
P.S./CHEMISTRY
P.S./CHEMISTRY
The University of the State of New York
REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION
PHYSICAL SETTING
CHEMISTRY
Friday, June 16, 2023 — 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only
The possession or use of any communications device is strictly prohibited when
taking this examination. If you have or use any communications device, no matter how
briey, your examination will be invalidated and no score will be calculated for you.
This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all
questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition
Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all
parts of this examination according to the directions provided in this examination
booklet.
A separate answer sheet for Part A and Part B–1 has been provided to you. Follow
the instructions from the proctor for completing the student information on your
answer sheet. Record your answers to the Part A and Part B–1 multiple-choice
questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in
Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to ll in the heading on
the front of your answer booklet.
All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and
drawings, which should be done in pencil. You may use scrap paper to work out the
answers to the questions, but be sure to record all your answers on your separate
answer sheet or in your answer booklet as directed.
When you have completed the examination, you must sign the statement printed
on your separate answer sheet, indicating that you had no unlawful knowledge of the
questions or answers prior to the examination and that you have neither given nor
received assistance in answering any of the questions during the examination. Your
answer sheet and answer booklet cannot be accepted if you fail to sign this declaration.
Notice. . .
A four-function or scientic calculator and a copy of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for
Physical Setting/Chemistry must be available for you to use while taking this examination.
DO NOT OPEN THIS EXAMINATION BOOKLET UNTIL THE SIGNAL IS GIVEN.

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [2]
1 Which phrase describes the nucleus of any atom?
(1) has an overall positive charge
(2) has an overall negative charge
(3) contains negative electrons
(4) contains positive electrons
2 Which two particles each have a mass of
approximately one atomic mass unit?
(1) an electron and a proton
(2) an electron and a positron
(3) a neutron and a proton
(4) a neutron and a positron
3 The wave-mechanical model of the atom
describes the location of electrons
(1) as loosely packed in the nucleus of an atom
(2) as densely packed in the nucleus of an atom
(3) in circular paths around the nucleus
(4) in orbitals outside the nucleus
4 When a ground state electron in an atom moves
to an excited state, the electron
(1) absorbs energy as it moves to a higher energy
state
(2) absorbs energy as it moves to a lower energy
state
(3) releases energy as it moves to a higher energy
state
(4) releases energy as it moves to a lower energy
state
5 Which statement describes a chemical property
of iron?
(1) Iron is malleable.
(2) Iron conducts electricity.
(3) Iron reacts with nitric acid.
(4) Iron has a high melting point.
6 Diamond and graphite are two forms of solid
carbon. These two forms of carbon have
(1) different crystal structures and different
properties
(2) different crystal structures and the same
properties
(3) the same crystal structure and different
properties
(4) the same crystal structure and the same
properties
7 Which substance can be broken down by a
chemical change?
(1) cobalt (3) krypton
(2) ethane (4) manganese
8 Based on Table I, which equation represents
conservation of mass and energy?
(1) CH
4
(g) 1 O
2
(g) 1 890.4 kJ → CO
2
(g) 1 H
2
O( )
(2) CH
4
(g) 1 O
2
(g) → CO
2
(g) 1 H
2
O( ) 1 890.4 kJ
(3) CH
4
(g) 1 2O
2
(g) 1 890.4 kJ → CO
2
(g) 1 2H
2
O( )
(4) CH
4
(g) 1 2O
2
(g) → CO
2
(g) 1 2H
2
O( ) 1 890.4 kJ
9 At STP, which property can be used to
differentiate a 10.-gram sample of NaCl(s) from
a 10.-gram sample of NaNO
3
(s)?
(1) mass of the sample
(2) temperature of the sample
(3) solubility in water
(4) phase at STP
10 What is the number of electrons shared between
the two atoms in an O
2
molecule?
(1) 6 (3) 3
(2) 2 (4) 4
Part A
Answer all questions in this part.
Directions (1–30): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the
word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. Some questions
may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry.

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [3] [OVER]
11 Which changes in both charge and radius occur
when an atom loses an electron?
(1) A negative ion is formed with a smaller
radius than the atom.
(2) A negative ion is formed with a larger radius
than the atom.
(3) A positive ion is formed with a smaller
radius than the atom.
(4) A positive ion is formed with a larger radius
than the atom.
12 Which statement describes what occurs when
two iodine atoms react to produce an iodine
molecule?
(1) A bond forms and energy is absorbed.
(2) A bond forms and energy is released.
(3) A bond breaks and energy is absorbed.
(4) A bond breaks and energy is released.
13 Which process can be used to separate a mixture
of two liquids having different boiling points?
(1) deposition (3) ltration
(2) distillation (4) sublimation
14 Which statement describes a solution of sodium
chloride in water?
(1) The mixture is heterogeneous, the solute is
NaCl and the solvent is H
2
O.
(2) The mixture is heterogeneous, the solute is
H
2
O and the solvent is NaCl.
(3) The mixture is homogeneous, the solute is
NaCl and the solvent is H
2
O.
(4) The mixture is homogeneous, the solute is
H
2
O and the solvent is NaCl.
15 At STP, which property would be the same for
1.0 liter of helium and 1.0 liter of argon?
(1) boiling point (3) mass
(2) density (4) number of atoms
16 The melting of an ice cube is an example of an
(1) endothermic, chemical change
(2) endothermic, physical change
(3) exothermic, chemical change
(4) exothermic, physical change
17 Which statement explains the low boiling point
of hydrogen, H
2
, at standard pressure?
(1) Hydrogen has strong covalent bonds.
(2) Hydrogen has weak covalent bonds.
(3) Hydrogen has strong intermolecular forces.
(4) Hydrogen has weak intermolecular forces.
18 In chemical reactions, which term is dened
as the difference between the potential energy
of the products and the potential energy of the
reactants?
(1) heat of fusion
(2) heat of reaction
(3) thermal conductivity
(4) electrical conductivity
19 Which phrase describes what happens to the
reaction pathway and activation energy of a
reaction to which a catalyst is added?
(1) the same pathway with the same activation
energy
(2) the same pathway with a lower activation
energy
(3) a different pathway with the same activation
energy
(4) a different pathway with a lower activation
energy
20 An atom of which element is bonded to the
carbon atom in the amide functional group?
(1) iodine (3) phosphorus
(2) nitrogen (4) sulfur
21 Which statement describes the two isomers of
butane?
(1) They have the same molecular formula but
different structural formulas.
(2) They have the same molecular formula and
the same structural formula.
(3) They have different molecular formulas and
different structural formulas.
(4) They have different molecular formulas but
the same structural formula.

