRAM
REQUIREMENTS
FEMA’s IA programs deliver support
to disaster survivors for unmet
needs caused by a Presidential-
declared incident. This chapter
describes the primary functions and
coordinated services available
under IA programs, including the
following:
• Individuals and Households
Program (IHP)
• Mass Care and Emergency
Assistance
• Other IA Program services
Figure 3 provides an overview of the actions that a Recipient must complete to receive IA
grant funding for survivor needs. Authorization of IA in the declaration automatically makes
many IA programs available. However, several IA programs require additional Recipient
actions before FEMA can allocate and disperse grant funding. Refer to Chapter 2: Disaster
Grant Program Preparations for guidance on tasks FEMA requires Recipients to complete
before applying for and receiving disaster grant assistance. For IA Program and subprogram
requirements, including important deadlines and cost share requirements for select IA
services, refer to Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist.
Figure 3: Key Recipient Actions for IA Grants
100-Percent Funded Individual Assistance
Several IA programs are 100-percent federally funded
following a disaster declaration and an approved
request for IA, including the following:
• IHP housing assistance (time limitations may
apply), and
• Other IA Program services:
o Disaster Case Management (DCM),
o Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training
Program (CCP),
o Disaster Legal Services (DLS), and
o Disaster Unemployment Assistance (DUA).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
18
Individuals and Households Program
IHP provides financial and direct services
to eligible individuals and households
affected by a disaster who have
uninsured or underinsured necessary
expenses and serious needs. IHP is not a
substitute for insurance and cannot
compensate for all losses caused by a
disaster. IHP is intended to meet the
survivor’s basic needs and supplement
disaster recovery efforts. FEMA provides
two categories of IHP assistance: ONA and housing assistance.
Special Compliance Considerations
Certain restrictions and conditions may apply to FEMA’s provision of IHP assistance in SFHAs
and other designated areas. FEMA and NFIRA regulations require Applicants that receive
federal financial assistance for flood-damaged property, flood-insurable real property,
and/or personal property to purchase and maintain flood insurance. Flood insurance
requirements apply to real and personal property that is within or will be within an SFHA and
that can be insured under the NFIP. Refer to the IAPPG and NFIP for additional details on
special insurance requirements.
Mass Care and Emergency Assistance
During Presidential-declared disasters, most Mass Care and Emergency Assistance services
are Direct Federal Assistance (DFA), which is funded under the Stafford Act, § 403 (a)(3)(B)
(commonly referred to as a PA Category B). The federal share of such assistance cannot be
less than 75-percent of the eligible cost. Some examples include non-congregate sheltering
through Transitional Sheltering Assistance (TSA), personal assistance services (PAS) through
the Individual Assistance Support Contract (IASC), and reunification services through the
National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC).
FEMA Mass Care and Emergency Assistance provides coordination and support to state,
territorial, tribal, and local governments or jurisdictions for the provision or direct delivery of
life-sustaining services to disaster survivors. All survivors impacted by a disaster are eligible
to receive Mass Care and Emergency Assistance services. There is no application process
for Mass Care and Emergency Assistance services because these are most often life
sustaining. Two notable exceptions to this general rule include TSA and the Blue Roof
Program (see Table 2). FEMA coordinates a group of supporting federal agencies and non-
governmental organizations (NGO) through Emergency Support Function (ESF) #6 to deliver
IHP Period of Assistance
IHP assistance is limited to 18 months following
the date of the Presidential disaster declaration.
The President may extend the period of
assistance because of extraordinary
circumstances. The governor or tribal chief
executive must request an extension in writing
through the Assistant Administrator for Recovery.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
19
services to disaster survivors and impacted communities, typically through state or local
partners and nonprofits, with technical assistance and resource support from FEMA.
FEMA field leadership, ESF #6 federal support agencies, and Voluntary Organizations Active
in Disasters support state,
territorial, tribal, and local
government management of
congregate sheltering,
feeding, emergency supplies,
and evacuation services for
impacted areas; these
services require limited effort
on the part of the Recipient.
Other services require greater
Recipient involvement. Most
notably, this includes
disability, access and
functional needs support, and
some non-congregate
sheltering options. Refer to
the IAPPG for more
information on Mass Care and
Emergency Assistance
services.
Other IA Program Services
Other IA Program services offered by FEMA to assist in disaster recovery include crisis
counseling, disaster legal services, disaster unemployment assistance, and disaster case
management. These services are completely federally funded. Refer to the IAPPG for more
information on each of these services.
Recipient Actions to Activate IA Program Functions
Table 2 provides a description of the assistance available under the IHP, Mass Care and
Emergency Assistance, other IA Program services, and the Recipient requirements to receive
assistance.
Individual Assistance Support Contract
The IASC is an optional contract intended to support
delivery of ESF #6 Mass Care and Emergency Assistance
services to disaster survivors. Activation of the IASC may
be appropriate where it is determined through market
research that no small business or local contract
possesses the resource capabilities to meet the
requirement. IASC provides support and services to
augment NGO and state, territorial, tribal, and local
government partner capabilities when there are gaps and
shortfalls with existing resources.
Recipients may request activation of an IASC using the
standard resource request form. FEMA evaluates and
validates all requests for IASC activation and will
coordinate with the Recipient to develop a scope of work
(SOW) and cost estimate to initiate the IASC. The IASC is
subject to a 25-percent state, territorial, or tribal
government cost share requirement.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
20
Table 2: IA Program Functions and Recipient Requirements
Available
Assistance
Description
Required Recipient Action
Individuals and Households Program (IHP)
Other Needs
Assistance
(ONA)
•
Financial assistance for specific disaster-
caused expenses and serious needs, including
the following:
o Personal Property Assistance
o Transportation Assistance
o Moving and Storage Assistance
o Group Flood Insurance Policy
o Funeral Assistance
o Medical and Dental Assistance
o Child Care Assistance
o Assistance for Miscellaneous Items
o Critical Needs Assistance (CNA)
o Clean and Removal Assistance (CRA)
•
Submit ONA
Administrative Option
Selection Form to
Individual Assistance (IA)
Division Director.
o Establish
reimbursement
maximums.
o Identify covered
personal property
line items.
• Submit ONA
administrative plan to the
Federal Coordinating
Officer (FCO) (if Recipient
elects to administer ONA
program funds).
• Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Section 425
Transportation
Assistance
•
Supports relocation of individuals to and from
alternative locations for short- or long-term
accommodation or returning individuals to their
pre-disaster primary residence or alternative
location.
•
Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Housing
Assistance
(Financial)
•
Funds provided to eligible Applicants for
temporary lodging expenses, rental of
temporary housing, or repair or replacement of
a damaged primary residence.
•
Activated by approved IA
declaration and signed
FEMA-
State/Territory/Tribe
Agreement.
Housing
Assistance
(Direct)
•
Housing solutions for Applicants unable to use
rental assistance because of a lack of available
housing resources.
• Includes temporary housing units, travel trailer
housing units, multi-family lease and repair,
direct lease, and repairs and new construction
when other housing options are not available,
feasible, or cost effective.
•
Submit a written request
to the Assistant
Administrator for
Recovery.
Mass Care and Emergency Assistance
Sheltering
Support
• Equipment, materials, supplies, and personnel
to support life-sustaining services in
congregate and non-congregate facilities for
displaced survivors.
• Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Transitional
Sheltering
Assistance (TSA)
• Provides a short-term alternative to non-
congregate sheltering for displaced disaster
survivors in emergency shelter locations other
than their pre-disaster primary residence.