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [4]
22 Which term represents an organic reaction that
produces soap?
(1) esterication (3) saponication
(2) fermentation (4) solidication
23 In which part of an electrochemical cell does
reduction occur?
(1) anode (3) wire
(2) cathode (4) voltmeter
24 Which energy change occurs in an operating
voltaic cell?
(1) chemical energy to electrical energy
(2) chemical energy to nuclear energy
(3) electrical energy to chemical energy
(4) electrical energy to nuclear energy
25 Which substance is an Arrhenius base?
(1) HNO
3
(3) LiOH
(2) KNO
3
(4) CH
3
COOH
26 Which statement represents neutralization?
(1) An Arrhenius acid and an Arrhenius base
react to produce water and a salt.
(2) An Arrhenius acid and a salt react to
produce water and an Arrhenius base.
(3) Water and an Arrhenius acid react to
produce an Arrhenius base and a salt.
(4) Water and a salt react to produce an
Arrhenius base and an Arrhenius acid.
27 A tenfold increase in hydronium ion concentration
is represented by
(1) a decrease of one unit of pH
(2) a decrease of 10 units of pH
(3) an increase of one unit of pH
(4) an increase of 10 units of pH
28 Based on Table N, which particle is emitted by
the radioactive decay of francium-220?
(1) an alpha particle (3) a positron
(2) a beta particle (4) a neutron
29 Which type of reaction releases the greatest
amount of energy per kilogram of reactant?
(1) acid-base reaction (3) organic reaction
(2) ssion reaction (4) redox reaction
30 Which risk is related to the radioactive isotopes
used to generate electricity?
(1) depletion of fossil fuels
(2) depletion of atmospheric ozone
(3) exposure to acid rain
(4) exposure to nuclear emissions

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [5] [OVER]
31 Which Lewis electron-dot diagram represents an
atom of nitrogen in the ground state?
N
( 1 )
N
( 2 )
N
( 3 )
N
( 4 )
32 The atomic masses and natural abundances of
the two naturally occurring isotopes of silver are
shown in the table below.
Silver Isotopes
Isotope Atomic Mass
(u)
Natural Abundance
(%)
Ag-107 106.905 51.8
Ag-109 108.905 48.2
Which numerical setup can be used to calculate
the atomic mass of silver?
(1) (106.905 u)(51.8) 1 (108.905 u)(48.2)
(2) (106.905 u)(51.8%) 1 (108.905 u)(48.2%)
(3) (106.905 u)(48.2) 1 (108.905 u)(51.8)
(4) (106.905 u)(48.2%) 1 (108.905 u)(51.8%)
33 A potassium atom has a mass number of 37. What
is the number of neutrons in this atom?
(1) 15 (3) 22
(2) 18 (4) 37
34 At room temperature, a student determines the
density of a sample of nickel to be 9.79 g/cm
3
.
Based on Table S, what is the student’s percent
error for the density of nickel?
(1) 0.091% (3) 9.1%
(2) 0.10% (4) 10.%
35 Compared to the metals in Period 2, the nonmetals
in Period 2 have
(1) lower rst ionization energies and lower
electronegativity values
(2) lower rst ionization energies and higher
electronegativity values
(3) higher rst ionization energies and lower
electronegativity values
(4) higher rst ionization energies and higher
electronegativity values
36 Which formula represents calcium hydride?
(1) CaH (3) CaOH
(2) CaH
2
(4) Ca(OH)
2
37 What is the number of moles in a 78.8-gram sample
of MgCO
3
(gram-formula mass 5 84.3 g/mol)?
(1) 0.949 mol (3) 0.843 mol
(2) 0.935 mol (4) 1.070 mol
38 Given the equation representing a reaction:
F
2
(g) 1 2KCl(aq) → 2KF(aq) 1 Cl
2
(g)
Which type of chemical reaction is represented
by the equation?
(1) synthesis
(2) decomposition
(3) single replacement
(4) double replacement
39 Based on Table H, which compound has the
strongest intermolecular forces at 60 kPa?
(1) ethanoic acid (3) propanone
(2) ethanol (4) water
Part B–1
Answer all questions in this part.
Directions (31–50): For each statement or question, record on your separate answer sheet the number of the
word or expression that, of those given, best completes the statement or answers the question. Some questions
may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry.

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [6]
40 Which particle diagram represents a sample of
xenon at STP?
Key
= atom of xenon
( 1 ) ( 3 )
( 2 ) ( 4 )
41 Based on Table G, which compound is less soluble
in water as the temperature increases from 0°C
to 100°C?
(1) KNO
3
(3) KClO
3
(2) NH
3
(4) NH
4
Cl
42 How many moles of KI are needed to make
0.50 L of a 0.20 M aqueous solution?
(1) 0.10 mol (3) 0.40 mol
(2) 0.25 mol (4) 0.70 mol
43 A solution is prepared using 9.80 grams of
NaHCO
3
in enough water to make 1500. grams
of total solution. What is the concentration of the
solution expressed in parts per million?
(1) 6.49 3 10
23
ppm (3) 6.49 3 10
3
ppm
(2) 6.53 3 10
23
ppm (4) 6.53 3 10
3
ppm
44 A potential energy diagram for a chemical
reaction is given below. Each interval on the
potential energy axis represents 100. kilojoules of
potential energy.
Potential Energy
Reaction Coordinate
What can be concluded from the diagram?
(1) The reaction is endothermic, and the heat of
reaction is 2200. kJ.
(2) The reaction is endothermic, and the heat of
reaction is 1200. kJ.
(3) The reaction is exothermic, and the heat of
reaction is 2200. kJ.
(4) The reaction is exothermic, and the heat of
reaction is 1200. kJ.
45 Given the formula representing a compound:
CH
H
C
C C
H
H
H
C
H
H
H
H
H
Br Br
What is a chemical name of this compound?
(1) 1,1-dibromopentane
(2) 2,2-dibromopentane
(3) 1,2-dibromopentane
(4) 4,5-dibromopentane

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [7] [OVER]
46 The diagram and equation below represent an
electrochemical cell.
Cathode
Anode
Cl
–
Na
+
Wire
Wire
Battery
2NaCl( ) 2Na( ) Cl
2
(g)+
Which process is represented by this diagram?
(1) chromatography (3) electrolysis
(2) distillation (4) polymerization
47 Which aqueous solution has the greatest ability
to conduct an electric current?
(1)
0.10 M NaCl(aq)
(2) 0.010 M NaCl(aq)
(3) 0.1
0 M C
6
H
12
O
6
(aq)
(4) 0.010 M C
6
H
12
O
6
(aq)
48 What fraction of an original sample of
131
I remains
unchanged after 24.063 days?
(1) 1/8 (3) 1/3
(2) 1/2 (4) 1/4
49 Given the equation representing a reaction:
2
1
H 1
3
1
H →
4
2
He 1
1
0
n 1 energy
Which type of reaction is represented by the
equation?
(1) nuclear ssion (3) combustion
(2) nuclear fusion (4) substitution
50 Given the nuclear equation and isotopic masses:
What is the amount of mass converted to energy
as a result of the reaction between the two reactant
nuclei?
(1) 0.0239 u (3) 8.0052 u
(2) 4.0265 u (4) 16.0343 u
6
3
Li 1
2
1
H → 2(
4
2
He) 1 energy
6.0151 u 2.0140 u 2(4.0026 u)

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [8]
Base your answers to questions 51 and 52 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
The element technetium, Tc, has several isotopes. The bright-line spectrum of technetium
has been observed in the spectra of some stars.
51 Compare the energy of an electron in the rst shell of a technetium atom to the energy
of an electron in the third shell of the same atom. [1]
52 State, in terms of protons and neutrons, why the various nuclides of technetium are
isotopes of each other. [1]
Base your answers to questions 53 and 54 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
A sample of a gas in a sealed, rigid cylinder with a movable piston has a volume of
0.250 liter at STP.
53 Show a numerical setup for calculating the volume of this sample of gas at 298 K and
1.00 atm. [1]
54 State a change in pressure that will cause the gas in the cylinder to behave more like an
ideal gas. [1]
Part B–2
Answer all questions in this part.
Directions (51-65): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may
require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry.

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [9] [OVER]
Base your answers to questions 55 through 57 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
During a laboratory activity, a student heats a beaker containing 120.0 grams of water as
shown in the diagram below.
Beaker containing water
Wire gauze
Iron ring
Candle
Ring stand
Glass square
Thermometer
The table below shows the mass of the water and the temperature of the water before
and after heating. During this laboratory activity, appropriate safety equipment is used and
safety procedures are followed.
Data for Heating Water
Mass of 120.0 mL of water 120.0 g
Temperature of water before heating 23.0°C
Temperature of water after heating 20.0 min 86.0°C
55 State the direction of heat ow between the candle ame and the beaker of water during
the time the candle is lit. [1]
56 Show a numerical setup for calculating the amount of heat, in joules, absorbed by the
water in the beaker as a result of the burning candle. [1]
57 State how the molecular motion of the water molecules in the beaker changes as the
temperature increases. [1]