• Submit activation request
package.
o Refer to Chapter 7:
New Recipient
Checklist and FEMA

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
21
Available
Assistance
Description
Required Recipient Action
•
TSA is funded under Section 403 of the
Stafford Act and is subject to Public Assistance
Program regulations on cost-share.
Mass Care Emergency
Assistance Disaster
Specific Guidance for
more specific
requirements for TSA.
Operation Blue
Roof Program
•
Free temporary roof for residential structures,
schools, daycares, and some publicly-owned
facilities; provides short-term relief until the
owner can make permanent repairs.
•
Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Feeding Support
•
Equipment, materials, supplies, and personnel
to support state, territorial, tribal or local
governmental feeding services to evacuees,
disaster survivors, and emergency workers.
•
Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Distribution of
Emergency
Supplies
• Targeted acquisition, storage, delivery, and
provision of life-sustaining resources, hygiene
items, and cleanup items to meet the
immediate, basic needs of evacuees and
disaster survivors.
• Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Disability,
Access, and
Functional
Needs Support
• Services and resources for people with
disabilities and others with access and
functional needs, including the following:
o Durable medical equipment,
o Consumable medical supplies, and
o Personal assistance services to support
survivors with disabilities maintain their
health, safety, and independence in
temporary sheltering situations.
• Refer to Chapter 7: New
Recipient Checklist for
more specific
requirements for
requesting resources for
people with disabilities or
access and functional
needs.
Reunification
Services
• Facilitation for the reunification of
unaccompanied minors with their custodial
parents/legal guardians, as well as voluntary
reunification of adults with their families.
• Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Household Pets
and Service
Animals Support
•
Coordination and support for the rescue,
transportation, shelter, reunification, essential
needs, and care of household pets and service
and assistance animals.
•
Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Mass Evacuee
Support
• Provision of life-sustaining services and
resources to mass evacuees.
• Coordinate with field
leadership, as needed.
Other IA Program Services
Crisis
Counseling
Assistance and
Training
Program (CCP)
•
Provides financial assistance to state,
territorial, tribal, and local government
agencies through a grant or a cooperative
agreement to provide crisis counseling services
or contract with local mental service providers
familiar with the affected communities to
provide services.
o Includes Immediate Services Program (ISP)
and Regular Services Program (RSP).
•
Refer to Chapter 7: New
Recipient Checklist for
more specific
requirements for CCP
services.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
22
Available
Assistance
Description
Required Recipient Action
Disaster
Unemployment
Assistance
(DUA)
•
Provides unemployment benefits and
reemployment services to individuals who have
become unemployed as a direct result of the
incident.
•
Request in declaration or
coordinate with field
leadership, as need
arises.
Disaster Legal
Services (DLS)
•
Provides confidential legal assistance to low-
income individuals who are unable to secure
legal services to meet their disaster-related
needs.
•
Request in declaration or
coordinate with field
leadership, as need
arises.
Disaster Case
Management
(DCM)
•
Provides supplemental federal financial
assistance to Recipients to provide case
management services to disaster survivors.
• Non-governmental organizations may be
Recipients of DCM and have full
responsibility
to comply with all applicable requirements.
•
Refer to Chapter 7: New
Recipient Checklist for
more specific
requirements for the DCM
program.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
23
CHAPTER 6: HAZARD MITIGATION GRANT
PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS
FEMA Hazard Mitigation Assistance
(HMA) disaster assistance grants
though HMGP provide funding for
eligible activities that reduce
community vulnerability from
disasters and their effects, promote
individual and community safety
and resilience, and promote
community vitality after an incident.
HMGP assistance aims to reduce
response and recovery resource
requirements in the wake of a
disaster or incident, which results in
a safer community that is less
reliant on future federal assistance.
Figure 4 provides an overview of
actions that a Recipient must
complete to receive HMGP funding.
Refer to Chapter 2: Disaster Grant
Program Preparations for guidance on tasks FEMA requires Recipients to complete before
applying for and receiving disaster grant assistance. Refer to Chapter 7: New Recipient
Checklist for more detailed program requirements, including important deadlines.
Figure 4: Key Recipient Actions for HMGP Grants
Hazard Mitigation Grant Program Award Cost Share
HMGP awards are required to have at least a 25-
percent non-federal cost share. Exceptions to the
standard cost share may be made for insular areas
when the non-federal share meets certain
requirements or when other special considerations
are met. Refer to the HMA Guidance for cost share
details.
Under the interim policy, “Hazard Mitigation Grant
Program Management Costs,” which applies
retroactively to disasters declared on or after August
1, 2017, FEMA may provide funding, up to 10-
percent for Recipients and 5-percent for
Subrecipients, for management costs incurred by a
Recipient or Subrecipient in administering an HMGP
grant. There is no cost share requirement for this
policy. Contact your FEMA regional hazard mitigation
officer for more information about this policy.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
24
Hazard Mitigation Planning
FEMA requires Recipients to have an
approved, up-to-date Mitigation Plan in
place before receiving HMGP disaster
grant funding and assistance for
Permanent Work categories of PA. Refer
to Chapter 2: Disaster Grant Program
Preparations for additional details on
Mitigation Plan requirements.
Recipients are responsible for
determining their mitigation priorities
through mitigation planning. The State
Hazard Mitigation Officer or equivalent
territorial or tribal representative should
identify hazards that pose the greatest threat and develop an appropriate mitigation
strategy. The mitigation strategy, a required component of the Mitigation Plan, identifies the
specific mitigation activities the Recipient has determined can reduce vulnerability and
includes information on the methodology used to identify, prioritize, and implement the
range of mitigation actions considered. If the mitigation priorities and strategies identified in
the Mitigation Plan do not align with conditions for implementation following a disaster, the
Recipient must update the plan before receiving approved funding.
Following a declaration, Recipients may submit applications for projects to FEMA for
determination of eligibility, feasibility, mitigation planning, cost effectiveness, and
environmental planning and historic preservation considerations. Applicants that wish to
apply for mitigation funding must submit selected mitigation projects to the Recipient for
review. The Recipient is responsible for prioritizing applications for submission to FEMA
based on criteria that align with its approved mitigation strategy with regard to funding and
project type.
Hazard Mitigation Funding
The amount of HMGP funding available to the Applicant is based on the estimated total
federal disaster assistance and is subject to a sliding scale formula outlined in Table 3.
4
Refer to Chapter 7: New Recipients Checklist for more detailed HMGP requirements,
including important deadlines.
4
44 CFR § 206.432(b).
Enhanced Mitigation Plan Incentives
FEMA provides additional funding to Recipients
that develop enhanced Mitigation Plans following
a disaster declaration. To receive FEMA approval
of an enhanced Mitigation Plan, a Recipient must
demonstrate that it has developed a
co
mprehensive mitigation program and is
capable of managing increased funding to
achieve its mitigation goals. Refer to FEMA’s
Hazard Mitigation Planning Frequently Asked
Questions for additional details regarding hazard
mitigation planning.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
25
Table 3: Amount of Available HMGP Assistance
Disaster Assistance Amount
Amount of HMGP
Funding
Up to $2 Billion
Up to 15-percent
$2 Billion to $10 Billion
Up to 10-percent
$10 Billion to $35.333 Billion
Up to 7.5-percent
Special Compliance Considerations
FEMA and NFIRA restrictions and conditions may impact HMGP eligibility. Applications for
HMGP projects located within an SFHA are eligible for funding only if the respective
jurisdiction participates in the NFIP. For additional requirements and details, refer to the
HMA Guidance.
Hazard Mitigation Planning Assistance
The Stafford Act authorizes financial assistance for Recipients to support hazard
identification and risk assessments leading to the development of a comprehensive
Mitigation Plan and strategy for reducing risks to life and property.