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [10]
Base your answers to questions 58 through 60 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
Nitrogen dioxide gas, NO
2
(g), can reach equilibrium with dinitrogen tetroxide gas, N
2
O
4
(g),
in a closed system. At 1.0 atmosphere, the boiling point of N
2
O
4
is 21°C. The equation below
represents this system.
2NO
2
(g) N
2
O
4
(g) 1 energy
58 Compare the rate of the forward reaction to the rate of the reverse reaction when the
system is at equilibrium. [1]
59 State how the equilibrium shifts when the pressure on the equilibrium system is
increased at constant temperature. [
1]
60 Compare the entropy of a sample of dinitrogen tetroxide gas at 25°C and
1.0 atmosphere to the entropy of the same sample of dinitrogen tetroxide liquid at 15°C
and 1.0 atmosphere. [1]
Base your answers to questions 61 through 63 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
When solid copper is placed in an aqueous silver nitrate solution, a reaction occurs, as
represented by the equation below.
Cu(s) 1 2AgNO
3
(aq) → 2Ag(s) 1 Cu(NO
3
)
2
(aq)
61 State the change in oxidation state of copper in this reaction. [1]
62 Based on Table J, state why Cu(s) reacts spontaneously with Ag
1
(aq). [1]
63 Write a balanced half-reaction equation to represent the reduction of the silver ions to
silver atoms. [1]
Base your answers to questions 64 and 65 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
During a laboratory activity, 15.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, HCl(aq), is exactly neutralized
by 18.2 mL of 0.11 M sodium hydroxide, NaOH(aq). During the laboratory activity,
appropriate safety equipment is used and safety procedures are followed.
64 Write the name of the laboratory procedure used in this activity. [1]
65 Show a numerical setup for calculating the molarity of the HCl(aq) solution. [1]

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [11] [OVER]
Base your answers to questions 66 through 69 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
Several elements are considered endangered because there is a risk of these elements
becoming unavailable for commercial uses in the next 100 years. Helium, zinc, gallium,
indium, and tellurium are included in the list of these endangered elements.
66 Identify the three endangered elements listed in the passage that are classied as metals. [1]
67 Explain, in terms of electrons, why gallium and indium have similar chemical properties. [1]
68 Compare the density of a sample of helium at STP with the density of a sample of
tellurium at STP. [
1]
69 Explain, in terms of electron shells, why the atomic radius of an atom of indium is
greater than the atomic radius of an atom of gallium when both atoms are in the ground
state. [1]
Part C
Answer all questions in this part.
Directions (66-85): Record your answers in the spaces provided in your answer booklet. Some questions may
require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry.

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [12]
Base your answers to questions 70 through 73 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
The Ostwald process is an industrial method to produce nitric acid, HNO
3
(aq), used in
the manufacture of fertilizers. Several steps are involved in this process. In the rst step,
ammonia and oxygen react in the presence of a catalyst, as represented by unbalanced
equation 1.
Equation 1: NH
3
(g) 1 O
2
(g) → NO(g) 1 H
2
O(g) 1 heat
In the second step, nitrogen(II) oxide reacts with oxygen to produce nitrogen(IV) oxide,
represented by balanced equation 2 below.
Equation 2: 2NO(g) 1 O
2
(g) → 2NO
2
(g) 1 heat
70 Determine the percent composition by mass of nitrogen in HNO
3
(gram-formula mass 5
63.0 g/mol). [
1]
71 Balance equation 1 in your answer booklet, using the smallest whole-number
coefcients. [
1]
72 Show a numerical setup for calculating the gram-formula mass of the NO
2
(g) produced in
equation 2. [
1]
73 Determine the number of moles of oxygen required to completely react with 4.0 moles
of NO(g) in equation 2. [1]

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [13] [OVER]
Base your answers to questions 74 through 78 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
As plants grow, light energy is converted into chemical energy during the process of
photosynthesis. The reaction produces glucose and oxygen. The balanced equation below
represents photosynthesis.
6CO
2
1 6H
2
O 1 light energy → C
6
H
12
O
6
1 6O
2
74 State the molecular polarity for each of the reactants in the equation. [1]
75 In the space in your answer booklet, draw a Lewis electron-dot diagram for a molecule
of water. [
1]
76 Based on Table S, compare the strength of attraction of a carbon atom for electrons with
the strength of attraction of an oxygen atom for the electrons in a bond between them.
[
1]
77 State, in terms of element classication, why CO
2
is a molecular compound. [1]
78 Write the empirical formula for glucose. [1]
Base your answers to questions 79 through 81 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
In the United States, nearly all fuel for automobiles is a mixture of gasoline and ethanol,
C
2
H
5
OH. The equation below represents a reaction between ethene and water to produce
ethanol.
H
H
C
C OH
H
H H
C C
H
H
H
H
H
2
O
+
catalyst
79 State the class of organic compound to which the product in the equation belongs. [1]
80 State, in terms of carbon-to-carbon bonds, why the hydrocarbon in the equation is
unsaturated. [
1]
81 Identify the element in the product of the reaction that allows it to be classied as an
organic compound. [1]

P.S./Chem.–June ’23 [14]
Base your answers to questions 82 through 85 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry.
In a laboratory activity, a student measures the pH values of four household liquids
and distilled water, as shown in the table below. During this laboratory activity, appropriate
safety equipment is used and safety procedures are followed.
Measured pH Value of Liquids Tested
Liquid Tested Measured pH Value
aqueous ammonia 11.9
black coee 4.9
lemon juice 2.1
vinegar 3.3
distilled water 7.0
82 Identify the liquid tested by the student that is most acidic. [1]
83 State the color of bromcresol green after the indicator is added to a sample of lemon
juice. [1]
84 Complete the equation in your answer booklet by writing the formula of the missing
product in the reaction of aqueous potassium hydroxide with the vinegar, acetic acid. [
1]
85 Based on the pH value in the table, compare the concentration of hydronium ions to
the concentration of hydroxide ions in the distilled water. [1]
P.S./CHEMISTRY
P.S./CHEMISTRY
Printed on Recycled Paper