FEMA’s Pre-Disaster Mitigation (PDM) Grant Program is designed to assist Recipients in
implementing a sustained pre-disaster natural hazard mitigation program to reduce overall
risk to the population and structures from future hazard events, while also reducing reliance
on federal funding in future disasters
5
. The PDM Grant Program is separate from HMGP
under HMA; as such, Recipients can use funds to support assessment of mitigation
requirements, project and strategy identification, and mitigation planning without an active
Presidential declaration. Refer to the HMA Guidance for more information on PDM.
Advance Assistance
Advance Assistance provides Recipients with resources to develop mitigation strategies and
obtain data to prioritize, select, and develop HMGP applications. Advance Assistance,
authorized by the Stafford Act (as amended), allows advancement of up to 25-percent of the
HMGP ceiling or $10 million, whichever is less, to accelerate implementation of HMGP.
Refer to the HMA Guidance for more information on Advance Assistance.
5
Stafford Act, 42 U.S.C. 5133 authorizes PDM.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
26
This Page Intentionally Left Blank

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
27
CHAPTER 7: NEW RECIPIENT CHECKLIST
This chapter provides a checklist of relevant programmatic dates, requirements, and Recipient tasks prior to—and following—
provision of Stafford Act program assistance (e.g., PA, IA, and HMGP). The checklist is not comprehensive of all program
requirements, options, and responsibilities. Recipients should execute the checklist with assistance from FEMA staff. Refer to
Appendix D: References for a list of guidance documents applicable to each of FEMA’s disaster assistance grant programs.
Table 4 provides an overview of the tasks a Recipient must perform before FEMA provides Stafford Act program assistance.
Table 4: Tasks in Preparation for Stafford Act Program Funds
Completed
Task
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Develop and maintain a
state, territorial, or tribal
Mitigation Plan.
6
R
• All Recipients must have a FEMA approved Mitigation Plan in place before receiving
disaster grant funding for the Hazard Mitigation Grant Program (HMGP) or the
Permanent Work Categories of PA. Mitigation Plans must be updated every five
years.
o Recipients must submit an updated Mitigation Plan to reflect any changes made
within the five-year period
• Recipients should identify risks and vulnerabilities associated with natural disasters
to protect against future hazards. Refer to the following planning guidance for more
information:
o Hazard Mitigation Planning Process.
Complete/review other
needs assistance (ONA)
Administrative Option
Selection Form and
submit it to FEMA.
7
R
•
All Recipients should indicate their option selection every year using Form FF 010-0-
11.
o The ONA Administrative Option Selection Form must be completed and
submitted to the FEMA Regional Administrator (RA) by
November 30th
.
o For more information on the ONA Administrative Option Selection Form and
process, refer to the Individual Assistance Program and Policy Guide (IAPPG).
Acquire a Data Universal
Number System (DUNS)
number for your
organization.
P
• First-time Recipients must look up their organization’s existing DUNS number or
register for a new DUNS number (allow up to 2 business days for processing) at
https://www.dnb.com/duns-number.html.
6
44 CFR §§ 201.4(d), 201.6(d)(3); 201.7(d); 206.434(b)(2)
7
44 CFR § 206.120(b) and 120(c)(1).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
28
Completed
Task
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Establish a direct deposit
account (Payment
Management System
[PMS]/Smartlink).
P
•
First-time Recipients must go to https://pms.psc.gov/ and select the “Request
Access to PMS” button to create a PMS account. Once registered, Recipients may
login to their account to complete the Payment Management Access Form.
• New Recipients must also submit a request letter and the Direct Deposit Sign-Up
Form (SF-1199A) to the RA to establish a direct deposit account.
Develop and maintain an
administrative plan for
Public Assistance (PA).
8
R
•
Recipients should renew their administrative plans for PA on an annual basis.
o For a new incident that occurs within the year, the Recipient must also submit
amendments to its administrative plan to address specifics of the new incident.
• Refer to the following guidance for more information on developing a plan:
o Sample Components of a Post-Declaration Administrative Plan .
Develop and maintain an
administrative plan for
HMGP.
9
R
•
Recipients should review and update their administrative plan for HMGP on an
annual basis.
• Recipients must review and update the plan following a Presidential major disaster
declaration to meet current policy guidance or changes to the administration of the
program.
Develop and maintain an
administrative plan for
ONA.
10
R
•
If a Recipient plans to administer a part of ONA, it must submit an ONA
administrative plan to the RA every 3 years.
Execute a FEMA-
State/Territory/Tribe
Agreement (FSA/FTA).
11
R
• Recipients must review and sign the FSA/FTA prior to receiving disaster grant
funding.
• Recipients may be required to submit programmatic addendums to the FSA/FTA,
depending on the assistance designated in the declaration and whether additional
terms and conditions for implementation of specific assistance are needed.
8
44 CFR § 206.207(b)(3).
9
44 CFR § 206.437.
10
44 CFR § 206.120(c)(1).
11
44 CFR § 206.44.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
29
Completed
Task
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Apply for Disaster Grant
Funding.
12
R
•
Recipients must submit an Application for Federal Assistance (SF-424) to FEMA to
formally request disaster grant funding following a declaration.
o Recipients may submit one SF-424 Form for all PA programs and designate
which PA programs they would like to receive.
o Recipients may submit individual SF-424 Forms for specific Individual Assistance
(IA) programs, as needed, including the Individuals and Households Program,
Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training Program (e.g., Immediate Services
Program and Regular Services Program), and the Disaster Case Management
Program.
(As
Needed)
Update Mitigation Plan. P
• Recipient must submit updates to the Mitigation Plan to FEMA before HMGP funds
are disbursed if the current plan does not reflect the priorities of the current disaster.
(As
Needed)
Update administrative
plan for PA.
13
R
• Recipient must submit updates to the administrative plan to FEMA before PA funds
are disbursed.
(As
Needed)
Update ONA
Administrative Option
Selection Form.
14
R
•
Recipient must submit updates within
72 hours
of IA Program authorization.
12
44 CFR §§ 206.202(e); 206.120(e); and 207.171(g)(2).
13
44 CFR § 206.207(b)(3).
14
44 CFR § 206.120(c)(3)(i) and (ii).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
30
Table 5 provides a description of post-declaration PA Program requirements.
Table 5: Post-Declaration Requirements for PA Program
Completed
Public Assistance (PA)
Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
PA Program Startup
Develop or update
Mitigation Plan.
15
Required before
delivery of PA funding.
Note:
Tribal government
Recipients must submit
an approved Mitigation
Plan within 30 days of
signing the FEMA-Tribal
Agreement.
R
•
Recipients should identify risks and vulnerabilities associated
with natural disasters to protect against future hazards.
• Tribal government Recipients may request an extension for
up to 90 days.
• Refer to the Hazard Mitigation Planning
Process for additional
information.
Develop or update an
administrative plan for
PA.
16
Required before
delivery of PA funding
R
•
Recipients should renew their administrative plan for PA on
an annual basis.
• For a new incident that occurs within the year, the Recipient
must also submit amendments to its administrative plan to
address specifics of the new incident.
• Refer to the following guidance for more information on
developing a plan:
o Sample Components of a Post-Declaration Administrative
Plan.
PA Initial Collaboration
Conduct Applicant
briefing.
Within 30 days of the
disaster declaration
date.
P
•
Recipient is responsible for conducting a briefing to provide
Applicants with high-level information regarding the PA
Program.
15
44 CFR §§ 201.4(d), 201.6(d)(3); 201.7(d); and 206.434(b)(2)
16
44 CFR § 206.207(b)(3).
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
31
Completed
Public Assistance (PA)
Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
(As
Needed)
Submit Request for
Public Assistance (RPA).
17
,
18
Within 30 days after
designation of the area
where the damage
occurred
R
•
The Recipient is responsible for ensuring Applicants submit
RPAs (
FEMA Form 90-49) through the PA Grants Portal to
apply for federal assistance through FEMA’s PA Program.
o If denied, Applicant must submit an appeal in writing to
the Recipient within 60 days of receipt of the notification.
Recipient must forward the appeal with its written
recommendation to the Regional Administrator (RA)
within 60 days of receipt.
o If the appeal is denied, Applicants have an additional
60 days to submit a second (and final) appeal to the
Recipient. The Recipient must send the appeal with its
written recommendation to the Assistant Administrator
for Recovery within 60 days.
Project Formulation
Contact Applicant to
schedule Recovery
Scoping Meeting (RSM).
Within 10 days of
receiving notice of RPA
approval.
P
•
The Recipient is responsible for scheduling an RSM with the
Applicant to discuss details of the Applicant’s impacts from
the incident.
•
Conduct RSM for
approved RPAs.
Within 21 days of
approval of the RPA.
P
•
The Recipient is responsible for hosting with FEMA an RSM
with the Applicant to provide an overview of requirements
and expectations.
Identify and report
damage inventory.
19
Within 60 days of RSM. R
•
The Recipient must identify and submit a list to FEMA of all
disaster-related damage, Emergency Work, and debris
quantities.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the
Public Assistance Program and
Policy Guide (PAPPG).
17
44 CFR § 206.202(c).
18
44 CFR § 206.206.
19
44 CFR § 206.202(d)(ii).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
32
Completed
Public Assistance (PA)
Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Conduct Exit Briefing.
When project
formulation is
complete, and all
claimed damage is
documented.
P
•
The Recipient must conduct an Exit Briefing with the
Applicant when project formulation is complete, and all
claimed damage is documented.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the PAPPG.
Grant Management and Administration
Complete all Emergency
Work.
20
Within 6 months of
disaster declaration
date.
R
• The Recipient should ensure completion of all Emergency
Work PA projects, including debris removal.
(As
Needed)
Request additional time
to complete Emergency
Work.
21
Within 6 months of
disaster declaration
date.
R
•
If an Applicant determines that it requires additional time to
complete a project, including direct administrative tasks
related to a project, it must submit a written request for a
time extension to the Recipient with supporting information.
The Recipient may grant a 6-month extension under
extenuating circumstances.
• If an extension greater than 6 months is necessary, the
Recipient must submit a written request for a time extension
to the RA with supporting information.
Complete all
Permanent Work.
22
Within 18 months of
disaster declaration
date.
R
•
The Recipient should ensure should ensure completion of all
Permanent Work PA projects.
(As
Needed)
Request additional time
to complete Permanent
Work.
23
Within 18 months of
disaster declaration
date.
R
•
If an Applicant determines that it requires additional time to
complete a project, including direct administrative tasks
related to a project, it must submit to the Recipient a written
request for a time extension, with supporting information. The
Recipient may grant a 30-month extension under extenuating
circumstances.
• If an extension greater than 30 months is necessary, the
Recipient must submit a written request for a time extension
to the RA, with supporting information.
20
44 CFR § 206.204(c)(1).
21
44 CFR § 206.204(c)(2)(ii) and (d).
22
44 CFR § 206.204(c)(1).
23
44 CFR § 206.204(c)(2)(ii) and (d).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
33
Completed
Public Assistance (PA)
Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Submit quarterly
progress reports.
24
No later than 30 days
after the end of each
quarter.
R
•
Recipient must submit quarterly reports on open and
uncompleted large projects by the following dates:
Q1 = Oct. 1
st
to Dec. 31
st
(Due Jan. 30
th
)
Q2 = Jan. 1
st
to Mar. 31
st
(Due Apr. 30
th
)
Q3 = Apr. 1
st
to Jun. 30
th
(Due Jul. 30
th
)
• Q4 = Jul. 1
st
to Sep. 30
th
(Due Oct. 30
th
)
Closeout
(As
Needed)
Submit a net small
project overrun
appeal.
25
Within 60 days of the
completion of the last
small project.
R
• The Recipient must submit a “net small project overrun
appeal” to support Subrecipient requests for additional
funding when the total actual costs of its small projects
combined exceed the total amount obligated for all of its
small projects.
• For more information on appeals requirements, refer to the
PAPPG.
Submit supporting
documentation to
Recipient.
26
Within 90 days of
completion of the last
small project.
R
•
Subrecipient must provide Recipient with supporting
documentation for all work completed.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the PAPPG.
Submit certification of
small project
completion.
27
Within 180 days of
project deadline.
R
•
Recipient must submit certification of completion for each
small project to FEMA, including a final payment of the claim
and supporting documentation.
• Recipient must submit certification that all incurred costs
associated with the approved statement of work (SOW) and
all work was completed in accordance with FEMA regulations
and policies.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the PAPPG.
Submit supporting
documentation to
Recipient.
28
Within 90 days of
completion of last large
project.
R
•
Subrecipient must provide Recipient with supporting
documentation for all work completed.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the PAPPG.
24
44 CFR § 206.204(f).
25
44 CFR § 206.204(e)(2).
26
2 CFR § 200.343(a).
27
2 CFR § 200.343(b).
28
2 CFR § 200.343 (a).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
34
Completed
Public Assistance (PA)
Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Submit certification of
large project
completion.
29
Within 180 days of
project deadline.
R
•
Recipient must submit certification of completion for each
large project to FEMA, including a final payment of the claim
and supporting documentation.
• Recipient must submit certification that all incurred costs
associated with the approved SOW and all work were
completed in accordance with FEMA regulations and policies.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the PAPPG.
29
2 CFR § 200.343(b).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
35
Table 6 provides a description of post-declaration IA Program requirements.
Table 6: Post-Declaration Requirements for IA Program
Completed
Individual Assistance
(IA) Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
IA Program Startup
Review and update
Other Needs Assistance
(ONA) Administrative
Option Selection
Form.
30
Prior to receiving ONA
funds.
R
•
Regardless of the administrative option selected, all
Recipients should indicate their option selection every year
using Form
FF 010-0-11.
o The ONA Administrative Form must be completed and
submitted to the Regional Administrator (RA) by
November 30th
.
o The Recipient has 72 hours following IA Program
authorization to update and submit the ONA
Administrative Form.
• For more information on the ONA Administrative Option
Selection Form and process, refer to the
Individual Assistance
Program and Policy Guide (IAPPG).
(As
Needed)
Develop or update a
state, territorial, or
tribal government ONA
Administrative Plan.
31
Prior to receiving ONA
funds to be
administered by the
Recipient.
R
•
If a Recipient plans to administer ONA or to jointly administer
with FEMA, it must submit an ONA Administrative Plan to the
RA every 3 years.
(As
Needed)
Submit Immediate
Services Program (ISP)
application for Crisis
Counseling.
32
Within 14 days of the
disaster declaration.
R
•
Recipient must submit an ISP application package to the RA.
o If denied, Recipient may appeal by submitting a written
letter to the IA Division Director, Federal Coordinating
Officer (FCO), or appropriate FEMA entity (Assistant
Administrator for Recovery or RA if the Joint Field Office
[JFO] has been demobilized) within 60 days of notification.
• For more information on submission requirements and
appeals, refer to the IAPPG and
Crisis Counseling Assistance
and Training Program Online Toolkit.
(As
Needed)
Request Critical Needs
Assistance (CNA).
Within 14 days of the
disaster declaration.