Examination Date
Question
Number
Scoring
Key
Question
Type
Credit Weight
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
1
1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
2 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
3
4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
4 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
5 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
6
1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
7
2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
8 4
MC
1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
9
3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
10
4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
11 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
12
2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
13
2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
14
3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
15 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
16 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
17 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
18 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
19 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
20 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
21 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
22 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
23 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
24 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
25 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
26 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
27 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
28 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
29 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
30 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
31 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
32 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
33 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
34 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
35 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
36 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
37 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
38 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
39 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
40 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
41 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
42 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
43 4
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
44 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
45 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
46 3
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
47 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
48 1
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
49 2
MC 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
50 1
MC 1 1
The State Education Department / The University of the State of New York
Regents Examination in Physical Setting/Chemistry – June 2023
Scoring Key: Parts A and B-1 (Multiple-Choice Questions)
P.S./Chemistry Scoring Key 1 of 2

Examination Date
Question
Number
Scoring
Key
Question
Type
Credit Weight
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
51 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
52
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
53 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
54 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
55
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
56 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
57 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
58 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
59 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
60 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
61
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
62 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
63 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
64
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
65 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
66 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
67 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
68
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
69 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
70 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
71 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
72 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
73 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
74
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
75 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
76 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
77 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
78 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
79 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
80 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
81
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
82
-
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
83 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
84 -
CR 1 1
Physical Setting/Chemistry
June '23
85 -
CR 1 1
Key
MC = Multiple-choice question
The chart for determining students' final examination scores for the June 2023 Regents
Examination in Physical Setting/Chemistry will be posted on the Department’s web site at
https://www.nysedregents.org/Chemistry/
on the day of the examination. Conversion charts
provided for the previous administrations of the Physical Setting/Chemistry examination must NOT
be used to determine students’ final scores for this administration.
Regents Examination in Physical Setting/Chemistry – June 2023
Scoring Key: Parts B-2 and C (Constructed-Response Questions)
CR = Constructed-response question
P.S./Chemistry Scoring Key 2 of 2

FOR TEACHERS ONLY
The University of the State of New York
REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION
PHYSICAL SETTING/CHEMISTRY
Friday, June 16, 2023 — 1:15 to 4:15 p.m., only
RATING GUIDE
Directions to the Teacher:
Refer to the directions on page 2 before rating student papers.
Updated information regarding the rating of this examination may be posted on the
New York State Education Department’s web site during the rating period. Check this
web site at: https://www.nysed.gov/state-assessment/high-school-regents-examinations
and select the link “Scoring Information” for any recently posted information regarding
this examination. This site should be checked before the rating process for this
examination begins and several times throughout the Regents Examination period.