P
•
Recipient must submit a written request to IA Division Director
through the RA.
• For more information on requirements, refer to the IAPPG.
30
44 CFR §§ 206.120(b) and 120(c)(1).
31
44 CFR § 206.120(c)(1).
32
44 CFR § 206.171.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
36
Completed
Individual Assistance
(IA) Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
(As
Needed)
Request Transitional
Sheltering Assistance
(TSA).
Up to 30 days after a
major disaster
(suggested).
P
•
Refer to FEMA Mass Care and Emergency Assistance Disaster
Specific Guidance or additional information on TSA
requirements and activation procedures, implementation
information, and tools.
• Unless waived, TSA is subject to a 25-percent Recipient cost
share requirement.
(As
Needed
Request Operation Blue
Roof Program
No deadline P
•
Submit a Resource Request Form to the RA, and coordinate
with field leadership for additional requirements (e.g.,
statement of work, and independent government cost
estimates).
• Mass care and Emergency Assistance support services are
subject to a 25-percent Recipient cost share requirement.
(As
Needed)
Request extension of
the IA registration
period.
Prior to the end of the
initial registration
period.
P
• Recipient may request the RA extend the registration period up
to 60 days when additional time is required to collect
registrations from the affected population. All subsequent
requests for extension must be submitted to the IA Division
Director.
Submit ISP mid-
program report.
Within 60 days of
disaster declaration
date. (with RSP
application)
P
• If ISP assistance is provided, Recipient must submit a mid-
program report to the appropriate RA when an RSP award
application is being prepared and submitted.
(As
Needed)
Notify FEMA/
Substance Abuse and
Mental Health Services
Administration
(SAMHSA) of intent to
apply for Regular
Services Program (RSP)
for Crisis Counseling.
Within 45 days of
disaster declaration
date.
P
• The Recipient must notify FEMA and SAMHSA if it is planning
to submit an application for the RSP award during the ISP
period of performance.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
37
Completed
Individual Assistance
(IA) Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
(As
Needed)
Submit RSP
application.
33
Within 60 days of
disaster declaration
date.
R
•
Recipients must submit an RSP application package to the
RA/SAMHSA.
o If denied, Recipients must submit a written letter to the IA
Division Director within 60 days of notification.
• Request for extensions to the period of performance or for
additional funds must be submitted to the RA.
o If denied, Recipients must submit a written letter to the IA
Division Director within 60 days of notification.
o For more information on submission requirements, refer
to the IAPPG and
Crisis Counseling Assistance and
Training Program Online Toolkit.
(As
Needed)
Request Clean and
Removal Assistance
(CRA).
Within 60 days of
disaster declaration
date.
P
•
Recipient must submit a written request to the FCO.
• For more information on submission requirements, refer to the
IAPPG
.
(As
Needed)
Apply for Disaster Case
Management (DCM)
Program.
Within 90 days of
disaster declaration
date.
P
•
Recipients should submit a DCM application package with
their IA declaration request.
o If denied, Recipients must submit a written letter of
appeal to IA Division Director within 60 days of the
notification.
o For more information on submission requirements, refer
to the IAPPG.
(As
Needed)
Request Section 425
Transportation
Assistance.
No deadline. P
•
Recipient must submit a written request to the Assistant
Administrator for Recovery through the RA.
• For more information on requirements, refer to the IAPPG.
(As
Needed)
Activate National
Center for Missing and
Exploited Children
(NCMEC) and the
National Emergency
Child Locator Center
(NECLC).
No deadline.
P
• A limited range of assistance is available to meet needs.
o Recipient must complete a Resource Request Form.
o Refer to American Red Cross Safe and Well.
33
44 CFR § 206.171.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
38
Completed
Individual Assistance
(IA) Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
(As
Needed)
Request Mass Care and
Emergency Assistance
support services.
No deadline. P
•
Submit Resource Request Form to the RA, and coordinate with
field leadership for additional requirements (e.g., statement of
work, and independent government cost estimates).
• Mass Care and Emergency Assistance support services are
subject to a 25-percent Recipient cost share requirement.
(As
Needed)
Request Direct Housing
Assistance.
No deadline. P
•
Submit a written request for Direct Housing Assistance to the
Assistant Administrator for Recovery following direct housing
assistance team determination that there is a lack of available
housing resources for survivors.
(As
Needed)
Request continued
Direct Housing
Assistance.
34
No less than 60 days
prior to the end period
of assistance or 16
months post-
declaration.
R
• If Recipients require an extension for Direct Housing
Assistance they must submit a written request from the State
Coordinating Officer, Territorial or Tribal Coordinating Officer,
tribal chief executive, or Governor’s Authorized Representative
to the RA.
Project Management and Reporting
(As
Needed)
Submit DCM quarterly
reports.
Within 30 days of the
end of each quarterly
reporting period.
P
• If DCM assistance is provided, Recipient must submit quarterly
reports by the following dates:
Q1 = Oct. 1
st
to Dec. 31
s
t
(Due Jan. 30
th
)
Q2 = Jan. 1
st
to Mar. 31
st
(Due Apr. 30
th
)
Q3 = Apr. 1
st
to Jun. 30
th
(Due Jul. 30
th
)
• Q4 = Jul. 1
st
to Sep. 30
th
(Due Oct. 30
th
)
Submit DCM financial
report.
Within 30 days of the
end of each quarterly
reporting period.
P
•
If DCM assistance is provided, Recipient must submit SF-425
for every quarter of the period of performance (POP) until the
end of the POP. The due dates are within 30 days of the
following:
Q1 = Oct. 1
st
to Dec 31
st
(Due Jan. 30th)
Q2 = Jan. 1
st
to Mar. 31
st
(Due Apr. 30th)
Q3 = Apr. 1
st
to Jun. 30
th
(Due Jul. 30th)
• Q4 = Jul. 1
st
to Sep. 30
th
(Due Oct. 30th)
34
42 U.S.C. § 5174(c)(1)(B)(iii) and 44 CFR § 206.117(b)(1)(ii)(F).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
39
Completed
Individual Assistance
(IA) Program Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Submit RSP quarterly
report.
Within 30 days of the
end of each quarterly
reporting period.
P
•
If RSP assistance is provided, Recipient must submit SF-425
for every quarter of the POP to the FEMA headquarters (HQ)
program specialist, the JFO specialist (or regional specialist if
the JFO is demobilized), and the SAMHSA project officer.
• The due dates are
within 30 days of the following:
Q1 = Oct. 1
st
to Dec 31
st
(Due Jan. 30
th
)
Q2 = Jan. 1
st
to Mar. 31
st
(Due Apr. 30
th
)
Q3 = Apr. 1
st
to Jun. 30
th
(Due Jul. 30
th
)
• Q4 = Jul. 1
st
to Sep. 30
th
(Due Oct. 30
th
)
Closeout
Request a DCM
extension.
No later than 90 days
prior to the end of the
current POP.
P
•
When DCM assistance is provided, if the original POP is
deemed inadequate because of disaster severity, the
Recipient may submit a written request to FEMA for an
additional 90-day (no-cost) extension.
Closeout of DCM
program.
Within 90 days of the
end of POP.
P
•
When DCM assistance is provided, Recipient must submit an
annual report and final
SF-425 detailing accomplishments of
the DCM program.
Closeout of ISP
program.
35
Within 90 days of the
end date of ISP award
POP.
R
•
When DCM assistance is provided, Recipient must submit a
final fiscal report,
SF-425, program report, and final voucher to
the RA.
Closeout of RSP
program.
36
Within 90 days of the
end date of RSP award
POP.
R
• When RSP assistance is provided Recipient must submit a
final fiscal report, SF-425 and program report to the
RA/SAMHSA.