P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [2]
Directions to the Teacher
Follow the procedures below for scoring student answer papers for the Regents Examination in Physical
Setting/Chemistry. Additional information about scoring is provided in the publication Information Booklet
for Scoring Regents Examinations in the Sciences.
At least two science teachers must participate in the scoring of the Part B–2 and Part C open-ended
questions on a student’s paper. Each of these teachers should be responsible for scoring a selected number
of the open-ended questions on each answer paper. No one teacher is to score more than approximately
one-half of the open-ended questions on a student’s answer paper. Teachers may not score their own
students’ answer papers.
Students’ responses must be scored strictly according to the Rating Guide. For open-ended questions,
credit may be allowed for responses other than those given in the rating guide if the response is a scientically
accurate answer to the question and demonstrates adequate knowledge, as indicated by the examples in the
rating guide. Do not attempt to correct the student’s work by making insertions or changes of any kind.
On the student’s separate answer sheet, for each question, record the number of credits earned and the
teacher’s assigned rater/scorer letter.
Fractional credit is not allowed. Only whole-number credit may be given for a response. If the student
gives more than one answer to a question, only the rst answer should be rated. Units need not be given
when the wording of the questions allows such omissions.
For hand scoring, raters should enter the scores earned in the appropriate boxes printed on the
separate answer sheet. Next, the rater should add these scores and enter the total in the box labeled
“Total Raw Score.” Then the student’s raw score should be converted to a scale score by using the conversion
chart that will be posted on the Department’s web site at: https://www.nysed.gov/state-assessment/
high-school-regents-examinations on Friday, June 16, 2023. The student’s scale score should be entered in
the box labeled “Scale Score” on the student’s answer sheet. The scale score is the student’s nal examination
score.
Schools are not permitted to rescore any of the open-ended questions on this exam after
each question has been rated once, regardless of the nal exam score. Schools are required to
ensure that the raw scores have been added correctly and that the resulting scale score has been
determined accurately.
Because scale scores corresponding to raw scores in the conversion chart may change from one
administration to another, it is crucial that, for each administration, the conversion chart provided for that
administration be used to determine the student’s nal score.
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [3]
51 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
An electron in the rst shell of a Tc atom has less energy than an electron in the third shell.
The third shell electron has greater energy.
The electron in the rst shell has less.
52
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Atoms of technetium have 43 protons, but can have different numbers of neutrons.
The Tc atoms have the same number of protons, but can have a different number of neutrons.
same number of p, different number of n
53
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
(1.00 atm)(0.250 L)
________________________
5
(1.00 atm)V
2
___________
273 K 298 K
(.250)(298) 5 (273)V
2
x 5 (.25)(298)
________
273
0.250 L
_______
5
V
2
_____
273 K 298 K
54
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Decrease the pressure.
lower
any pressure less than 1.00 atm
Part B–2
Allow a total of 15 credits for this part. The student must answer all questions in this part.
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [4]
55 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
from the candle ame to the beaker of water
from the ame to the beaker.
from the candle ame to the water
from candle to water
56
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
(120.0 g)(4.18 J/g•K)(86.0°C 2 23.0°C)
(120.0 g)(4.18 J/g
•K)(359 K 2 296 K)
(120)(4.2)(63)
57
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The water molecules move faster as the temperature increases.
The water molecules collide more often and hit harder as the temperature increases.
The average kinetic energy of the molecules increases.
Molecular motion increases.
58
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The rate of the forward reaction is the same as the rate of the reverse reaction.
The rates are equal.
equal
same
59
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Increasing the pressure favors the forward reaction.
Equilibrium shifts to the right.
Equilibrium shifts to the side with fewer moles of gas, N
2
O
4
(g).
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [5]
60 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The entropy of the dinitrogen tetroxide in the gaseous phase is higher than the entropy of the
liquid dinitrogen tetroxide.
The entropy at 15°C is less than at 25°C.
The entropy of the N
2
O
4
is greater at 25°C.
greater in gas
61
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
from 0 to
1
2
from zero to positive two
from Cu
0
to Cu
21
62 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Copper is more active than silver.
Silver is less active than copper.
Cu is above Ag on Table J.
Note: Do not allow credit for Cu is more active than Ag
1
.
63
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Ag
1
(aq) 1 e
2
→ Ag(s)
Ag
1
1 e
2
→ Ag
2Ag
1
1 2e
2
→ 2Ag
Note: Do not allow credit for the e without the minus sign (2).
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [6]
64 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
titration
volumetric analysis
Note: Do not allow credit for neutralization.
65
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
M
A
(15.0 mL) 5 (0.11 M)(18.2 mL)
(0.11 M)(18.2 mL)
_______________
15.0 mL
x 5 (.11)(18.2)
_________
15
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [7]
66 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Zn, Ga, In
gallium, indium, zinc
67
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Atoms of gallium and indium each have three valence electrons.
Atoms of Ga and In have the same number of electrons in their outermost shells.
same number of valence e
2
68 [1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The density of He is lower than the density of tellurium.
Tellurium is more dense.
Helium is a gas, so it is less dense.
69
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Indium atoms have 5 shells of electrons; gallium atoms have only 4 shells of electrons.
Indium has one more electron shell than gallium.
The In has more shells.
Part C
Allow a total of 20 credits for this part. The student must answer all questions in this part.
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [8]
70 [1] Allow 1 credit for 22.2% or for any value from 22% to 22.24%, inclusive.
71
[1] Allow 1 credit for 4
___
NH
3
(g) 1 5
___
O
2
(g) → 4
___
NO(g) 1 6
___
H
2
O(g) 1 heat.
72
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
14.0067 g/mol 1 2(15.9994) g/mol
2(16.0 g/mol) 1 14.0 g/mol
14 1 32
73
[1] Allow 1 credit for 2.0 mol or 2 mol.
74
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
CO
2
: nonpolar molecule
H
2
O : polar molecule
CO
2
: nonpolar
H
2
O : polar

P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [9]
75 [1] Allow 1 credit.
Examples of 1-credit responses:
O
H
H
O
H H
O H
H
O H
H
Note: Do not allow credit for or or for a bond, because each represents one
electron and each represents two electrons.
76
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The oxygen atom has a greater strength of attraction for electrons than the carbon atom in the
bond between them.
The carbon atom has a weaker strength of attraction for the bonded electrons.
Carbon has an electronegativity value of 2.6, which is lower than oxygen’s electronegativity
value of 3.4.
77
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Carbon and oxygen are nonmetals; the nonmetal atoms share electrons, producing a molecular
compound.
The nonmetals C and O form covalent bonds with each other and produce molecular
compounds.
Carbon dioxide is a molecular compound because it is composed of two nonmetals.
78
[1] Allow 1 credit for CH
2
O. The order of the elements may vary.
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [10]
79 [1] Allow 1 credit for alcohol or alcohols.
80
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
Ethene is classied as an unsaturated hydrocarbon because each molecule of ethene contains
a carbon-to-carbon double bond.
There is a C5C bond in each molecule.
Ethene molecules contain a multiple carbon-carbon bond.
Two more hydrogen atoms can be added to the double-bonded carbon atoms.
81
[1] Allow 1 credit for C or carbon.
82
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
lemon juice
lemon
83 [1] Allow 1 credit for yellow.
84 [1] Allow 1 credit for H
2
O or HOH.
85
[1] Allow 1 credit. Acceptable responses include, but are not limited to:
The hydronium ion concentration and hydroxide ion concentration in the distilled water are
equal.
The hydronium ion and hydroxide ion concentrations in the distilled water are both equal to
1
3 10
27
M.
concentration of H
3
O
1
(aq) 5 concentration of OH
2
(aq)
equal
same

P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [11]
Regents Examination in Physical Setting/Chemistry
June 2023
Chart for Converting Total Test Raw Scores to
Final Examination Scores (Scale Scores)
The Chart for Determining the Final Examination Score for the June 2023
Regents Examination in Physical Setting/Chemistry will be posted on the
Department’s web site at: https://www.nysed.gov/state-assessment/high-school-
regents-examinations on Friday, June 16, 2023. Conversion charts provided
for previous administrations of the Regents Examination in Physical Setting/
Chemistry must NOT be used to determine students’ nal scores for this
administration.
Online Submission of Teacher Evaluations of the Test to the Department
Suggestions and feedback from teachers provide an important contribution to the test development
process. The Department provides an online evaluation form for State assessments. It contains spaces for
teachers to respond to several specic questions and to make suggestions. Instructions for completing the
evaluation form are as follows:
1. Go to https://www.surveymonkey.com/r/8LNLLDW.
2. Select the test title.
3. Complete the required demographic elds.
4. Complete each evaluation question and provide comments in the space provided.
5. Click the SUBMIT button at the bottom of the page to submit the completed form.
P.S./Chem. Rating Guide–June ’23 [12]
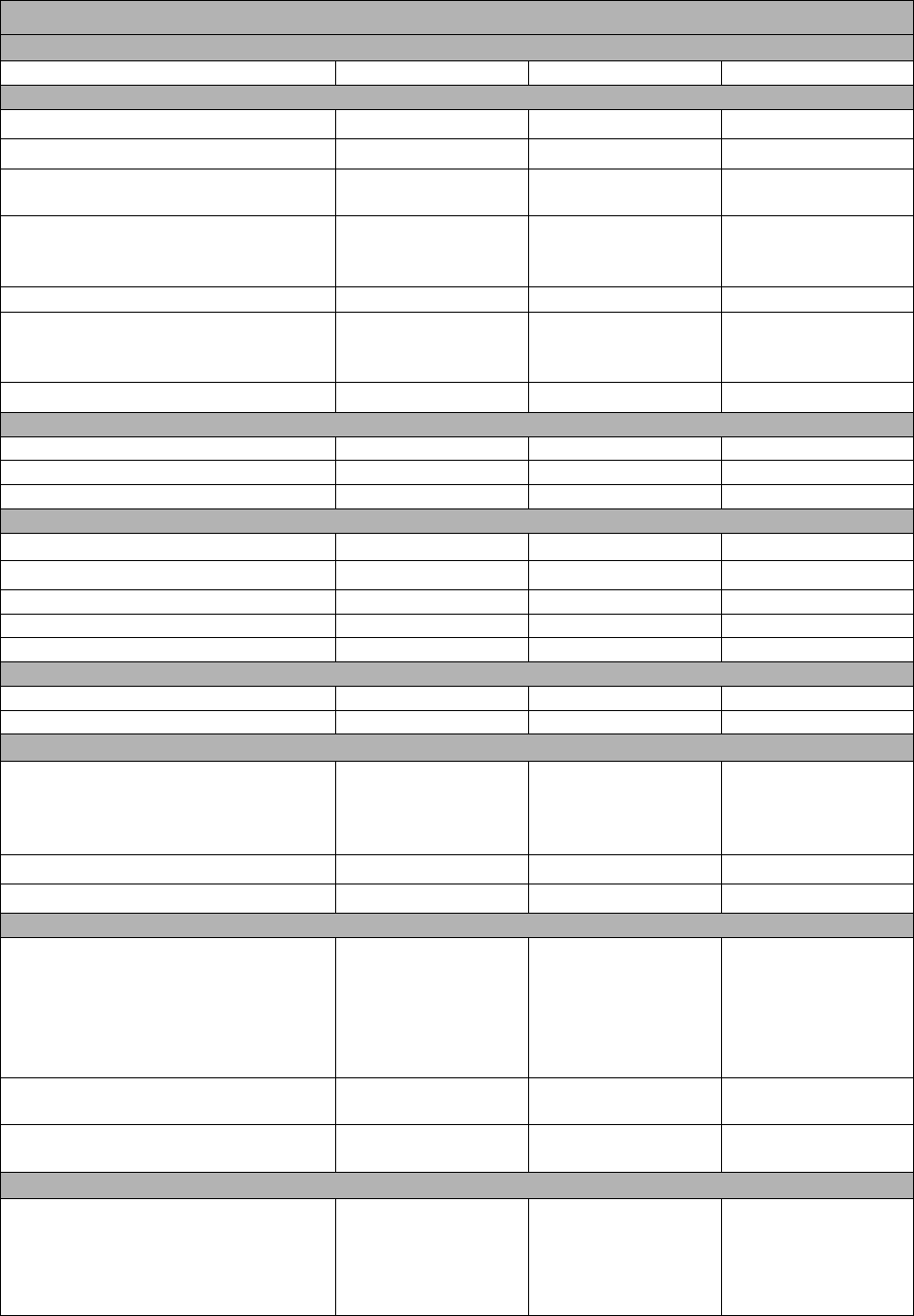
Map to Core Curriculum
June 2023 Physical Setting/Chemistry
Question Numbers
Key Ideas/Performance Indicators
Part A
Part B
Part C
Standard 1
Math Key Idea 1
32, 53,56, 65
70, 72
Math Key Idea 2
39, 41, 44
71, 73
Math Key Idea 3
33, 34, 36, 37, 42,
43, 48, 50, 61
70, 73, 78
Science Inquiry Key Idea 1
35, 41, 45, 46, 51,
52, 54, 55, 57, 58,
59, 60, 64
66, 71,76, 77, 78,
80, 82, 84, 85
Science Inquiry Key Idea 2
Science Inquiry Key Idea 3
31, 36, 38, 39, 40,
41, 45, 46, 47, 49,
57, 58, 59, 60, 61
66, 71, 76, 77, 78,
80, 82, 84, 85
Engineering Design Key Idea 1
Standard 2
Key Idea 1
Key Idea 2
Key Idea 3
Standard 6
Key Idea 1
55
Key Idea 2
31, 34, 40, 45, 63
75
Key Idea 3
Key Idea 4
Key Idea 5
Standard 7
Key Idea 1
Key Idea 2
Standard 4 Process Skills
Key Idea 3
31, 32, 33, 35, 37,
38, 40, 41, 42, 43,
45, 53, 58, 59, 60,
62, 63, 65
66, 67, 69, 71, 72,
73, 77, 78, 79, 82,
83, 84, 85
Key Idea 4
44, 48, 56, 57
Key idea 5
75
Standard 4
Key Idea 3
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8,