35
44 CFR § 206.171(f)(3)(2).
36
44 CFR § 206.171(g)(3)(ii) and (iii).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
40
Table 7 provides a description of post-declaration HMGP requirements.
Table 7: Post-Declaration Requirements for HMGP
Completed
Hazard Mitigation Grant
Program (HMGP) Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
HMGP Program Startup
Develop or update
Mitigation Plan.
37
Required before
delivery of HMGP
funding.
Note:
Tribal government
Recipients must submit
an approved Mitigation
Plan within 30 days of
signing the FEMA-Tribal
Agreement.
R
•
Recipients should identify risks and vulnerabilities associated
with natural disasters to protect against future hazards.
• Tribal government Recipients may request an extension of up
to 90 days.
• Refer to the Hazard Mitigation Planning
Process for additional
information.
Develop and maintain
an Administrative Plan
for HMGP.
38
Required before
delivery of HMGP
funding.
R
• Recipients should review and update the Administrative Plan
for HMGP on an annual basis.
• Recipients must review and update the administrative plan
following a major disaster declaration, if necessary, to meet
new policy guidance or changes to the administration of the
program.
Submit application for
HMGP.
39
Within 12 months of
the date of Presidential
declaration.
R
•
Applicants must submit applications for HMGP through the
Application Development Module of the National Emergency
Management Information System (NEMIS) to create project
applications and submit them to the appropriate FEMA region.
o If denied, Applicants must submit a written appeal to the
RA within 60 days of notification.
40
37
44 CFR §§ 201 and 206.437.
38
44 CFR § 206.437.
39
44 CFR § 206.436.
40
44 CFR § 206.440(c).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
41
Completed
Hazard Mitigation Grant
Program (HMGP) Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
(As
Needed)
Extend application
deadline.
41
Within 12 months of
the date of Presidential
declaration.
R
•
Recipients may request extension of the application deadline
in 30- to 90-day increments, not to exceed 180 days, with
written justification in the event of extraordinary conditions.
Submit sub-applications
(including management
costs).
42
Within 12 months of
date of disaster
declaration.
R
• The Recipient must submit all HMGP sub-applications to
FEMA.
Project Management and Reporting
Submit quarterly
performance reports.
43
No later than 30 days
after the end of each
quarter.
P
•
Recipient must submit quarterly performance reports on
projects by the following dates:
Q1 = Oct. 1
st
to Dec. 31
st
(Due Jan. 30
th
)
Q2 = Jan. 1
st
to Mar. 31
st
(Due Apr. 30
th
)
Q3 = Apr. 1
st
to Jun. 30
th
(Due Jul. 30
th
)
Q4 = Jul. 1
st
to Sep. 30
th
(Due Oct. 30
th
)
Submit quarterly
financial report.
No later than 30 days
after the end of each
quarter.
P
• Recipient must submit quarterly financial reports (SF-425) via
Smartlink by the following dates:
Q1 = Oct. 1
st
to Dec. 31
st
(Due Jan. 30
th
)
Q2 = Jan. 1
st
to Mar. 31
st
(Due Apr. 30
th
)
Q3 = Apr. 1
st
to Jun. 30
th
(Due Jul. 30
th
)
Q4 = Jul. 1
st
to Sep. 30
th
(Due Oct. 30
th
)
• The final SF-425 is due no later than 90 days after the end of
the period of performance (POP).
41
44 CFR § 206.436(e).
42
44 CFR § 206.436(d).
43
44 CFR § 206.438(c).

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
42
Completed
Hazard Mitigation Grant
Program (HMGP) Task
Program Deadline
Policy (P) or
Regulatory (R)
Description of Requirements
Closeout
Submit request for
extension to award
POP.
No later than 60 days
prior to expiration of the
award POP.
P
•
Recipient must submit a written request to the RA with
justification for the extension request.
•
Note:
The POP may be extended for up to 12 months with the
approval of the Regional Administrator.
• Any additional extension requests must be approved by FEMA
HQ.
Submit all financial,
performance, and other
reports.
44
No later than 90 days
after the end of the
POP.
R
•
The final SF-425 is due via Smartlink.
• The final performance report is due to FEMA.
Liquidate all
obligations.
45
No later than 90 days
after the end of the
POP.
R
• The Recipient is required to liquidate all obligations incurred
under the award and return all unobligated funds to FEMA via
Smartlink.
Submit a closeout
letter.
46
No later than 90 days
after the end of the
POP.
R
•
The Recipient is required to submit a closeout letter, signed by
the tribal chief executive or Governor’s Authorized
Representative, to FEMA with supporting documentation.
• For more information on reporting and documentation
requirements, refer to the
Hazard Mitigation Assistance
Guidance or Closeout Toolkit: Checklists for Hazard Mitigation
Grant Program.
44
2 CFR § 200.343.
45
2 CFR § 200.343.
46
44 CFR § 206.438(d).
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
A-1
APPENDIX A: LIST OF ACRONYMS
CCP Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training Program
CFR Code of Federal Regulations
CNA Critical Needs Assistance
COB Close of Business
CRA Clean and Removal Assistance
CRMT Community Recovery Management Toolkit
D&B Dun and Bradstreet
DCM Disaster Case Management
DLS Disaster Legal Services
DUA Disaster Unemployment Assistance
DUNS Data Universal Number System
ESF Emergency Support Function
FEMA Federal Emergency Management Agency
FMAG Fire Management Assistance Grant
FSA Federal-State Agreement
FTA FEMA-Territory/Tribe Agreement
GAR Governor’s Authorized Representative
HMA Hazard Mitigation Assistance
HMGP Hazard Mitigation Grant Program
HQ Headquarters
IA Individual Assistance
IAPPG Individual Assistance Program and Policy Guide
IASC Individual Assistance Support Contract
IHP Individuals and Households Program
ISP Immediate Services Program
JFO Joint Field Office
NCMEC National Center for Missing and Exploited Children
NECLC National Emergency Child Locator Center
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
A-2
NEMIS National Emergency Management Information System
NFIP National Flood Insurance Program
NFIRA National Flood Insurance Reform Act
NGO Non-governmental Organization
ONA Other Needs Assistance
PA Public Assistance
PAPPG Public Assistance Program and Policy Guide
PAS Personal Assistance Services
PDM Pre-Disaster Mitigation
PMS Payment Management System
POP Period of Performance
RA Regional Administrator
RPA Request for Public Assistance
RSM Recovery Scoping Meeting
RSP Regular Services Program
SAMHSA Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration
SCO State Coordinating Officer
SFHA Special Flood Hazard Area
SMP State Mitigation Plan
SOW Statement of Work
TSA Transitional Sheltering Assistance
U.S.C. United States Code
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
B-1
APPENDIX B: GLOSSARY
Access and Functional Needs. Provision of services and resources for people with
disabilities or access and functional needs.
Administrative options. FEMA requires state, territorial, and Indian tribal (tribal) governments
to complete an ONA Administrative Option Selection Form to establish the maximum amount
of assistance that may be awarded to eligible individuals. All Recipients must submit their
ONA selections to FEMA yearly, regardless of the administrative option selected. This
process requires an evaluation of a Recipient’s capacity to administer ONA and identifies
cost thresholds and item exemptions for certain categories of ONA.
Administrative Plan. Recipients must develop and submit to FEMA an administrative plan to
receive PA and HMGP funding. The administrative plan must describe how the Recipient
intends to use the grant funding. Recipients must have a current administrative plan for
each program approved by FEMA before they are able to receive PA or HMGP funds.
Advance Assistance. Advance assistance provides Recipients with resources to develop
mitigation strategies and obtain data to prioritize, select, and develop HMGP impacted
applications. Advance assistance, authorized by the Stafford Act (as amended), allows
advancement of up to 25-percent of the HMGP ceiling or $10 million, whichever is less, to
accelerate implementation of the HMGP.
Applicant. A non-federal entity that applies to be a Subrecipient of assistance under a
Recipient’s federal award (e.g., local government agency, housing authority, and private
nonprofit organizations).
Cost Share. An adjustment to the public assistance cost, with the authority to adjust residing
with the President. FEMA will recommend an increase in the federal share to not more than
90-percent for public assistance when a disaster is so extraordinary that actual federal
obligations under the Stafford Act, excluding administrative costs, meet or exceed a
qualifying threshold.
Data Universal Number System (DUNS). Recipients must obtain a DUNS number to receive
disaster assistance grant funding from FEMA. The DUNS number allows the Federal
Government to track the allocation of federal funds.
Declaration Award. The declaration request, once approved by the President, designates
disaster-impacted areas and establishes the incident period, the type of incident, the type(s)
of assistance available, and the federal cost share amount for the provision of requested
assistance, if applicable.
Direct Federal Assistance: When the impact of an incident is so severe that the state,
territorial, tribal, and local governments lack the capability to perform or contract eligible
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
B-2
Emergency Work, the Recipient may request that the Federal Government provide this
assistance directly. FEMA may task another Federal agency to perform or contract the work
provided it is an eligible activity. FEMA issues a Mission Assignment to task the work and
refers to it as Direct Federal Assistance. FEMA cannot task work that another Federal
agency has its own authority to perform. Direct Federal Assistance has the same cost-share
provisions applicable to the declaration.
Disaster Grant Funding. Funding that authorizes FEMA disaster assistance grant programs
and results from a Presidential declaration.
Emergency Work: Emergency Work categories provide emergency assistance to save lives
and protect property.
Federal-State/Territory/Tribe Agreement (FSA/FTA). This agreement states the
understandings, commitments, and conditions for assistance under which FEMA disaster
assistance will be provided. The FSA/FTA imposes binding obligations on FEMA, states and
their local governments, tribes, and private nonprofit organizations within the states in the
form of conditions for assistance that are legally enforceable.
Hazard Mitigation Grant Program (HMGP). Assistance to state, territorial, tribal, and local
governments and certain private nonprofit organizations for actions taken to prevent or
reduce long-term risk to life and property from natural hazards.
Individual Assistance (IA). IA is provided by FEMA to individuals and families who have
sustained losses because of disasters. This type of assistance comes in the form of housing
assistance and other needs assistance, such as medical and dental expenses, funeral
costs, or clothing.
Individual Household Program (IHP). IHP provides financial and direct services to eligible
individuals and households affected by a disaster who have uninsured or underinsured
necessary expenses and serious needs. IHP is intended to meet the survivor’s basic needs
and supplement disaster recovery efforts. FEMA provides two types of IHP assistance: other
needs assistance (ONA) and housing assistance.
Large Project. A project for which the final obligated (federal and non-federal) amount is
greater than the annually adjusted cost threshold for small project grants.
Mitigation Plan. The plan that Recipients must have in place before receiving disaster grant
program funding for HMGP or the Permanent Work categories of PA. The Mitigation Plan
requirement encourages Recipients to engage in hazard mitigation planning to identify risks
and vulnerabilities associated with natural disasters and to develop long-term strategies for
protecting people and property against future hazards.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
B-3
Payment Management System. The direct deposit account system that Recipients must
have to access federal funds. Recipients must submit a written request to the RA to
establish an account, including completing a Direct Deposit Form SF-1199A.
Permanent Work. Permanent Work categories assist with permanently restoring community
infrastructure affected by a declared incident.
Pre-Disaster Mitigation (PDM) Grant Program. FEMA’s PDM Grant Program is designed to
assist Recipients implement a sustained pre-disaster natural hazard mitigation program to
reduce overall risk to the population and structures from future hazard events, while also
reducing reliance on federal funding in future disasters.
Presidential Disaster Declaration. A declaration by the President, including major disaster
and emergency, that allows for the different levels of government to request federal
assistance.
Public Assistance (PA). A grant program provided by FEMA that provides federal assistance
to government organizations and certain private nonprofit organizations following a
Presidential disaster declaration.
Recipient. A non-federal entity that receives an award from a federal agency (e.g., state,
territorial, or tribal government) to carry out an activity under a federal program.
Small Project. A project for which the final obligated (federal and non-federal) amount is less
than the annually adjusted cost threshold for small project grants.
Subrecipient. An Applicant that receives a sub-award from a Recipient to carry out part of a
federal program.
Tribal Chief Executive. The person who is the chief, chair, chairman, chairwoman, governor,
president, or similar executive official of a tribal government.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
B-4
This Page Intentionally Left Blank
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
C-1
APPENDIX C: AUTHORITIES AND FOUNDATIONAL
DOCUMENTS
Robert T. Stafford Disaster Relief and Emergency Assistance
Act (Public Law 93-288, as amended, 42 U.S.C. 5121-5207)
The Stafford Act, signed into law on November 23, 1988, amended the Disaster Relief Act of
1974 (Public Law 93-288). The Stafford Act constitutes the statutory authority by which the
Federal Government provides disaster and emergency assistance to state, territorial, and
local governments; tribal nations; eligible private nonprofit organizations; and individuals
affected by a declared major disaster or emergency. The Stafford Act covers all hazards,
including natural disasters and terrorist events. The Stafford Act is the primary law governing
all new Recipient requests for federal assistance.
Title 2 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) § 200
2 CFR § 200 is an Office of Management and Budget (OMB) reform of regulations that apply
to federal financial assistance, streamlining the language from eight existing OMB circulars
into one consolidated set of guidance in the Code of Federal Regulations. 2 CFR § 200
provides guidance on the administrative aspects of federal grants (e.g. how grants are
awarded, managed, audited, and closed-out).
Title 44 CFR §§ 201 and 206
44 CFR §§ 201 and 206 contain requirements and procedures to implement hazard
mitigation planning provisions and federal disaster assistance under the Stafford Act.
Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance, January 2017
The Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance, released January 10, 2017, describes the process
which tribal governments will use to request Stafford Act declarations and the criteria FEMA
will use to evaluate direct tribal declaration requests and make recommendations to the
President. The Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance is a culmination of over 3 years of tribal
consultation and development of a Stafford Act declarations process specifically for tribal
nations. The Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance incorporates key changes based on
comments FEMA received from tribes. The release of the Tribal Declarations Pilot Guidance
marks the official beginning of the pilot period for federally recognized tribal governments to
use the authority provided by the Stafford Act (as amended) to directly request a Presidential
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
C-2
emergency or major disaster declaration in order to receive federal grant funds for IA, PA,
and HMGP.
FEMA Damage Assessment Operations Manual, April 2016
The Damage Assessment Operations Manual is part of a greater effort to provide a user-
friendly, streamlined post-disaster damage assessment process that builds on the existing
knowledge and expertise of state, territorial, or tribal governments and local partners to
identify damage after a natural or man-made disaster. The Damage Assessment Operations
Manual is aimed at clarifying FEMA damage assessment guidance, promoting standardized
information collection, and assisting in the development of requests for disaster grant
funding. The Damage Assessment Operations Manual will inform the damage assessment
processes and procedures that must be completed in order for new Recipients to receive
individual assistance grant funding.