9, 13, 14, 15, 19,
20, 21, 22, 23, 24,
25, 26, 27
31, 32, 33, 34, 35,
36, 37, 38, 40, 41,
42, 43, 45, 46, 47,
51, 52, 53, 54, 58,
59, 60, 61, 62, 63,
64, 65
66, 67, 68, 69, 70,
71, 72, 73, 78, 79,
81, 82, 83, 84, 85
Key Idea 4
16, 18, 28, 30
44, 48, 49, 55, 56,
57
Key Idea 5
6, 10, 11, 12, 17,
29
39, 50
74, 75, 76, 77, 80
Reference Tables
2011 Edition
2, 7, 8, 9, 15, 17,
20, 25, 28
31, 32, 33, 34, 35,
36, 37, 39, 40, 41,
42, 43, 45, 48, 51,
52, 53, 56, 61, 62,
63, 65
66, 67, 68, 69, 70,
72, 74, 75, 76, 77,
79, 80, 81, 83, 84
85
100
63
74
41
59
19
39
84
98
62
73
40
58
18
38
83
96
61
72
39
58
17
36
82
94
60
72
38
57
16
35
81
93
59
71
37
56
15
33
80
91
58
70
36
56
14
32
79
90
57
70
35
55
13
30
78
89
56
69
34
54
12
29
77
87
55
68
33
53
11
27
76
86
54
68
32
52
10
25
75
85
53
67
31
51
9
23
74
84
52
66
30
51
8
21
73
83
51
66
29
50
7
19
72
82
50
65
28
49
6
17
71
81
49
64
27
48
5
14
70
80
48
64
26
47
4
12
69
79
47
63
25
46
3
9
68
78
46
62
24
45
2
6
67
77
45
62
23
44
1
3
66
76
44
61
22
43
0
0
65
75
43
60
21
41
64
75
42
60
20
40
Because scale scores corresponding to raw scores in the conversion chart change from one administration to
another, it is crucial that for each administration the conversion chart provided for that administration be used to
determine the student’s final score. The chart above is usable only for this administration of the Regents Examination
in Physical Setting/Chemistry.
The State Education Department / The University of the State of New York
Regents Examination in Physical Setting/Chemistry – June 2023
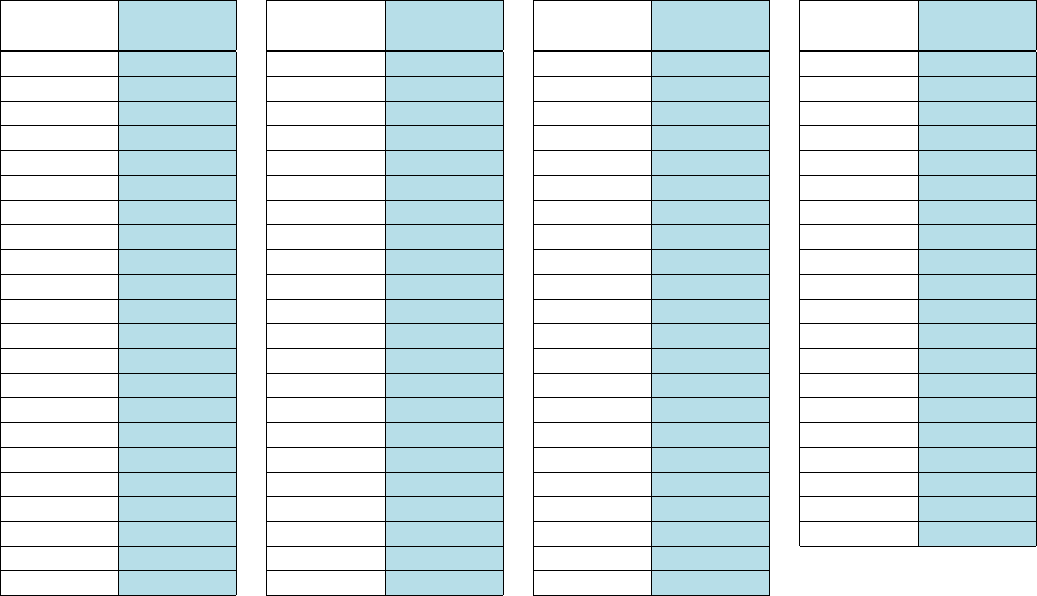
Chart for Converting Total Test Raw Scores to Final Examination Scores (Scale Scores)
To determine the student’s final examination score, find the student’s total test raw score in the column labeled “Raw
Score” and then locate the scale score that corresponds to that raw score. The scale score is the student’s final
examination score. Enter this score in the space labeled “Scale Score” on the student’s answer sheet.
Raw
Score
Raw
Score
Raw
Score
Raw
Score
Scale
Score
Scale
Score
Scale
Score
Scale
Score
Schools are not permitted to rescore any of the open-ended questions on this exam after each question has
been rated once, regardless of the final exam score. Schools are required to ensure that the raw scores have
been added correctly and that the resulting scale score has been determined accurately.
P.S./Chemistry 1 of 1