FEMA National Disaster Recovery Framework (Second
Edition), June 2016
The National Disaster Recovery Framework is a guide that enables effective recovery
support to disaster-impacted states, territories, tribes, and local jurisdictions. The National
Disaster Recovery Framework provides a flexible structure that enables disaster recovery
managers to operate in a unified and collaborative manner; it focuses on how best to
restore, redevelop and revitalize the health, social, economic, natural, and environmental
fabric of the community and build a more resilient nation.
FEMA Individual Assistance Program and Policy Guide, March
2019
The Individual Assistance Program and Policy Guide (IAPPG) combines all IA policy into a
single volume and provides an overview of the IA Program implementation process with links
to other publications and documents that provide additional process details, requirements,
and deadlines outlined in Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist.
FEMA Public Assistance Program and Policy Guide, April
2018
The Public Assistance Program and Policy Guide (PAPPG) combines all PA policy into a single
volume and provides an overview of the PA Program implementation process with links to
other publications and documents that provide additional process details, requirements,
and deadlines outlined in Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
C-3
FEMA Hazard Mitigation Assistance Guidance, February 2015
The Hazard Mitigation Assistance (HMA) Guidance is a comprehensive document that
details the specific criteria of the three Hazard Mitigation Assistance (HMA) programs
(Hazard Mitigation Grant Program, Flood Mitigation Assistance, and Pre-Disaster Mitigation
Grant Program). The HMA Guidance consolidates the common requirements for all HMA
programs and explains the unique elements of the programs. Additionally, the HMA
Guidance provides information for federal, state, and territorial governments; federally
recognized tribes; and local officials on how to apply for and manage HMA funding for a
mitigation project, as outlined in Chapter 7: New Recipient Checklist.
State Mitigation Plan Review Guide, FP 302-094-2, March
2015
The State Mitigation Plan Review Guide is FEMA’s official policy on and interpretation of the
requirements for state standard and enhanced mitigation planning found at 44 Code of
Federal Regulations (CFR) § 201, “Mitigation Planning.” The intended use of the State
Mitigation Plan Review Guide is to facilitate consistent evaluation and approval of State
Mitigation Plans (SMP), as well as to facilitate state compliance with the mitigation planning
requirements when updating plans.
Tribal Mitigation Plan Review Guide, FP 306-112-1,
December 2017
The Tribal Mitigation Plan Review Guide is FEMA’s updated policy on and interpretation of
the requirements for tribal standard and enhanced mitigation planning found at 44 CFR §
201, “Mitigation Planning.” The intended use of the Guide is to facilitate consistent
evaluation and approval of tribal mitigation plans, as well as to facilitate compliance with the
mitigation planning requirements when developing or updating plans. The Tribal Mitigation
Plan Review Guide became effective as FEMA’s official policy for FEMA Tribal Mitigation Plan
Review on December 5, 2018.
FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
C-4
This Page Intentionally Left Blank

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
D-1
APPENDIX D: REFERENCES
Table 8 provides a list of guidance documents applicable to each of FEMA’s disaster
assistance grant programs.
Table 8: FEMA Disaster Assistance Grant Programs Guidance References
Document Title
Summary
Public Assistance Program and
Policy Guide (PAPPG)
•
Provides an overview of the Public Assistance (PA) Program
implementation process with links to other publications and
documents that provide additional process details.
Public Assistance Donated
Resources Policy
• Authorizes Applicants to apply the value of donated
resources used during the performance of eligible
Permanent Work toward the non-federal cost share of its
eligible Permanent Work projects.
Public Assistance
Administrative Plan Template
•
Provides a sample format for Recipients to use to develop
their Administrative Plan for PA.
Public Assistance Alternative
Procedures Pilot Guide for
Permanent Work
• Provides guidance to FEMA, Recipients, and Subrecipients
for implementing the alternative procedures for Permanent
Work.
Individual Assistance Program
and Policy Guide (IAPPG)
• Provides an overview of the Individual Assistance Program
with links to other publications and documents that provide
additional process details.
Crisis Counseling Assistance
and Training Program Toolkit
• Includes guides and training materials to help state,
territorial, and Indian tribal (tribal) governments apply for
and establish a Crisis Counseling Assistance and Training
Program.
Personal Assistance Services
Frequently Asked Questions
• Provides answers to frequent Recipient questions on
personal assistance service contracts.
Hazard Mitigation Assistance
Guidance (HMA Guidance)
•
Provides an overview of the Hazard Mitigation Assistance
programs, including the Hazard Mitigation Grant Program,
with links to other publication and documents that provide
additional process details.
Hazard Mitigation Planning
Process
• Describes the general process to develop or update a
hazard mitigation plan.
Tribal Mitigation Plan Review
Guide
•
Facilitates consistent evaluation and approval of tribal
Mitigation Plans, as well as to facilitate compliance with the
mitigation planning requirements when developing or
updating plans.
Hazard Mitigation Planning
Frequently Asked Questions
• Provides answers to frequent Recipient questions on hazard
mitigation planning.
Fire Management Assistance
Grant Program Guide
• Describes the FMAG program basic provisions, application
procedures, and other related program guidance.
Community Recovery
Management Toolkit (CRMT)
•
Compilation of guidance, case studies, tools, and training to
assist local communities to manage long-term recovery post-
disaster.
State Mitigation Plan Review
Guide
•
FEMA’s official policy on and interpretation of natural hazard
mitigation planning requirements.

FEMA New Recipients of Disaster Grants Guide
D-2
Document Title
Summary
Restrictions on Grant
Obligations to State, Tribal and
Local Governments without a
FEMA-Approved Mitigation Plan
• Describes the implications to state, tribal, and local
governments that do not have a FEMA-approved hazard
mitigation plan relative to receiving assistance under eligible
FEMA grant programs.
MT-PL#1: Disaster Declaration
Procedures After May 1, 2005
for States Without an Approved
State Mitigation Plan
• Guidance for FEMA regional offices and Federal
Coordinating Officers on procedures for processing requests
for major disaster declarations
from states and territories
that do not have
a FEMA-approved State Mitigation Plan
(SMP).
MT-PL #1A: Implementation
Procedures for States,
Territories, & Indian Tribal
Governments Without
Approved State Mitigation Plan
• Supplemental guidance to MT-PL #1 that applies to major
disaster declarations and fire management assistance
declarations for all state, territorial, and tribal governments
that do not have an approved SMP, including state-level
plans for tribes.
Table 9 provides a list of forms and Websites applicable to each of FEMA’s disaster assistance grant
programs.
Table 9: FEMA Disaster Assistance Grant Programs Form References
Form/Website Title
Purpose
Direct Deposit Form (SF-
1199A)
•
Complete to sign up for direct deposit to receive federal
disaster grant funds.
Individuals and Households -
Other Needs Assistance
Administrative Option Selection
Form (FF 010-1-11)
• Complete and submit to indicate Other Needs Assistance
administrative option selections.
Application for Federal
Assistance (SF-424)
•
Standard form that all Applicants must complete to apply for
federal funding.
SF-424D/OMB Number 4040-
0009
• Accompanies the application for federal assistance for
Public Assistance (PA) and Hazard Mitigation Grant
Programs.
• Provides assurances for construction projects or programs.
Request for Public Assistance
(FF 90-49)
• FEMA form used to request public assistance through the PA
Program.
Resource Request Form (FF
010-0-7)
•
FEMA form used to request resources.
Federal Financial Report (SF-
425)
• Standard form that all Recipients must complete to report
on financial status for disaster grants.
Data Universtal Number
System (DUNS) Number
Search/Request
•
Dun and Bradstreet site to search for existing DUNS number
or to register for new DUNS number.
Payment Management System
Program Support System
•
Access to payment management system to manage disaster
grant funds.
